Firewall Fehlerdiagnose/en: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „If the firewall becomes inaccessible, you can troubleshoot the firewall using the console connection (https://manage.terracloud.de/):<br> <br> Here the access data can be used like on the web interface.<br> border|Firewall login mask <br> <br> The network configuration is displayed using the command <b><i>interface address get</i></b> <br> border|interface address get<br> <br> The network objects (nodes) a…“ |
Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „=== If the tunnel is open but no traffic is going through, check the following on both sides: ===“ |
||
| Zeile 59: | Zeile 59: | ||
This may not be allowed in the port filter or a DESTNAT directs the traffic past the server. | This may not be allowed in the port filter or a DESTNAT directs the traffic past the server. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
< | <span id="Wenn_der_Tunnel_steht,_aber_kein_Traffic_durchgeht,_ist_folgendes_auf_beiden_Seiten_zu_prüfen:"></span> | ||
=== | === If the tunnel is open but no traffic is going through, check the following on both sides: === | ||
* Routes | |||
* | * Port filters / implicit rules | ||
* | * Packet filter log | ||
* | * Verify via TCPDUMP that there really is no traffic going over the tunnel. <font color="red">(Must be requested via Support@terracloud.de)</font> | ||
* | Often end devices simply do not respond despite traffic. | ||
<span id="Wenn_Traffic_über_den_Tunnel_läuft,_aber_es_allgemeine_Verbindungsprobleme_gibt,_ist_folgendes_zu_prüfen:"></span> | |||
< | === If traffic is running over the tunnel but there are general connection problems, check the following: === | ||
=== | |||
* Internet connection between both endpoints | |||
* | * There are also a few adjustment screws to achieve good VPN quality despite poor internet connection. | ||
* | Here you have to test something and see what achieves the desired effect.<br> | ||
These include: | |||
# MTU → Reduce value to 1400 or lower as a test | |||
# MTU → | # Increase replay values – ideally double them straight away | ||
# | # Switch protocol from UDP to TCP | ||
# | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
< | <span id="IPSec_S2S_Probleme"></span> | ||
== IPSec S2S problems == | |||
== IPSec S2S | |||
< | <span id="Baut_sich_der_Tunnel_nicht_auf,_ist_folgendes_auf_beiden_Seiten_zu_prüfen:"></span> | ||
=== | === If the tunnel does not build, check the following on both sides: === | ||
* Certificates | |||
* | * Cipher + Hash – generally compare the IKE values, PSK etc. from phases 1 and 2 | ||
* Cipher + Hash – | The firmware version is also crucial here.<br> | ||
New versions may no longer support old ciphers.<br> | |||
Therefore, in the best case scenario, client and server should be on the same firmware version.<br> | |||
* IP + Ids + start behavior in phase 1 of the tunnel | |||
* IP + Ids + | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
< | <span id="Wenn_der_Tunnel_steht,_aber_kein_Traffic_durchgeht,_ist_folgendes_auf_beiden_Seiten_zu_prüfen"></span> | ||
=== If the tunnel is open but no traffic is going through, check the following on both sides === | |||
=== | |||
* Port filters / implicit rules | |||
* | NAT in particular causes problems with IPSEC.<br> | ||
For this purpose, it is best to always have “No NAT for IPSec connections” active in the “implicit rules”. | |||
* Packet filter log | |||
* | * Here too, it may be that the packet goes into the tunnel but the end device does not respond. | ||
* | ** However, IPSec does not have a dedicated interface on which one could execute a TCPDUMP. | ||
** IPSec | The best way to check whether a packet is going into the tunnel is as follows: | ||
# Send a ping to the remote network with a packet size on a device that is in the local UTM network. | |||
# | ## On Windows: ping $target-IP$ -l 1000 | ||
## | ## For Linux: ping $target-IP$ -s 1000<br> | ||
## | # Now you send a TCPDUMP on the UTM interface over which the tunnel is set up. Packages of the appropriate size should then be visible here. | ||
# | # Example for TCPDUMP: tcpdump -i $Interface$ -nnp port 500 or port 4500 or esp and host $IP_der_Gegenstelle$ | ||
# | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
< | <span id="Wenn_Traffic_über_den_Tunnel_läuft_aber_es_allgemeine_Verbindungsprobleme_gibt,_ist_folgendes_zu_prüfen:"></span> | ||
=== If traffic is running over the tunnel but there are general connection problems, check the following: === | |||
=== | |||
Basically, the current setting recommendations should be set.<br> | |||
The key data for this are: | |||
* IKEv2 | * IKEv2 | ||
* | * Start option route + flag GENERATE_TRAFFIC | ||
* | * Set “ike_lifetime” to “0” and “ike_rekeytime” to “2”. | ||
If possible a DH group from “ecp” | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
< | <span id="Beispiel_für_CLI_Änderungen"></span> | ||
== Example of CLI changes == | |||
== | |||
For Route + Generate Traffic: | |||
# Use “ipsec get” to find out the id of the tunnel you want to change | |||
# | # Issue command | ||
# | |||
## ipsec set id $tunnel_id$ flags [ ROUTE DPD GENERATE_TRAFFIC MULTI_TRAFFIC_SELECTOR ] | ## ipsec set id $tunnel_id$ flags [ ROUTE DPD GENERATE_TRAFFIC MULTI_TRAFFIC_SELECTOR ] | ||
# | # Save the config with “system config save”. | ||
# | # It's best to restart the IPsec service again to be on the safe side. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
For Lifetimes: | |||
# | # Use “ipsec get” to find out the id of the tunnel you want to change | ||
# | # Issue commands, please note that “ike_lifetime” must be greater than “ike_rekeytime” unless “ike_lifetime” is “0”. | ||
## ipsec set id $tunnel_id$ | ## ipsec set id $tunnel_id$ “ike_lifetime” 3 | ||
## ipsec set id $tunnel_id$ | ## ipsec set id $tunnel_id$ “ike_rekeytime” 2 | ||
## ipsec set id $tunnel_id$ | ## ipsec set id $tunnel_id$ “ike_lifetime” 0 | ||
# | # Save the config with “system config save”. | ||
# | # It's best to restart the IPSec service again to be on the safe side. | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 23. Januar 2024, 13:18 Uhr
General
In all scenarios it can be helpful to look at the syslog (application and kernel messages).
There is usually also a specific note about the relevant problem.
For IPSec, the log must be set to “Verbatic”.
In addition, the log on the UTMs must be enlarged. The following CLI command can be used for this:
syslog backlog set type messages limit 500000
Firewall cannot be reached
If the firewall becomes inaccessible, you can troubleshoot the firewall using the console connection (https://manage.terracloud.de/):
Here the access data can be used like on the web interface.
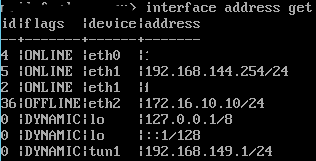
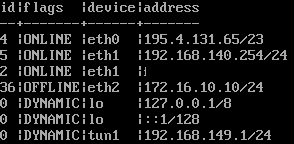
The network configuration is displayed using the command interface address get
The network objects (nodes) are output using the command node get
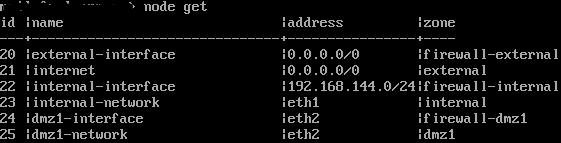
The first comparison can take place here. Among the nodes, the address of the internal interface must match eth1 under the network configuration.
Alternatively, the value “eth1” can be entered as the address.
If there is a difference here, as in the following example, it can be adjusted with a command:
![]()
![]()
The following command makes the new address available and sets the old one to “dynamic” so that further work can be carried out if necessary.
Interface address set id “5” address “192.168.140.254/24”
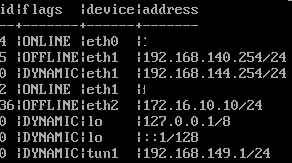
Then two more commands must be made:
system update interface
With this command the new IP goes online.
Last but not least, run system config save to save the configuration
OpenVPN S2S problems
If the tunnel does not build, check the following on both sides:
- Certificates
- Cipher + Hash
The firmware version is also crucial here.
New versions may no longer support old ciphers.
Therefore, both sides should ideally be on the same firmware version.
Otherwise, you can explicitly reactivate old ciphers for a connection using the “Allowed ciphers for automatic negotiation (NCP)” option.
- IP + port of the remote station
- Can the client reach the OpenVPN server?
This may not be allowed in the port filter or a DESTNAT directs the traffic past the server.
If the tunnel is open but no traffic is going through, check the following on both sides:
- Routes
- Port filters / implicit rules
- Packet filter log
- Verify via TCPDUMP that there really is no traffic going over the tunnel. (Must be requested via Support@terracloud.de)
Often end devices simply do not respond despite traffic.
If traffic is running over the tunnel but there are general connection problems, check the following:
- Internet connection between both endpoints
- There are also a few adjustment screws to achieve good VPN quality despite poor internet connection.
Here you have to test something and see what achieves the desired effect.
These include:
- MTU → Reduce value to 1400 or lower as a test
- Increase replay values – ideally double them straight away
- Switch protocol from UDP to TCP
IPSec S2S problems
If the tunnel does not build, check the following on both sides:
- Certificates
- Cipher + Hash – generally compare the IKE values, PSK etc. from phases 1 and 2
The firmware version is also crucial here.
New versions may no longer support old ciphers.
Therefore, in the best case scenario, client and server should be on the same firmware version.
- IP + Ids + start behavior in phase 1 of the tunnel
If the tunnel is open but no traffic is going through, check the following on both sides
- Port filters / implicit rules
NAT in particular causes problems with IPSEC.
For this purpose, it is best to always have “No NAT for IPSec connections” active in the “implicit rules”.
- Packet filter log
- Here too, it may be that the packet goes into the tunnel but the end device does not respond.
- However, IPSec does not have a dedicated interface on which one could execute a TCPDUMP.
The best way to check whether a packet is going into the tunnel is as follows:
- Send a ping to the remote network with a packet size on a device that is in the local UTM network.
- On Windows: ping $target-IP$ -l 1000
- For Linux: ping $target-IP$ -s 1000
- Now you send a TCPDUMP on the UTM interface over which the tunnel is set up. Packages of the appropriate size should then be visible here.
- Example for TCPDUMP: tcpdump -i $Interface$ -nnp port 500 or port 4500 or esp and host $IP_der_Gegenstelle$
If traffic is running over the tunnel but there are general connection problems, check the following:
Basically, the current setting recommendations should be set.
The key data for this are:
- IKEv2
- Start option route + flag GENERATE_TRAFFIC
- Set “ike_lifetime” to “0” and “ike_rekeytime” to “2”.
If possible a DH group from “ecp”
Example of CLI changes
For Route + Generate Traffic:
- Use “ipsec get” to find out the id of the tunnel you want to change
- Issue command
- ipsec set id $tunnel_id$ flags [ ROUTE DPD GENERATE_TRAFFIC MULTI_TRAFFIC_SELECTOR ]
- Save the config with “system config save”.
- It's best to restart the IPsec service again to be on the safe side.
For Lifetimes:
- Use “ipsec get” to find out the id of the tunnel you want to change
- Issue commands, please note that “ike_lifetime” must be greater than “ike_rekeytime” unless “ike_lifetime” is “0”.
- ipsec set id $tunnel_id$ “ike_lifetime” 3
- ipsec set id $tunnel_id$ “ike_rekeytime” 2
- ipsec set id $tunnel_id$ “ike_lifetime” 0
- Save the config with “system config save”.
- It's best to restart the IPSec service again to be on the safe side.
