Backup/en: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „===== Replication Schedule =====“ |
Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „== Installation ==“ |
||
| Zeile 1.949: | Zeile 1.949: | ||
You can find extensive documentation and further information in [https://drive.terracloud.de/dl/fiLpZboTGRPeqzW1cqwS6yin/Documentation%20and%20Release%20Notes/Documentation/DE/vSphere%20Recovery%20Agent%20v9.1%20-%20User%20Guide.pdf?inline vSphere Recovery Agent User Guide]. | You can find extensive documentation and further information in [https://drive.terracloud.de/dl/fiLpZboTGRPeqzW1cqwS6yin/Documentation%20and%20Release%20Notes/Documentation/DE/vSphere%20Recovery%20Agent%20v9.1%20-%20User%20Guide.pdf?inline vSphere Recovery Agent User Guide]. | ||
== Installation == | == Installation == | ||
<div lang="de" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="de" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Version vom 22. Januar 2024, 12:53 Uhr
Introduction
What characterizes the TERRA CLOUD backup solution?
Communication between all components involved is always encrypted. All you need to do is install an agent on the server to be backed up.
This then connects to our data center via ports 8086 and 8087.
Since the connection is from the server to be secured to the outside, no incoming firewall rules or NAT need to be configured.
Administration is carried out centrally via our backup portal.
In this portal you can see all the servers that have been linked to your account through agent registration.
The backup solution essentially consists of three components: Agent, Portal and Vault. The agent is the software component that runs as a service on your servers.
The portal is used to configure and administer these agents. The Vault is the data vault in which the data is stored.
Function overview
| Function overview | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuse | Agent based Windows | Agent based Linux | Host based VMware | Host-based Hyper-V |
| Entire system including bare-metal restore | ||||
| Change Protected Backups(WORM) |
||||
| Hybrid Cloud Backup (Satellite) | ||||
| Virtual server backup | ||||
| Backup attempts again | ||||
| Initialbackup ext. HDD/FTP | ||||
| Protocol truncation (MS Exchange and MS SQL) | ||||
| Microsoft VSS Support | ||||
| Backup of physical servers | ||||
| Backup of network shares | ||||
| Backup of files and folders | ||||
| Ransomware Detection |
||||
| Windows backup event trigger | ||||
| Restore | ||||
| Bare-Metal Restore | ||||
| Restore files and folders | ||||
| Recovery to IaaS Cloud (DRaaS) |
||||
| Start VM from backup (Rapid VM Recovery)[[File:Star.png|15px] ] | ||||
| Automation | ||||
| Script-based control | ||||
| Automated BMR test restores |
||||
| Fully automated setup |
||||
| Patch management of the backup software | ||||
| Monitoring | ||||
| Backup sensors (Server-Eye, PRTG, Nagios,...) | ||||
| Mail notification via the backup portal | ||||
Product presentation and initial setup
Would you like to get an overview of the TERRA CLOUD backup? Then we recommend the recordings of the TERRACASTS of the “TERRA CLOUD Backup” theme week.
Requirements
Supported operating systems
Windows Agent
Windows Server:
- Windows Server 2022: Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Server Core
- Windows Server 2019: Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Server Core
- Windows Server 2016: Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Server Core
- Windows Server 2012 R2: Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Server Core
- Windows Server 2012: Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Server Core
- Windows Storage Server 2012: Standard, Workgroup
Windows Client:
- Windows 11: Home, Pro, Enterprise A)
- Windows 10: Home, Pro, Enterprise (version 20H2)
- Windows 8.1: Enterprise
- Windows 8: Enterprise
Notes:
A) UEFI firmware is mandatory.
Plugins:
Please refer to the release notes for the supported platforms and applications of the respective plug-ins:
Agent Doku/Release Notes
Linux Agent
- CentOS 7 (up to Update 9) A)
- Debian 12
- Debian 11 (up to Update 7)
- Debian 10 (up to Update 13)
- openSUSE Linux 15 (up to Service Pack 5) B)
- Oracle Linux 9 (up to Update 2)
- Oracle Linux 8 (up to Update 8)
- Oracle Linux 7 (up to Update 9)
- Rocky Linux 9 (up to Update 2)
- Rocky Linux 8 (up to Update 8)
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server 9 (up to Update 2)
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server 8 (up to Update 8)
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server 7 (up to Update 9)
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 (up to Service Pack 5) B)
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 (up to Service Pack 5) B), C)
- Ubuntu Server 22.04
- Ubuntu Server 20.04
- Ubuntu Server 18.04
- Ubuntu Server 16.04
Notes:
A) The Linux agent will be supported on CentOS 7 until end of support on June 30, 2024.
Because CentOS Stream is a pre-release version of RHEL and does not have long-term, stable releases, the Linux agent is not supported on CentOS Stream.
B) This platform is not supported when using the standard BTRFS file system.
A) The agent is supported on this platform, but BMR backups are only supported for BIOS-based systems (not for UEFI-based systems).
Supported file systems on Linux:
- ext2
- ext3
- ext4
- XFS
- GFS
- ReiserFS
- JFS
The BTRFS file system is not supported.
Supported Agent Versions
For Windows, Hyper-V and vSphere agents, the following agent versions must be used from February 26, 2024. Other agent versions can no longer be used for backups and restores. There are no specific minimum requirements for Linux agents.
| Operating system | Agent version x86 | Agent version x64 | Notice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2003 | 7.34.4009a | 7.34.4009a | EOL |
| Windows Server 2008 + R2 | 10/9/1013 | 9.30.1009 | EOL |
| Windows Server 2012 + R2 | - | 9.30.1009 | EOL |
| Windows Server 2016 | - | 9.30.1009 | - |
| Windows Server 2019 | - | 9.30.1009 | - |
| Windows Server 2022 | - | 9.30.1009 | - |
| Windows 7 | 10/9/1013 | 9.30.1009 | EOL |
| Windows 8 + 8.1 | 10/9/1013 | 9.30.1009 | EOL |
| Windows 10 | 10/9/1013 | 9.30.1009 | - |
| Windows 11 | - | 9.30.1009 | - |
Any operating system marked "EOL" can still be backed up with the appropriate agent version. However, neither Microsoft nor our software publisher offers support for these platforms. We would like to point out that TERRA CLOUD can only provide “best effort support”. In the event of an error, we cannot rely on the software manufacturer. It is strongly recommended that you keep operating systems up to date. If an update is not possible, periodic test restores should be performed.
| Operating system | Agent version x86 | Agent version x64 | Notice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Server >= 2012 R2 | - | 12/9/1002 | - |
| Operating system | Agent version x86 | Agent version x64 | Notice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Server >= 2012 R2 | - | 9.20.1008 | - |
| Operating system | Agent version x86 | Agent version x64 | Notice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supported Linux distributions | 8.90.1020 | 9.21.1002 | See Release Notes for supported Linux distributions |
Network configuration
| Protocol | Port | Source | Goal | Function | Notice |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCP | 443 | agent | Portal | Automatic agent updates | OLD 185.35.12.130 (until February 26, 2024) / NEW 185.35.13.210 (from February 26, 2024) |
| TCP | 2546 | agent | Vault | Connection to the Vault for data backup, synchronization and restore | Secondary Vault also needs to be released. See Backup Portal -> Quick Links -> Vault Finder |
| TCP | 8086 | agent | Portal | Registration of an agent on the portal | OLD 185.35.12.130 (until February 26, 2024) / NEW 185.35.13.210 (from February 26, 2024) |
| TCP | 8087 | agent | AMP | Management of agents via the portal | OLD 185.35.12.160/27 (until February 26th, 2024) / NEW 195.4.212.128/25 (from February 26th, 2024) < /span> |
| Protocol | Port | Source | Goal | Function | Notice |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UDP | 123 | satellite | Internet | NTP time synchronization | - |
| TCP | 443 | satellite | Portal | Interface updates and Support Connect function | - |
| TCP | 2547 | satellite | Basevault | Heartbeat / Management | ALT Satellite Vault Version <= 8.62 |
| TCP | 12546 | satellite | Basevault | Heartbeat / Management | NEW Satellite Vault Version > 8.62 |
| TCP | 12547 | satellite | Basevault | Data transfer for replication of data backups | - |
Vault
A vault is a virtual system that is operated in the TERRA CLOUD or a partner data center.
This system communicates with the backup agents and receives backups and stores them according to the defined retention periods.
Backup packages include access to a shared backup platform in the form of a Vault account.
Vault-Account
The Vault account is a unique organizational unit on a Vault system; it is required for the authentication of a backup agent on the Vault.
The name of the vault account is made up of your customer number at Wortmann AG and the name of your end customer in the TERRA CLOUD Center in capital letters.
Example:
12345-ENDKUNDEXY
You need the Vault account, for example when you create a new Vault profile, so that the agent can use the data from the profile to authenticate itself to the Vault system.
The Vault account is stored for the “Account” and “Username” fields.
Process of the handshake between agent and vault system
Currently, the connection setup between an agent and its vault during a backup looks like this:
- The agent creates an encrypted tunnel to the vault and checks the public key of the TLS certificate.
- The Vault checks the agent's so-called Unique Identifier and approves the backup if there is a match.
- The agent then performs the backup and transmits the encrypted data via the previously opened tunnel.
On February 26th, 2024 we will make an adjustment to our vault systems so that the process will proceed as follows in the future:
- The agent creates an encrypted tunnel to the vault and checks the public key of the TLS certificate.
- The vault (also known as the primary vault) checks the agent's unique identifier and delegates it to its replication partner (also known as the secondary vault) if there is a match.
- The agent then checks whether a connection can also be established to the secondary vault.
- After the verification is complete, the secondary vault delegates the agent back to the primary vault to initiate the backup.
- The agent performs the backup and transmits the encrypted data via the previously opened tunnel.
These adjustments enable smooth pivoting between the primary and secondary vault, for example during an outage. In addition, a software check ensures that the agent can restore from the secondary vault in case of doubt or to improve performance.
Please note that starting February 26, 2024, backups will be completed with warnings if there is no connectivity to the replication partner:
RSYN-W-07716 Failed to connect to or negotiate backup with alternate vault.
Therefore, you should ensure that all your agents can reach the secondary vault via TCP port 2546 by February 26, 2024.
To find out the address / IP of the secondary vault, you can use the Vault Finder from the quick links in the Backup Portal:
General
Retention periods
TERRA CLOUD Backup offers you a data backup retention period of up to 365 days.
The information about how long a data backup should be kept on the vault is defined by the retention type used.
Regardless of whether a data backup is carried out manually or automatically, a retention type must always be selected.
Retention Types
A retention type consists of two parameters that are configured to retain the data backup.
Backup storage:
This parameter specifies the minimum number of days the data backup must be stored on the Vault.
Number of backup copies to keep:
This parameter specifies the minimum number of backup copies required for this backup job.
Important: Linking the parameters
In order for a data backup to be considered expired and to be removed, BOTH parameters must be exceeded.
The safeset must therefore be at least the defined X days old AND there must be at least Y data backups for the backup job.
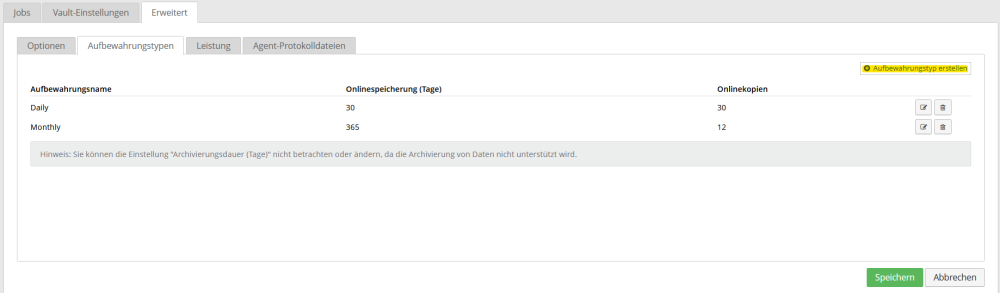
Preconfigured retention types
The following retention types have already been preconfigured for you and are stored when the agents are installed.
Please note that 41 safe sets are included free of charge per backup job; additional backup points can be configured for an additional charge.
Daily:
This retention type is suitable for one backup per day. In total, the data backups are retained for 30 days each and there must be at least 30 data backups in the job.
Monthly:
This retention type is suitable for one backup per month. In total, the data backups are kept for 365 days and there must be at least 12 data backups in the job.
4xDaily:
This retention type is suitable for four backups per day. In total, the data backups are kept for 10 days each and there must be at least 40 data backups in the job.
Note:
The 4xDaily retention type was activated in December 2022 and is not yet automatically stored on older systems and may still need to be created.
Create individual retention types
If you do not want to use or add to the predefined global retention types, you have the option of defining your own retention types at agent level:
Safeset consumption regulation
The consumption values of the safe sets of a backup job are measured on the 15th calendar day of a month.
You will receive a monthly Reports consumption report with all relevant information such as computers created in the respective Vault account,
the backup jobs created on the vault, the amount of natively protected data per backup job and also the number of active safesets.
Basically, you have 41 safe sets available per job. Both the storage types and the prioritization in the schedule are crucial.
In this case, please note our schedule recommendations.
The following image shows you when it becomes chargeable:

Depending on when the vault systems perform the cleanup work, more than 41 safesets may exist despite a correctly configured schedule.
For such cases, we have a free reserve of 10 additional safe sets as a buffer. If you have saved 52 or more safe sets, you will be charged for "extra consumption" per safe set.
Portal
The configuration is carried out as an example as documented in the following sections. The administrator account “backupadmin@terracloud.de” was used for this configuration.
This corresponds to your specialist dealer administrator account (backup master account).
Structure of TERRA CLOUD Backup Portal
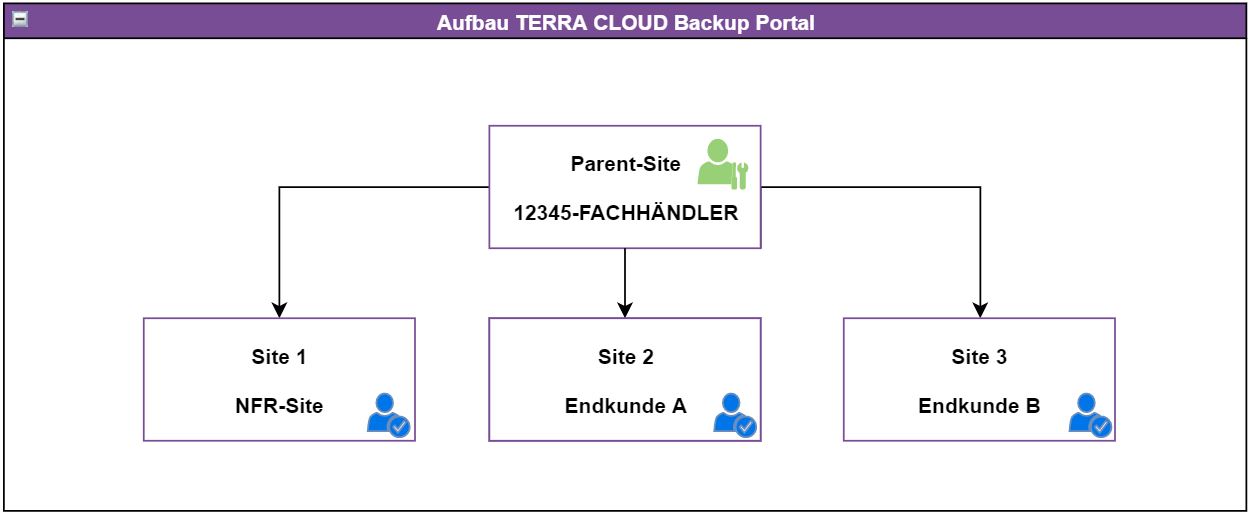
Description:
This diagram shows the structure of the backup portal.
The upper level consists of the parent site, which you can recognize by its name consisting of your Wortmann AG customer number and the name of your company.
You can use this level to administer (child) sites and use all functions of the portal centrally. You can create users for both levels, these are stored in the diagram in green for the parent site and in blue for the end customers' sites.
Please create your own site for your company, as marked with the NFR site in the diagram.
You can then move the agents for your systems into this site or register them directly into it via a user within the site.
Note:
Please only register agents in the parent site if they will then be moved to the associated customer site for further configuration.
Create site
A site is a sub-area within your portal to separate and manage a group of computers to be secured.
Subsites ensure the clear separation of agents and backups from different customers.
Click Sites in the navigation bar, then click Create New Site.
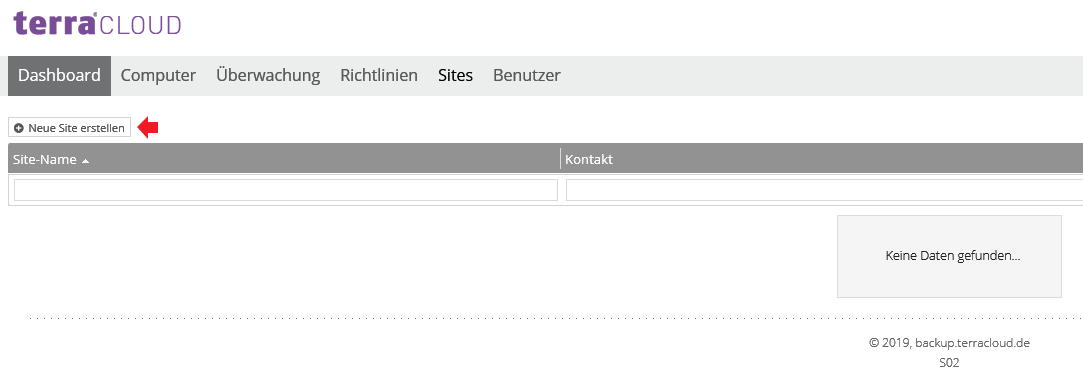
Now give the site a name.
A useful name is the name of the end customer, which can be combined with a customer number assigned by you, e.g. 12345-End Customer.
Optionally, you can configure the customer number and contact addresses for the site. Then click “Save Site”.
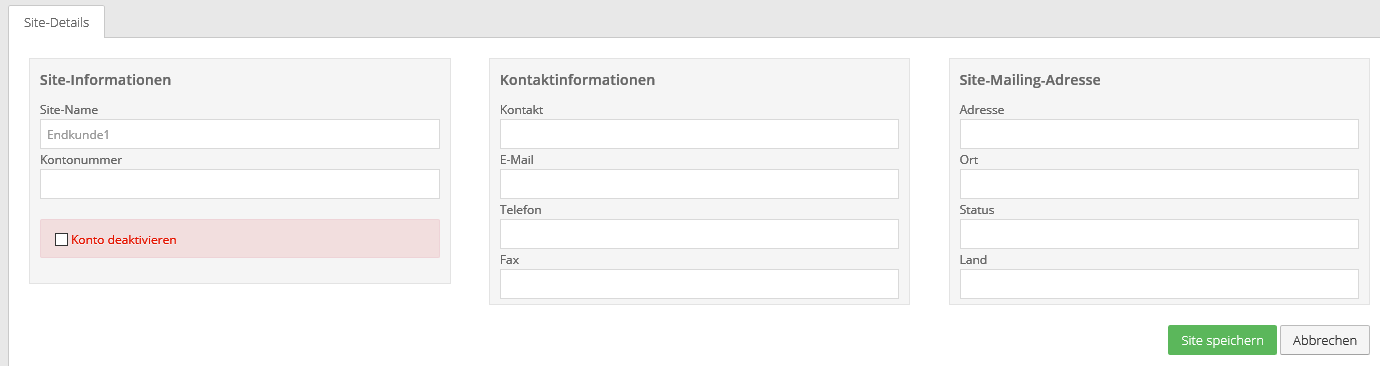
Now give the site a name. A useful name here would be the name of the end customer.
Optionally, you can configure the customer number and contact addresses for the site. Then click “Save Site”.
Create user
You can create different users for your end customer's site.
If you specify a user with the role "User" or "Administrator" instead of your parent site administrator when registering the agent, the agent will be registered in the end customer site.
Note:
Further information about the different user roles can be found in the Authorization Concept.
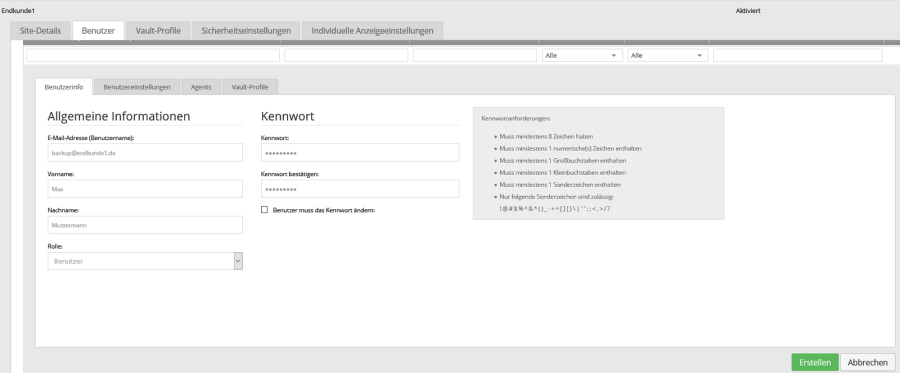
In the following screenshot you can see the configuration of a user with the "User" role.
Please note that you can still Assign Agents to Users.
to users who do not have the "Administrator" user role
Configure notifications
You can configure email notification for the site using the “Notifications” tab.
The address on file will be notified as soon as the selected events occur.
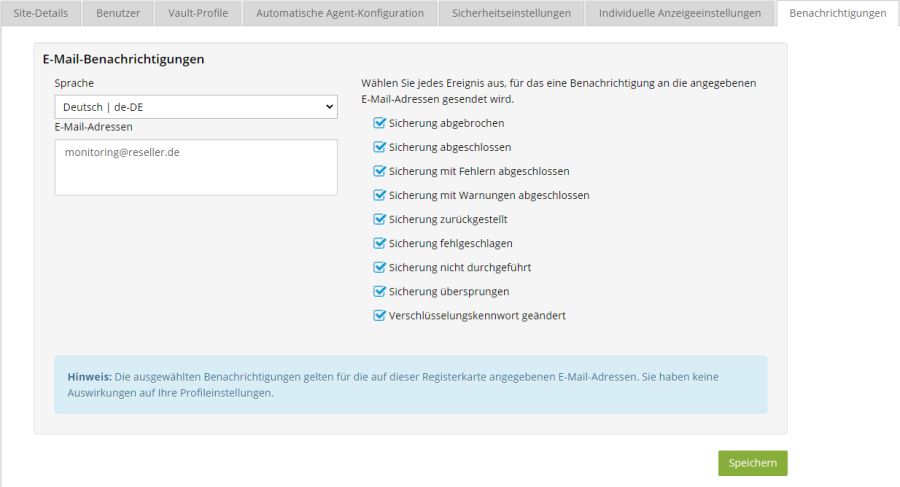
Please note that the portal-side email notification is currently not yet available for all agents. See function overview
Encryption password changed' option:
This can, for example, warn you in the event of unauthorized access if an attacker wants to gain access to future backups by changing the encryption password.
The encryption password cannot be changed retroactively for existing safesets.
Note:
The change in the encryption password is also reflected in the "Status Feed".
The basic configuration for your first end customer site is now complete.
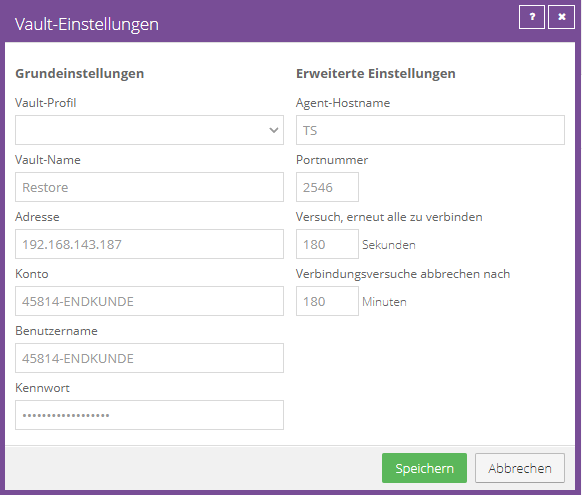
Configure Vault Profiles
After providing a TERRA CLOUD backup package, you will receive the access data for the vault account for your tenant.
The credentials are required for authentication between the agents and the vault (storage target).
You can save the credentials in a Vault profile, e.g. For example, you don't have to enter it manually when registering an agent with the Vault.
Please click "Add New" to create a Vault profile.
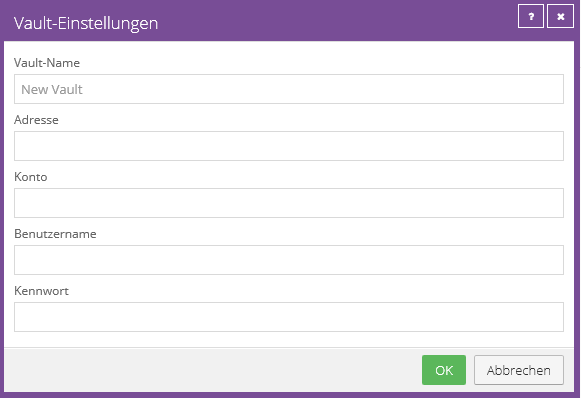
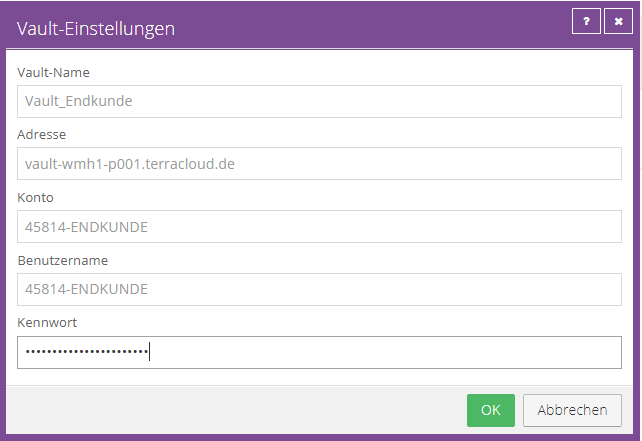
Vault name:
The Vault Name is the displayed name of the Vault profile.
Recommendation: To simplify matters, we recommend the FQDN of the vault (e.g. vault-wmh2-P001.terracloud.de).
The chosen vault name has no technical function, but only serves as a designation.
Address:
Please enter the FQDN of the vault (e.g. vault-wmh1-P001.terracloud.de).
Account:
Please enter the submitted Vault account (e.g. 45814-ENDCUSTOMER).
Username:
Please also enter the submitted Vault account (e.g. 45814-ENDCUSTOMER).
The account and user name have been created identically to simplify setup.
Password:
Please enter the submitted password. This Vault password is used to authenticate the Vault account and is not used to encrypt user data.
Create the Vault profile via "OK".
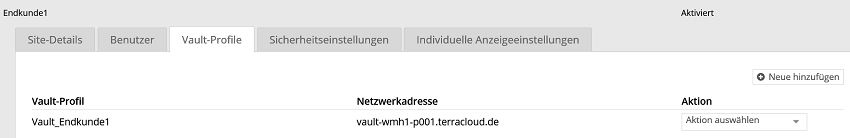
The saved Vault profile should then be visible.
Automatic agent configuration
To have new agents automatically configured in the portal, please activate the "Automatically configure new agents" option under the "Automatic agent configuration" tab.
Requirements:
- Agent version 8.90a or newer
- Submission of a default encryption password in the installation process
Please select a Vault profile and a job template. You can either use the already stored best practice template "Entire System Image" or create your own template.
Default encryption password:
In order to create a backup job completely automatically, an encryption password must be defined.
With automatic agent configuration, the encryption password is passed as the default encryption password during the installation process.
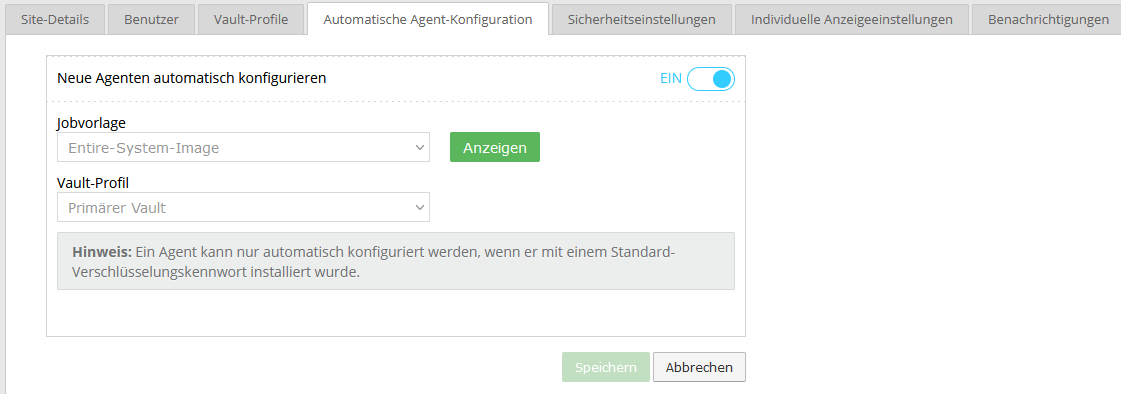
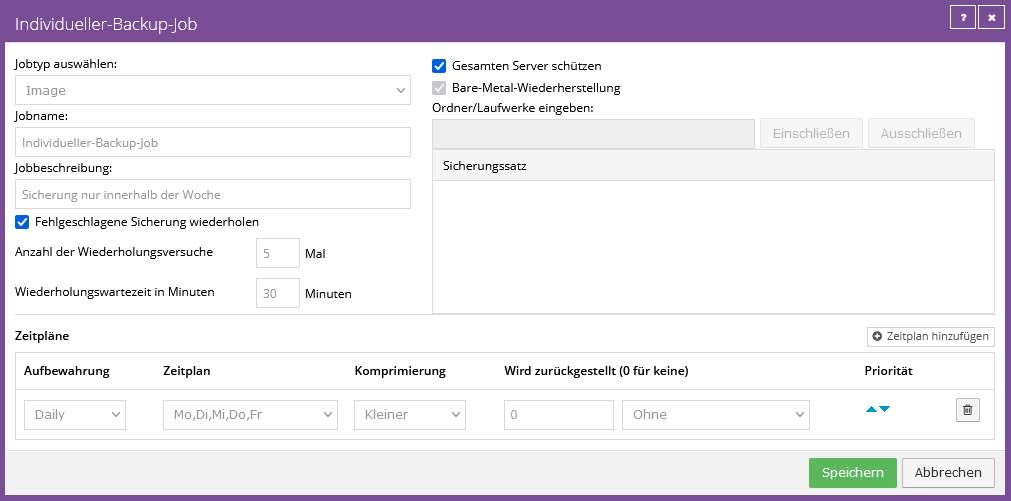
Create your own job templates
You can create your own job templates by clicking on the "View" button next to the preset job template and creating an editable copy of the job template.
You can adapt this copy as you wish and, after saving it, use it for automatic agent configuration.
Example for your own job template:
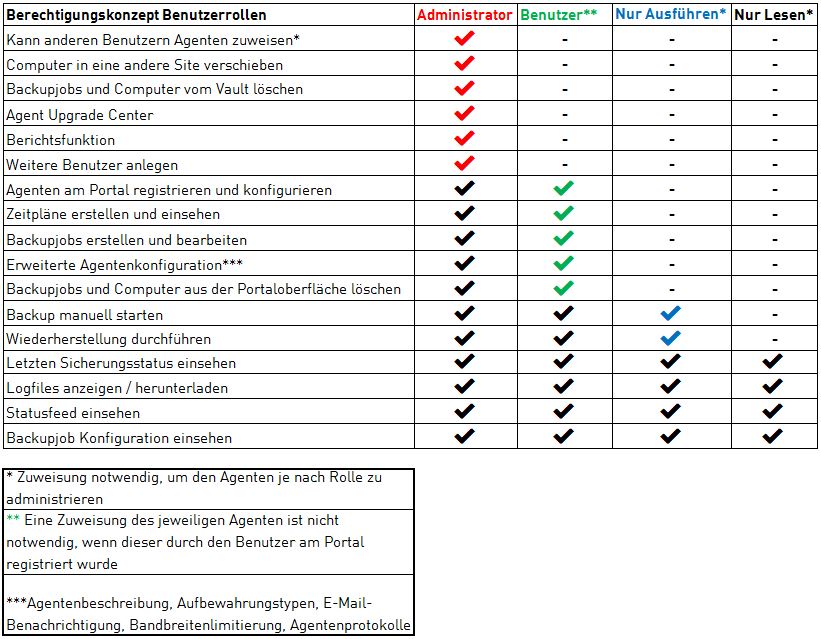
Authorization concept
This diagram shows the four different roles that can be assigned to a user.
You can create users either within a site or at the reseller level in your parent site; further information can be found in the diagram for the Structure TERRA CLOUD Backup Portal
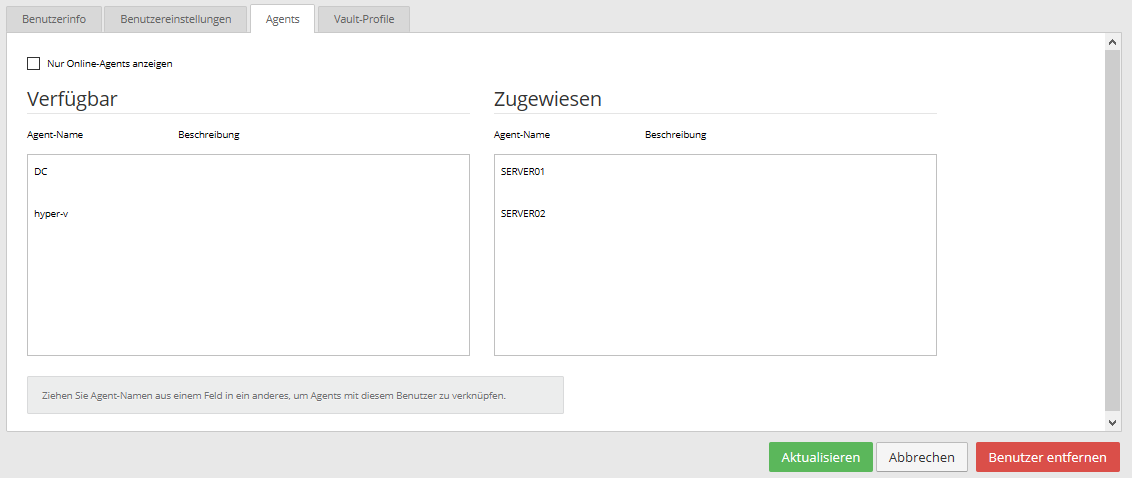
Assign agents to users
Users who do not have the "Administrator" role must be assigned to agents who can be managed by them.
You can do this either via the user configuration within the site or via the Sites tab within your parent site.
In this example, only SERVER01 and SERVER02 have been assigned to the user for management.
Deletion of data backups
Delete computers from the portal and vault
You can have a computer's data backups completely deleted as an administrative user via the Backup Portal.
This type of deletion includes:
- Deletion of the computer from the portal (online or offline computer)
- Delete the backup of all backup jobs of this computer on the primary and secondary vault
- Delete the registered computer on the Vault
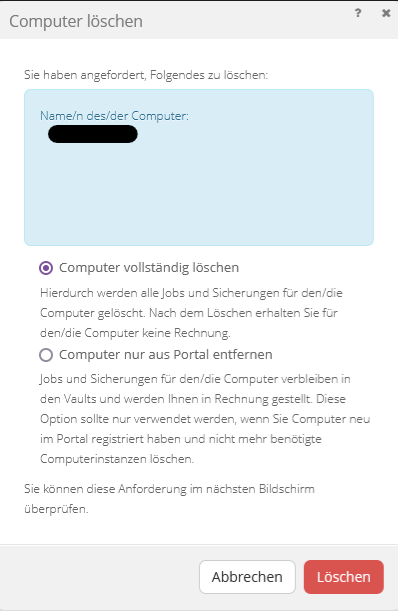
Procedure for deleting a computer:
- Select the desired system using the checkbox on the left side of the backup portal
- Under Actions, select Delete selected computer(s).
- Switch to the “Completely Wipe Computer” option
- Enter "CONFIRM" in the input field of the dialog to confirm the deletion
The deletion job will be executed after a quarantine period of 24 hours.
Cancel deletion job:
Within the quarantine period of 24 hours, you can select the computer as described above and cancel the deletion request using the "Cancel deletion of the selected computer(s)" action.
Delete backup jobs from the portal and vault
You can have the data backups of a backup job completely deleted as an administrative user via the Backup Portal.
This type of deletion includes:
- Delete the backup job from the portal
- Delete all data backups of the backup job on the primary and secondary vault
- Delete the registered backup job on the Vault
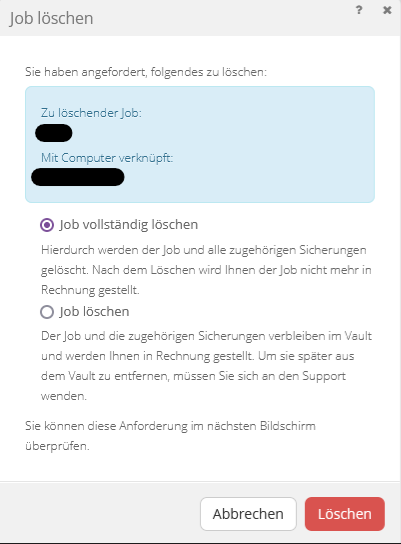
Procedure for deleting a backup job:
- Open the "Select Action" drop-down menu for the desired job under the "Job" tab of the respective computer
- Choose the “Delete Job” option
- Switch to the “Delete Job Completely” option (screenshot below)
- Enter "CONFIRM" in the input field of the dialog to confirm the deletion
The deletion job will be executed after a quarantine period of 24 hours.
Cancel deletion job:
Within the quarantine period of 24 hours, you can select the backup job as described above and cancel the deletion job using the "Cancel deletion" action.
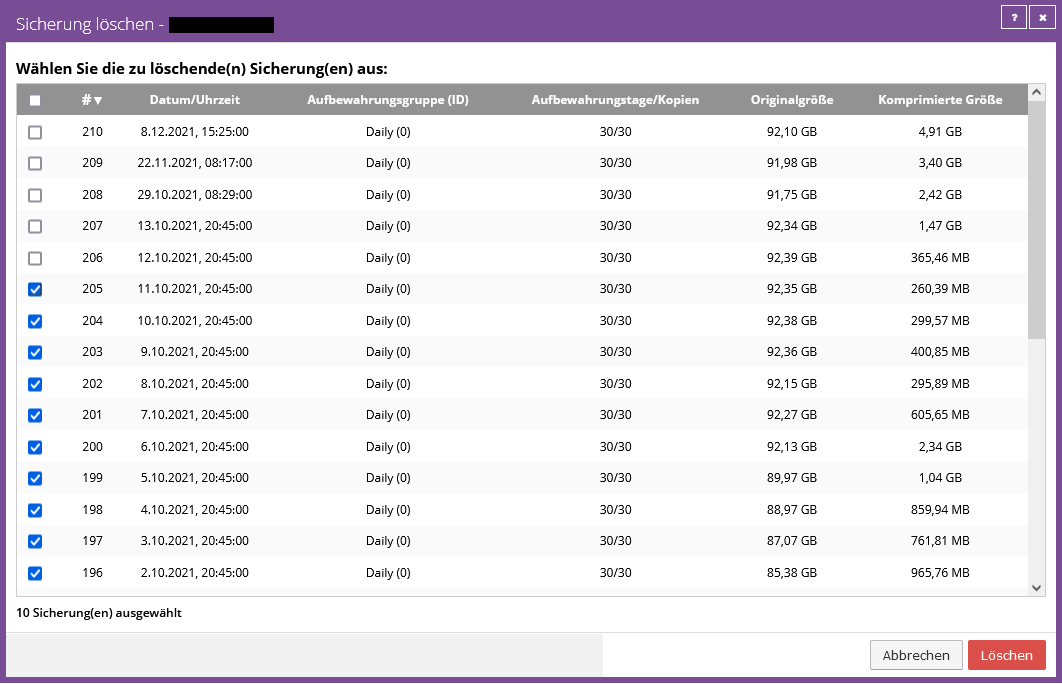
Delete individual data backups (safesets) from the vault
You can have selected data backups of a backup job completely deleted as an administrative user via the Backup Portal.
This type of deletion includes:
- Delete the selected data backup of the backup job on the primary and secondary vault and, if applicable, the satellite
Procedure for deleting individual data backups (safesets):
- Open the "Select Action" drop-down menu for the desired job under the "Job" tab of the respective computer
- Choose the “Delete Backup” option
- Select the safesets to be deleted and click "Delete" (screenshot below)
- Enter "CONFIRM" in the input field of the dialog to confirm the deletion
Note:
The deletion of individual data backups (safesets) is carried out immediately and cannot be stopped after confirmation!
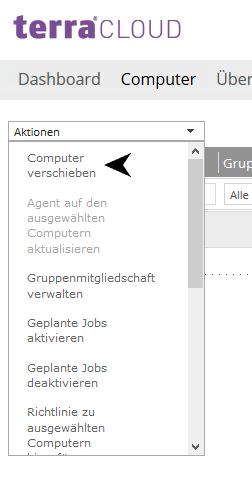
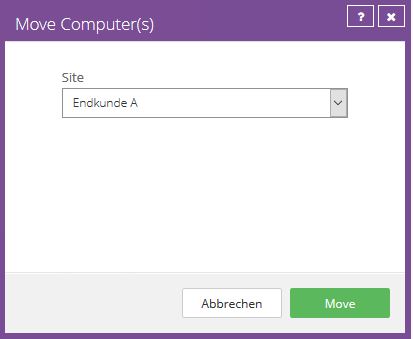
Move computer to another site
You can move as many computers as you want to another site using the Move Computers action.
This function makes it possible, for example, to assign systems that were accidentally registered in the Parent-Site to the end customer's site.
Adjustment in the backup portal after a data migration
After migrating the data/backups to, for example, a dedicated vault system, the configuration must be adjusted in the backup portal.
After the migration, the backup agent should connect to another vault system and, if necessary, also use other access data for authentication.
The procedure differs slightly depending on the migration method. Please make the following adjustments after consultation in the migration process (support ticket).
Vault account migration
With this variant, the entire vault account is moved to another vault system. A vault account is an organizational unit for an end customer.
You will receive the access data and the name of the vault account when you provide the account, e.g. 12345-DEMO.
Please carry out the following steps after successfully moving the account:
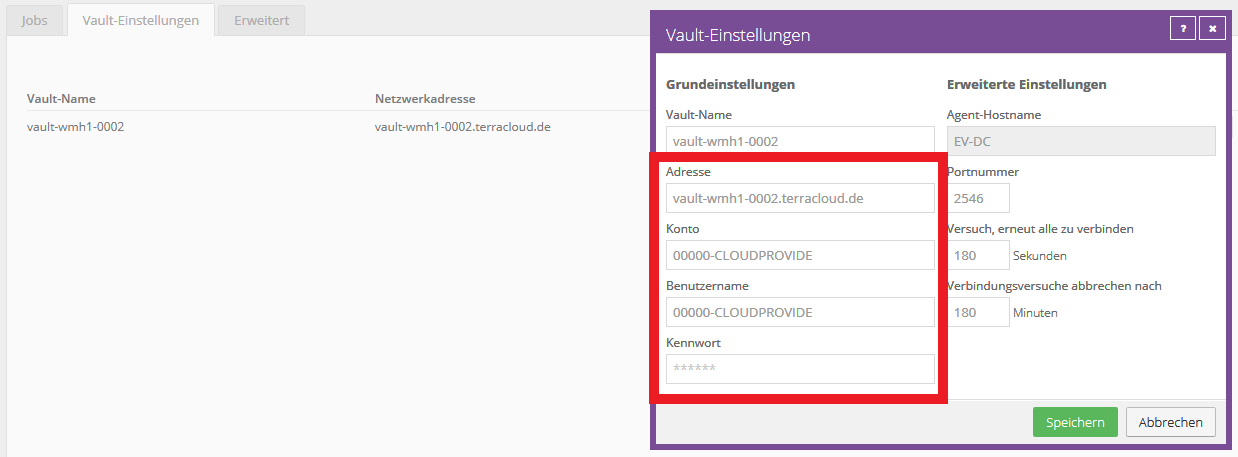
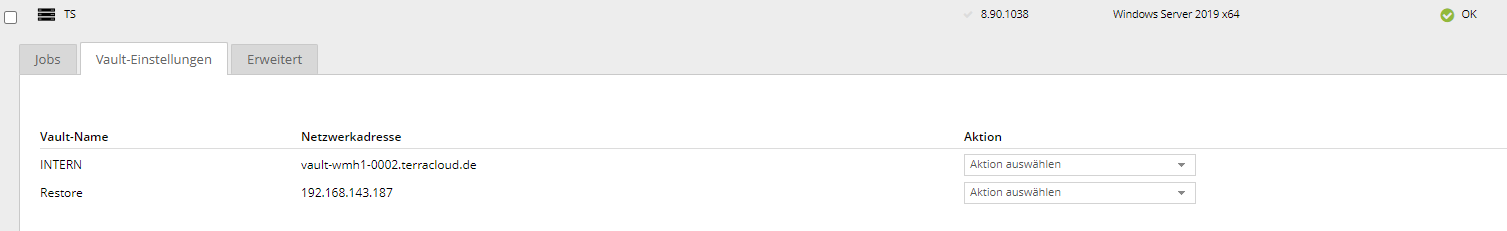
- For each agent, access the "Vault Settings" in the Backup Portal
- Edit the current vault connection and swap the FQDN of the old vault system with that of the new vault system
- Also customize the vault profile for this site
The following screenshot shows the current vault connection that needs to be edited.
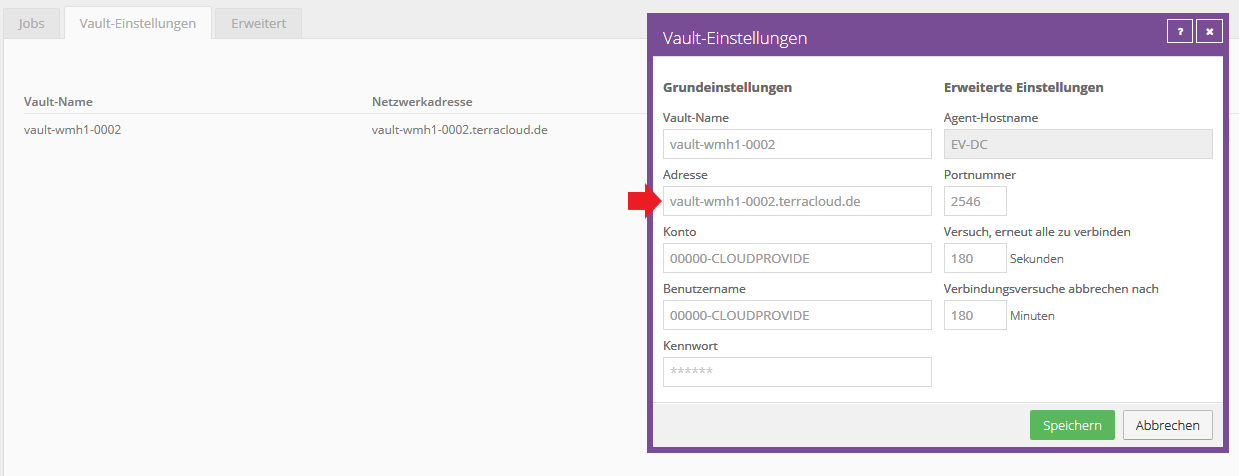
Migration of data to a new vault account
The prerequisite for this method is a new vault account, e.g. B. on a TCBE vault system. With this variant, only the affected computers and their backup jobs are moved.
Since authentication will now take place via the new account, all positions in the vault connection must be changed.
- For each agent, access the "Vault Settings" in the Backup Portal
- Edit the current vault connection and replace all vault credentials with those of the new vault account
- Also adjust the vault profile of the affected site
Guidelines
We currently recommend not using any guidelines!
Guidelines currently have some unpleasant side effects. In particular, there may be confusion regarding storage types.
In the past, this has occasionally led to increased Safeset consumption.
We recommend setting the advanced settings manually.
Reports
The reporting function gives you access to various data sets from the TERRA CLOUD backup via various preconfigured reports.
The underlying database receives new records twice a day through the TERRA CLOUD Vaults.
Please note that in connection with a TERRA CLOUD backup satellite, only data sets for the existing safe sets and consumption as of the base vault are available.
TERRA CLOUD backup satellites are not connected to the reporting function.
Requirements:
In order to view reports, the “Vault account” must be synchronized with the respective site.
Automatic synchronization of the Vault account – How it works:
- Below the “Vault Settings” is the Vault Registration (1)
- the “Vault Account” (2) will be transferred to the site (3)
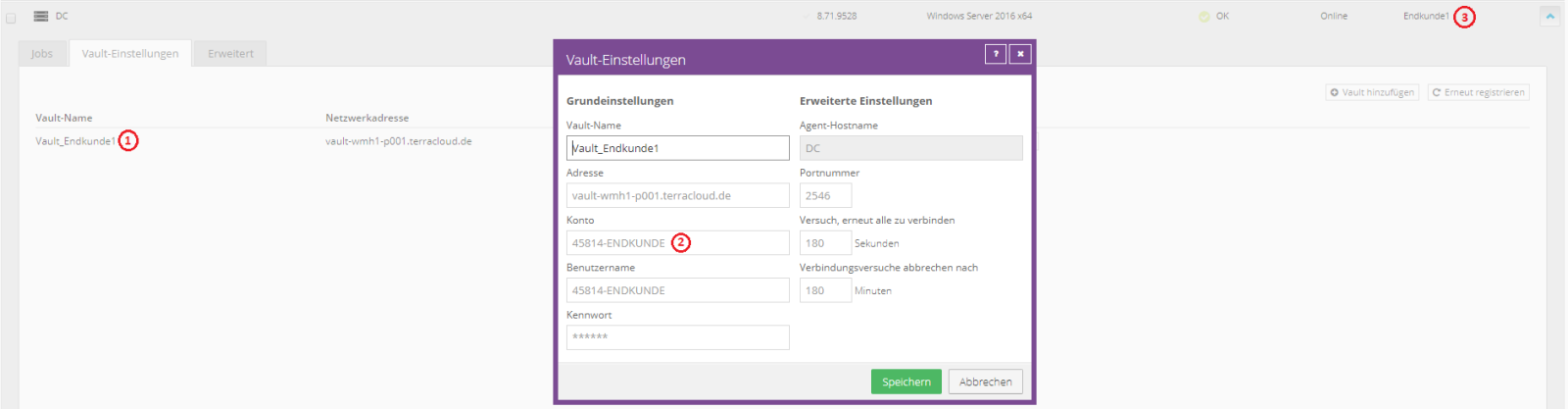
For the synchronization to work, the following requirements must be met:
- The Vault account may NOT be used across sites (same Vault account in different sites)
- The agent was registered in a self-created site (https://backup.terracloud.de/Sites).
Different Vault accounts can be used within a site as long as they are not used in other sites.
Necessary permission of the user:
To access the Reports page, you must be logged in as a user with the Administrator role.
Reports can be scheduled and automatically sent by email (PDF, XLS, CSV).
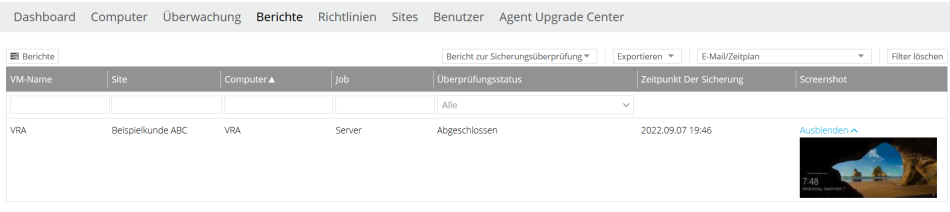
Backup Verification Report
This report provides you with an overview of the most recently performed automated Recovery Tests by your vSphere Recovery Agents.
On the one hand, you have the option of exporting this view as a PDF document, and on the other hand, you can configure a regular export including email delivery using the "E-mail/Schedule" menu item.
Agent Upgrade Center
The Agent Upgrade Center offers you the opportunity to upgrade Windows agents from version 8.7x via portal.
Update Individual Agents
You can select systems via the “Computer” tab and initiate the agent update under “Actions”.
Status display
In addition to the current version, you can use the icon to see whether the agent can be updated (purple dot) or is currently being updated.
As soon as an agent has been successfully updated, a checkmark will be displayed next to the version number. If you move the cursor to the symbol next to the version number, the respective meaning will be displayed, e.g. "New agent version available".
In the following screenshot you can see an agent that is currently being updated.
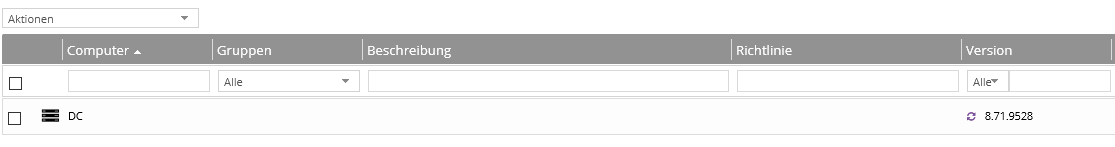
Update Agents for Entire Sites
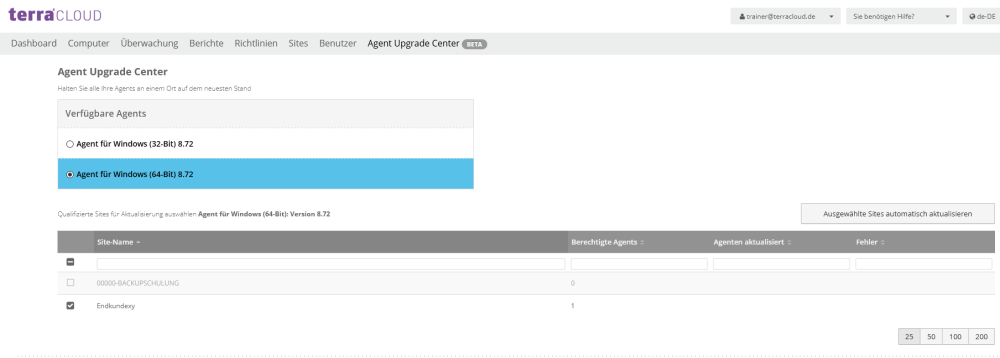
To do this, access the Agent Upgrade Center via your master login and select the desired agent and then the respective sites.
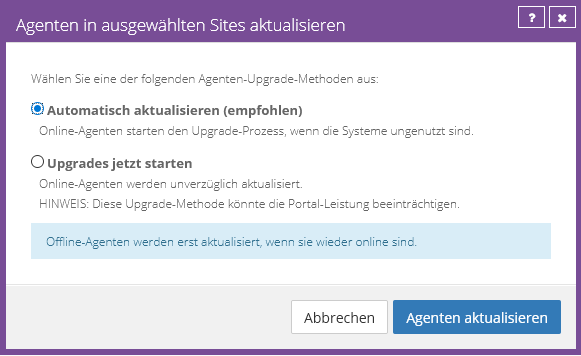
Then select whether you want the agents to be updated automatically or immediately:
Windows Agent
Installation via Setup
Please download TERRA Backup Agent. To do this, log in to your portal and select the appropriate version under Downloads on the right.
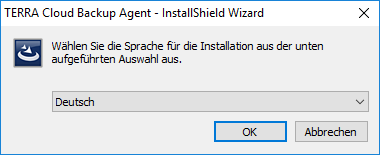
Now start the installation on the server to be backed up. First select the desired language in which you would like to be guided through the installation.
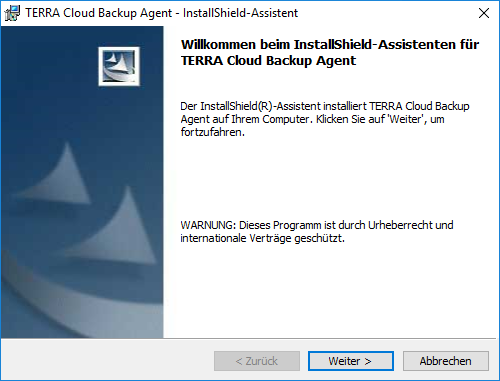
On the "Support Information and Release Notes" page, click Next
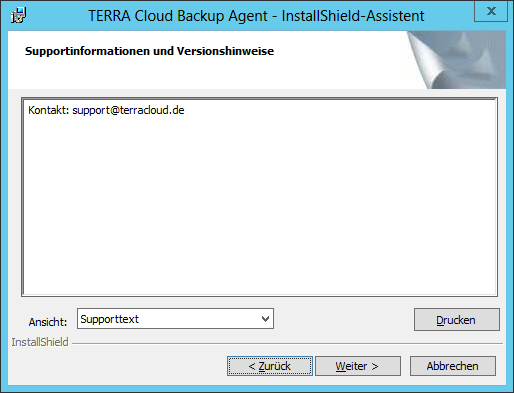
Accept the license terms and click Next.
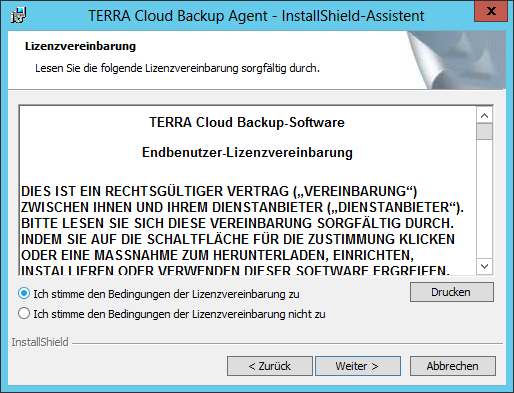
In the next installation step, select “Custom” and click Next.
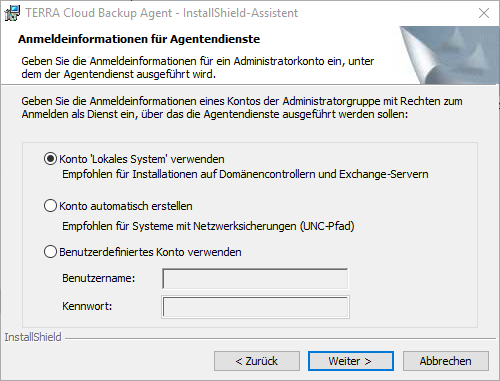
The local logon credentials can usually be adopted. Click on Continue.
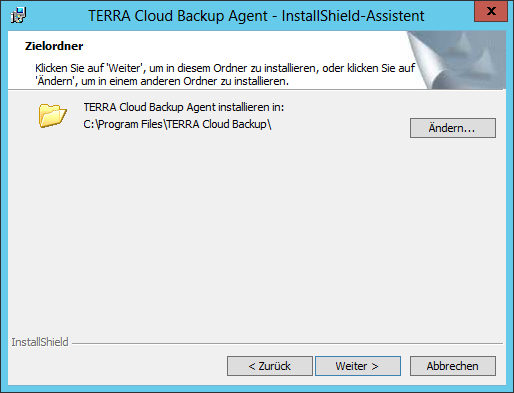
Select the desired installation directory. Then click Next.
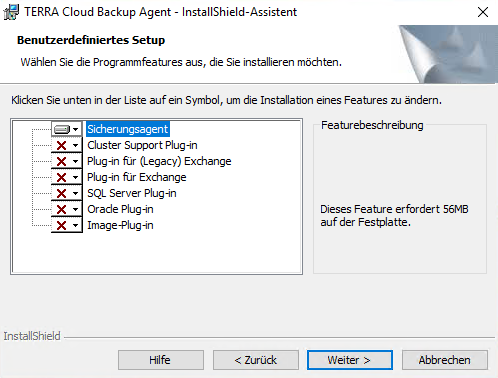
In addition to the actual backup agent, other plug-ins can be installed. Depending on the type of server, individual Microsoft SQL database instances or Exchange mailboxes can be backed up.
Select the plug-ins you want and then click Next.
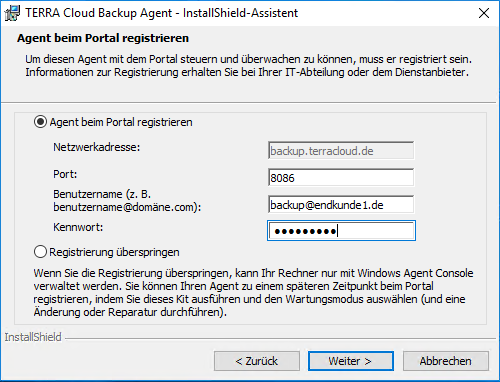
Enter the email address and password of the user created in 4.2.2. Confirm with Next.
Confirm with Install.
If you are then redirected back to agent registration, the access data you entered is probably incorrect or you are having problems with the
Network connection. First try pinging backup.terracloud.de. If this works, you can use Telnet to check whether port 8086 can be reached.
After 5 minutes at the latest, the server you just registered should appear under “Computer” within your portal.
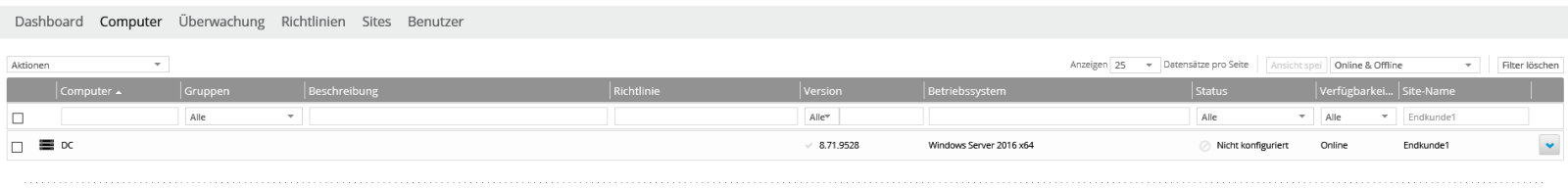
On the right side under “Site Name” you can read “End Customer1” in our case. This is because we registered the agent with the user backupkunde@endkunde1.de,
which belongs to the “End Customer1” subsite. This way we can now filter for computers that belong to the “End Customer1” subsite. This allows you to quickly list all computers in an organizational unit.
Silent installation under Windows
The agent can also be installed in silent mode. This is helpful if the agent is to be rolled out automatically on multiple systems.
An example of the silent installation including the image plug-in:
Agent-Windows-x64-x-xx-xxxx.exe /s /v" REGISTERWITHWEBCC=True AMPNWADDRESS=backup.terracloud.de AMPUSERNAME=backupkunde@firmaXYZ.de AMPPASSWORD=password FEATUREVOLUMEIMAGE=ON /qn"
Explanation:
Agent-Windows-x64-x-xx-xxxx.exe: The agent (x64) setup is called.
REGISTERWITHWEBCC=True: The agent should be registered on the backup portal.
AMPNWADDRESS=backup.terracloud.de: The address of the backup portal is passed.
AMPUSERNAME=backupkunde@firmaXYZ.de: The user of the customer site is transferred.
AMPPASSWORD=password: The password you assigned for the customer site user.
Parameters for plugins:
Plug-ins can be added after the AMPPASSWORD separated by a space as in the example above.
Image Plugin: FEATUREVOLUMEIMAGE=ON
Exchange Plugin (Legacy): FEATUREEXCHANGE=ON
Exchange Plug-in (From 2010): FEATUREEXCHANGE2010=ON
SQL Plugin: FEATURESQL=ON
Cluster plugin: FEATURECLUSTER=ON
Oracle Plugin: FEATUREORACLE=ON
Installation in another directory:
If required, please specify the following parameter directly after /s /v" to install in another directory:
SILENTINSTALDIR=\"Path
Example:
SILENTINSTALLDIR=\"C:\Program Files\Example\
Silent Agent Registration
The following entry in the command line is sufficient to re-register the agent on the portal:
C:\Program Files\TERRA Cloud Backup\Agent\buagent.exe" -cmdline --reregister --amplogin backupkunde@firmaXYZ.de --amppassword USERPW --ampserver "backup.terracloud.de" --ampport 8086' '
The Terra Cloud Backup services must then be restarted.
To do this, start Powershell with administrator rights and enter the following:
Get-Service -DisplayName "TERRA Cloud Backup*" | Restart service
Associate Agent with Vault
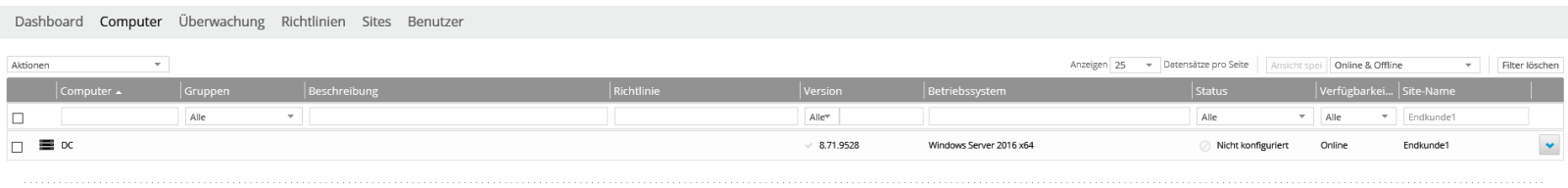
Every newly registered computer is initially displayed as “Not configured” in the portal. First, at least one vault (data safe) must be assigned to the computer.
Click on the server you want to configure (DC in this example). This will open the settings for this computer. Then click on “Configure manually” on the right.
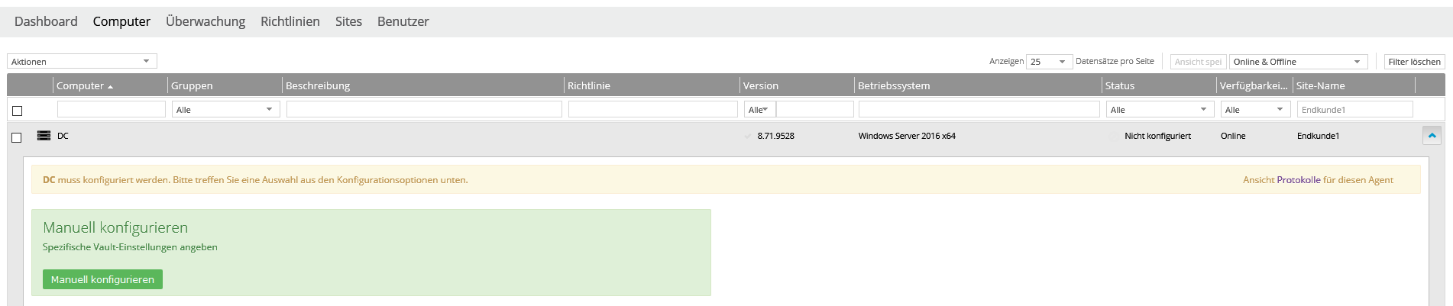
Now click on “Add Vault” on the right.
Then select the Vault profile created in 4.2.1 under “Vault profile”, in our case this is “Vault_Endkunden1”. All fields should then be automatically filled with the set values.
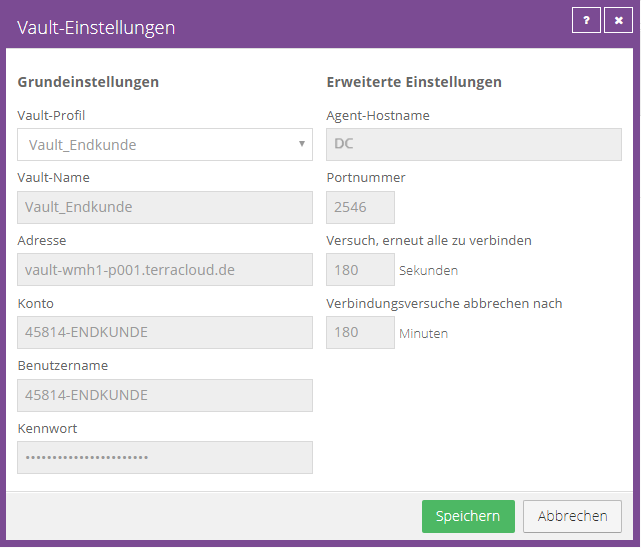
The agent establishes a test connection to the vault. If the connection cannot be established, for example because incorrect access data was entered, you will receive an error message.
If everything is OK, the vault will now appear under the “Vault Settings”.
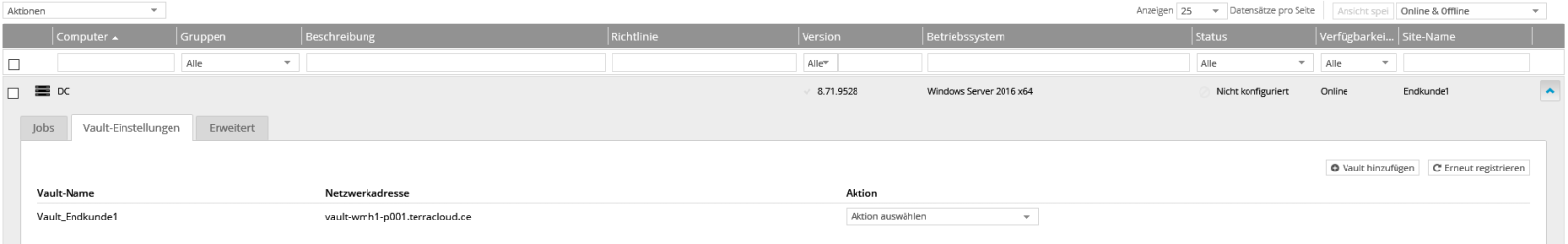
Advanced Agent Configuration
Individual settings can be configured for each computer. These include, for example: B. Mail notification and bandwidth limitation.
Go to “Computer” in the portal. Select a server and then click on “Advanced” to make specific settings.
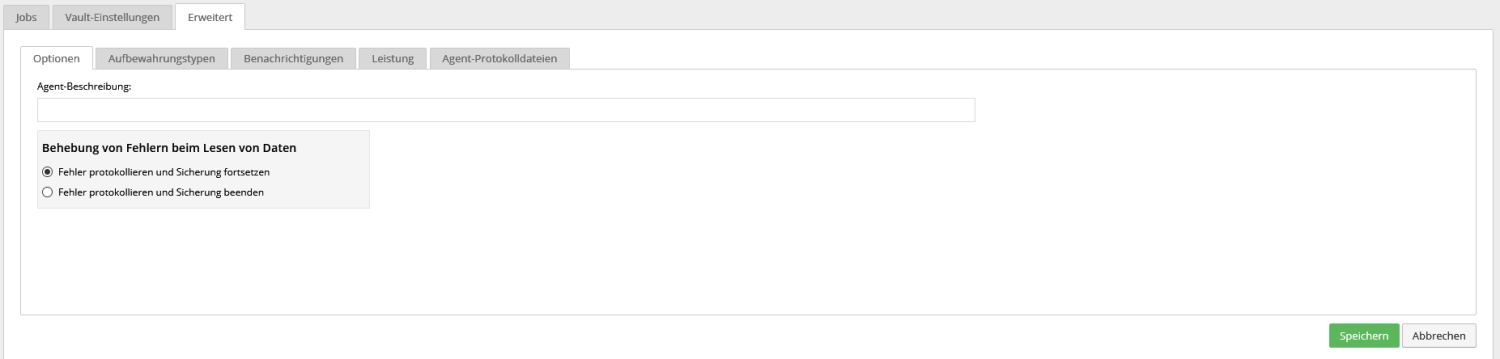
Options:
Under this point you can add a description to the system, for example: B. to store the ticket number in the description in a support case.
We recommend the option “Log errors and stop backup” for current Windows agents; this is the default setting after installation or update.
The option "Log errors and continue backup" offers the advantage that backups can also be carried out if, for example, B. VSS problems can sometimes go through.
The files not backed up in this job will result in an increased delta afterwards.
Retention Types:
The currently stored retention types are displayed here; after installation, “Daily” and “Monthly” are stored by default.
You can use this tab to create your own storage types, which you can then choose from in the schedule. When configuring, please note that 41 safe sets per job are included free of charge.
Notifications (agent side):
As of August 2021, the “Notifications” tab is only available if an agent-side mail notification is already configured.
This agent function has been replaced by the Notification via the TERRA CLOUD Backup Portal.
Enable agent-side notification manually:
If you want to continue using agent-side notification, you can configure it using the following steps.
1. Stop the "TERRA Cloud Backup Agent" and "TERRA Cloud Backup BUAgent"
services on the desired system
2. Open the "global.vvc" file in the TERRA CLOUD Backup Agent
installation directory
3. Please add the following lines, if they are not present, after the curly braces of the "OpenFile" block
notification {
MailOnError = True
MailOnFailure = True
MailOnSuccess = True
}
4. Start the services "TERRA Cloud Backup Agent" and "TERRA Cloud Backup BUAgent"
on the desired system
5. Open the TERRA CLOUD Backup Portal and update your browser if necessary
6. Complete the configuration using the “Notification” tab, which is now visible again
Performance:
Bandwidth limitation and execution priority can be configured under this point.
According to current knowledge, changing the execution priority has no noticeable effect, so we recommend keeping the default value.
Bandwidth limitation is particularly recommended for weak connections during your customer's working hours.
At least 1.5 Mbps should be allocated for a backup.
Agent log files:
Under this tab you can view all global (cross-job) log files of the agent, which can be helpful for troubleshooting.
For example, log files of the BUAgent can be viewed; this service (TERRA Cloud Backup BUAgent) is responsible for the agent's communication with the backup portal.
Agent Update
The TERRA CLOUD Backup Agent can be updated as follows:
Windows (manual):
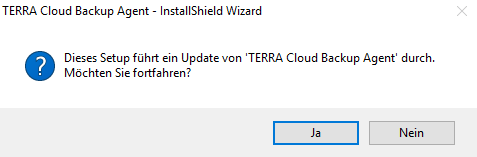
- As of agent version 8, the agent can be updated directly via the setup of the newer agent version
- When you start a setup of a newer agent, you will be asked if you want to update
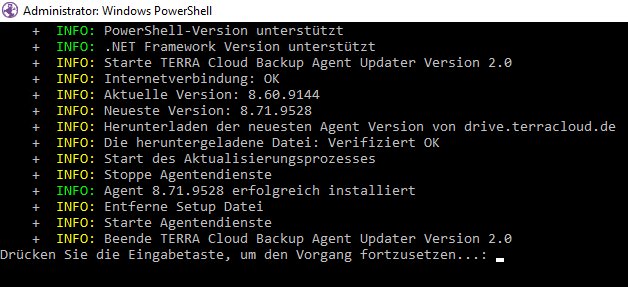
Windows (Agent Updater):
- Agents from agent version 8 can be updated using the Windows Agent Updater
- You can find the Windows Agent Update in the download area of the backup portal
- You will receive feedback about the individual steps, as shown in the illustration
Windows (Agent Upgrade Center):
You can update multiple agents centrally via the TERRA CLOUD Backup Portal. Instructions can be found at:
Agent Upgrade Center
Linux Agent
Installation
Please download TERRA Backup Agent. To do this, log in to the backup portal and select the appropriate version under Downloads on the right.
Please unpack the archive with tar -zxf PACKAGE-NAME.tar.gz.
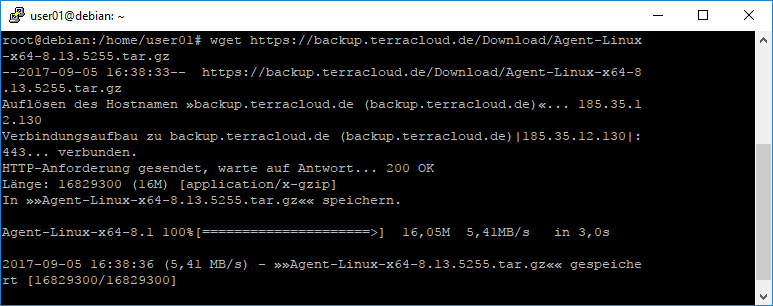
Then change to the directory and call install.sh.
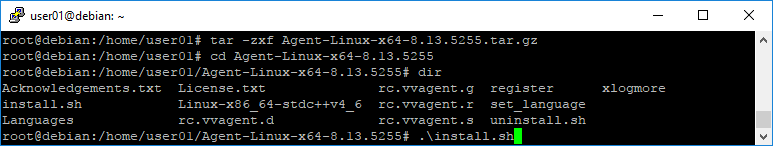
The installation is very simple and largely self-explanatory.
First the wizard asks for the installation directory. By default this is /opt/BUAgent.
If you agree, press Enter, alternatively you can enter a different path. If the installation directory does not yet exist,
you must then confirm the creation of the directory.
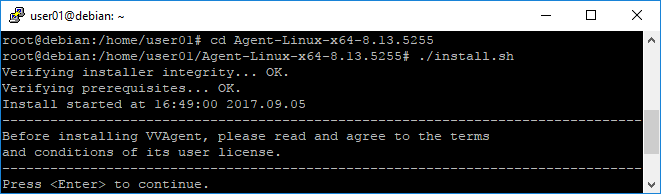
In the next step you can either confirm or change the “default language” using ENTER.
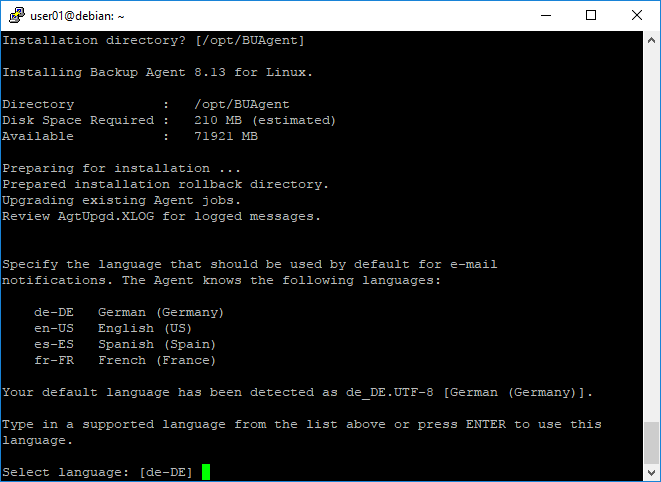
Under “Do you wish to register to a Web-based Agent Console server” you can also confirm the default value [Y] by pressing ENTER.
Now the address of the portal to which the agent should connect must be specified. Please enter backup.terracloud.de here.
In the next step, the default connection port 8086 must be confirmed using ENTER.
Enter the user name and password of the user created in 4.2.2 and confirm with ENTER.
The agent should now connect to the portal and complete the registration.
As soon as the message “Registered to the Portal” appears, the registration has been successfully completed.
The machine should now appear in the portal after a few seconds or minutes and can be configured.
Backup Jobs
File-based backup
How it works
The backup software accesses the file system of the system to be backed up. The files are read and divided into 32KB blocks; a checksum is calculated for each of these blocks. The delta can be determined in subsequent backups using the checksums. The blocks identified for backup are compressed and encrypted.
Fast File Scan
The "Quick File Scan" or "QFS Quick File Scanning" function allows the Windows agent to pre-filter files based on the timestamp (modified date) in the file system to determine the delta. Files whose modification date is newer than the last backup are read in and compared with the delta file of the last backup using the calculated checksums of the 32KB blocks. Only blocks that have not yet been backed up will be included in the backup.
Advantages and disadvantages file-based
Advantages:
- BMR backup possible
- Included as standard with the agent, no additional plugin is required
- No reboot required after installation
- Granular troubleshooting possible
- Files/directories can be excluded
- Can be administered from the agent console without portal access
- Script-based restore possible via VPR file
- Threat detection feature can be used
Disadvantages:
- Slower with lots of small files
- Navigation via portal when restoring individual files
Best Practice
1.In the best case scenario, use a file-based backup job only to back up individual files and folders 2.Add the “Entire Server” option to existing file-based BMR backup jobs 3.Use an image-based job to configure new BMR backups 4. File-based backup jobs are only recommended for up to a million files; above a million files we recommend an image backup job
Create file-based backup job
Click on the “Jobs” tab. Then click “Create new job for local system”.
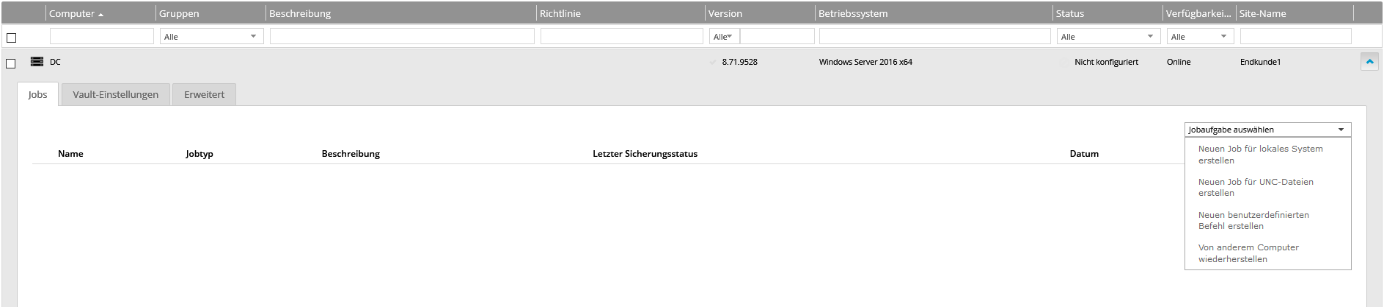
The “Create new job” window opens.
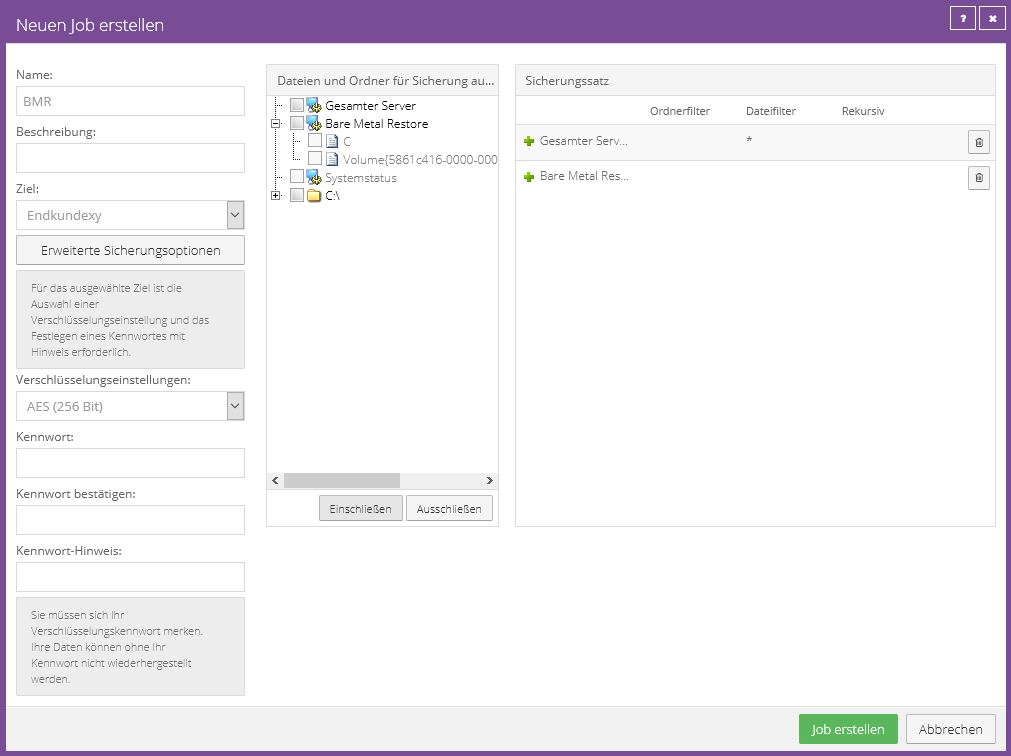
Please first give the job a name. The name “BMR” (for Bare Metal Restore) is used in the example.
The default encryption algorithm is AES 256 bit, which is considered very secure.
Then enter an encryption password (maximum 31 characters). Resetting an encryption password is not possible!
In the middle area you will find the directory structure that the agent transmits to the portal.
Here you can easily select all the directories and folders you want to back up.
In this example, the BMR and Entire Server options have been configured. Please note our
This not only backs up the actual system files, but also the bootloader. This means you can restore an entire server later.
With the “Bare Metal Restore” the entire c:\ system partition is backed up in addition to the data required for booting.
On the right you will then see the backup set. Objects marked with “+” are saved. If you would like to exclude individual data from the backup,
select the file and click “Exclude”. Objects marked with “-” are excluded from the backup.
Confirm the setting by clicking on “Create job”.
A window will then automatically open to configure the schedule.
Configure complex exclusions/inclusions in file-based jobs
The following instructions can be used for both local file-based backup jobs and UNC jobs (network shares).
When configuring one of the job types mentioned above, the portal can only be excluded or included to a limited extent.
Using the Backup Portal, you can only select one directory per exclusion entry in the job configuration and exclude folders and/or files in the respective subdirectory.
This means that the entry only applies to the level below.
Example complex exclusion:
You want to exclude all directories that end with _Backup in a backup job because they
Contains data backups that should not be included in the TERRA CLOUD backup.
D:\Data\*\*\*_Backup\*.*
In this exclusion there are two levels of different directories, each containing subdirectories ending in _Backup.
These directories and their contents are excluded using the syntax shown.
However, this complex exclusion expression cannot be configured in the portal and must therefore be copied manually into the job's configuration file.
Deposit exclusion in the job configuration:
1. Configure any exclusion
for the job
2. Stop both TERRA CLOUD Backup Agent
services
3. Open the JOBNAME.vvc file in the agent installation directory
4. Swap the exclusion created by step 1 with the one you want as in the following example
Exclude = "D:\*\*\*_Backup\*.*"
5. Start both services again
6. In the Backup Portal, check the job configuration and schedule and save it again if necessary
7. If you modify it manually, you will receive a warning in the Backup Portal, which you can simply confirm
8. After confirming the warning, please check whether the configuration has been applied as desired
For a complex inclusion, you can use these instructions analogously.
Ransomware Threat Detection
This file-based backup option allows the agent to scan the system for potential threats during backup.
If a possible threat is detected, the data backup is marked as a “potential threat”.
The current and all subsequent backups will retain this flag until one of the actions is taken.
Note: The agent does not check for possible errors in a seed backup or the first backup
Ransomware threats when threat detection is enabled in a job.

Handling potential threats
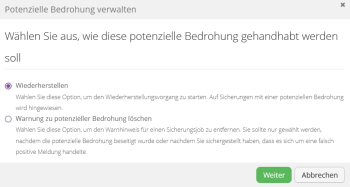
If ransomware threat detection fails, the following options are available through the Manage Potential Threat action.
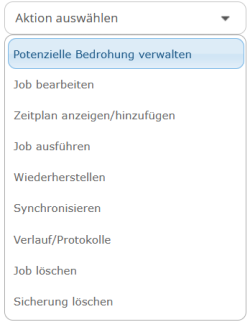
1. The "Recovery" option allows you to configure granular recovery and delete the infected backup individually after recovery.
2. In case of a hoax, you can select the "Delete a potential threat alert" option and confirm the deletion of the alert.
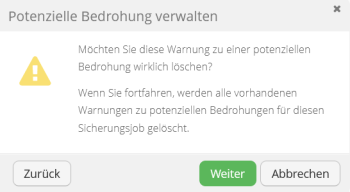
Image-based backup
How it works
In contrast to a file-based backup job, which protects individual files and folders when backing up, an image job backs up all blocks of a selected volume. It is possible to set up a BMR backup if all system-relevant volumes are backed up.
Changed Block Tracking
The image plug-in installs a changed block tracking driver, which requires a restart after installation. This can be used to determine which blocks have changed in relation to the last backup.
Advantages and Disadvantages Image-based
Advantages:
- BMR backup possible
- Faster for lots of small files
- Recommended for natively protected data volumes of 1TB or more
- Requires less processing power than file-based backup
- Convenient Restore (Image is attached)
- Navigation via Explorer when restoring
Disadvantages:
- Exclusion of individual files and folders is not possible
- Restore only possible on disks of the same size/larger
- Restart required after plugin installation
- No granular troubleshooting possible
- ReFS is not supported
- Threat detection feature cannot be used
Best Practice
1. The restart can be done at a later point in time (usually after the end of work). The agent can be configured without restarting. 2. To protect the entire system, including the possibility of a bare metal restore, select the "Entire Server" and "BMR" options. 3. If data (such as local backups / dumps) needs to be excluded, you can move it to a separate volume and explicitly not include this volume in the backup set. The "Entire Server" option cannot be used in this case.
Create image-based backup job
Requirement:
The image plug-in must be installed on the system.
If the plug-in is not yet installed, you can run the agent setup again and use the "change" option to install the plug-in later.
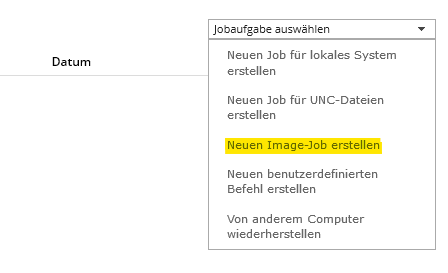
Create job:
In the backup portal, please select the image job under "Select job task" as shown in the following screenshot:
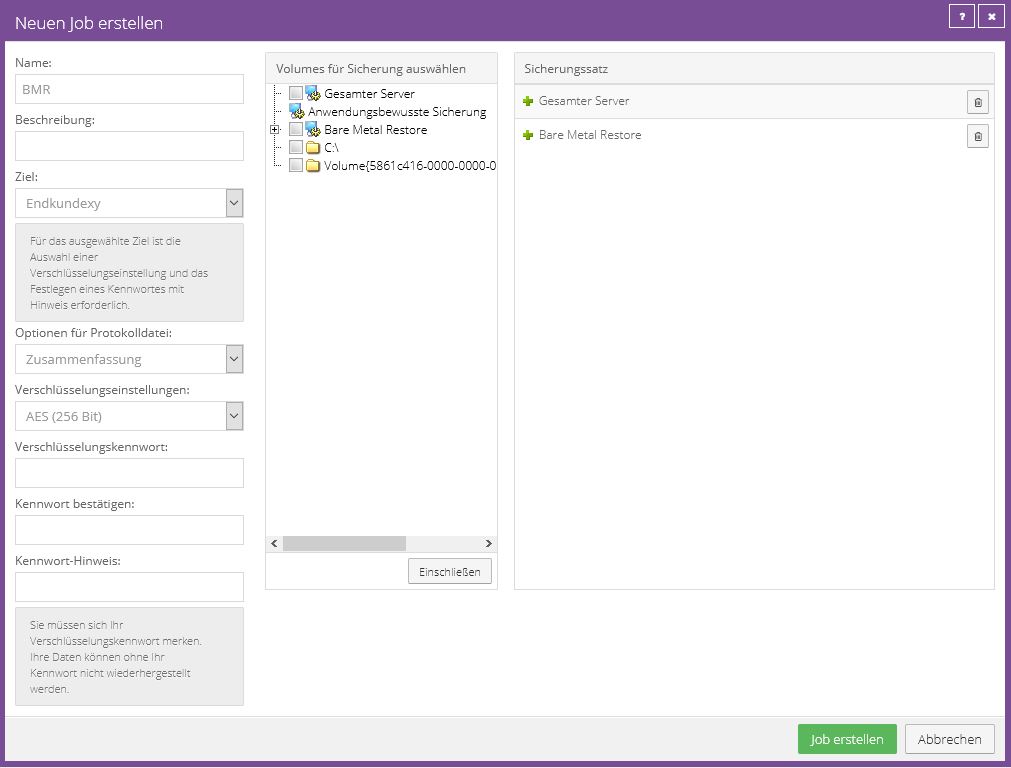
Configure job:
In this screenshot you can see an example configuration from an image job. In this, the “Bare Metal Restore” and “Entire Server” options were selected and included in the backup set.
Instead of showing the file system, the agent only shows individual volumes.
Application Aware Backup' option:
In addition to a BMR backup, this option also enables the transaction logs of a Microsoft SQL Server to be truncated and backed up.
In order to use this, you must provide the access data required for the SQL instance.
We recommend not using this option and using your own SQL job for a comprehensive backup of a SQL instance.
Entire Server' option:
If you add this option to the backup set, all partitions (volumes) of a system will be included in the backup. This excludes removable storage media (e.g. external hard drives or USB sticks). Partitions (volumes) added later are automatically included; there is no need to adjust the configuration.
Note:
For an image-based backup job, BMR protection is automatically provided by the "Entire Server" option, but in order to be able to offer a standard configuration for file- and image-based backup jobs, the option was changed BMR additionally added in the screenshot above.
UNC-Backup Job
Documentation
Complete setup instructions can be found in the User Guide of the Windows Agent Chapter 5.4.
How it works
The Windows agent connects to the stored network share and saves the selected files. For authentication, a user must be provided with read and write permissions.
Best Practice
1. A UNC backup job should protect a maximum of 500,000 files or 1 TB of native data. If more data needs to be backed up, we recommend distributing it across several UNC backup jobs. 2. Since backing up a network share via a DFS namespace is not supported, we recommend backing up the server share directly without using the namespace. 3. Recommended backup method for files stored on NAS systems (e.g. from Synology, QNAP).
Schedule Recommendations
Daily and Monthly Backup
This schedule runs one backup per day, using a Daily or Monthly retention type.
The last calendar day uses the Monthly retention type, and all other days use the Daily retention type.
The time was configured identically due to the priority, so that every day except the last calendar day, line 1 does not apply and line 2 must be checked.
Since the conditions in line 2 are met on any other day, this is executed.
This configuration prevents daily and monthly backups from being created on the last calendar day.
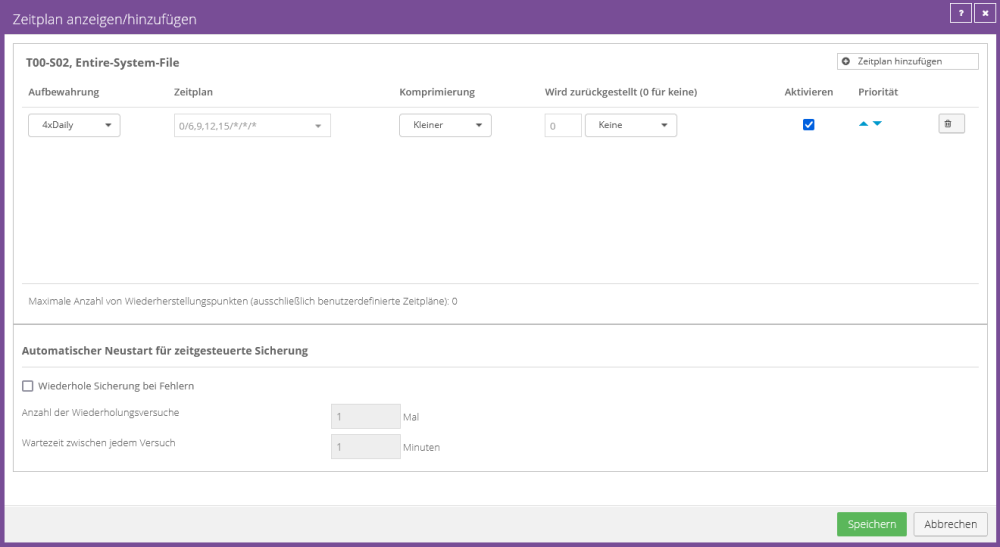
Example configuration:
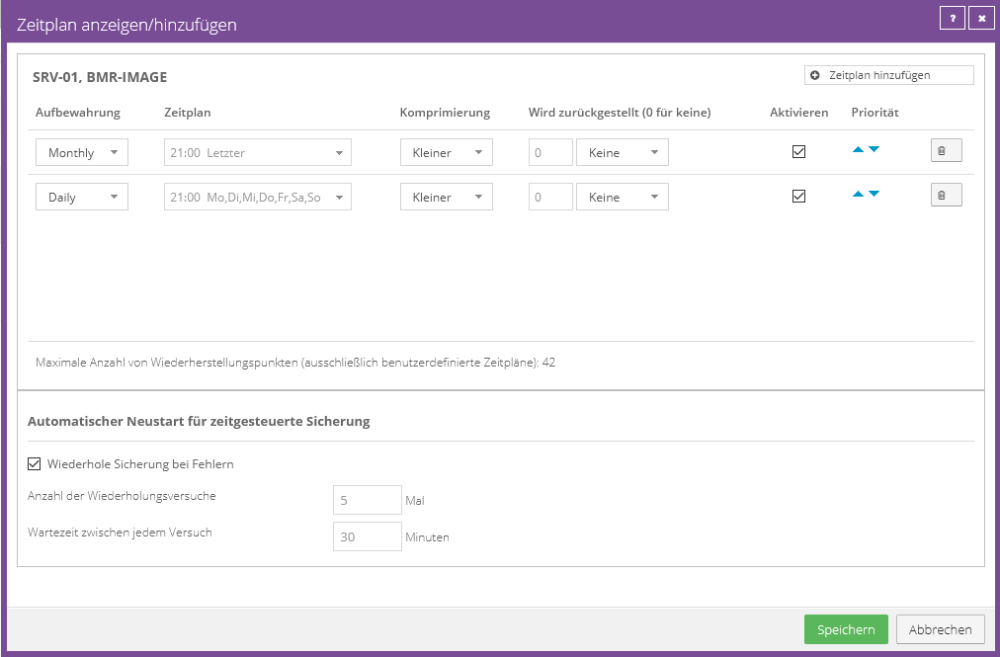
Four daily backups
This schedule runs four backups per day, with retention type "4xDaily".
The backup times were set at the beginning and end of the working day plus two additional backups within the working day.
In the example configuration below, the backup is performed on the hour at 6 a.m., 9 a.m., 12 p.m. and 3 p.m.
If the system data is changed 24/7, it is recommended to distribute it at equal intervals, e.g. E.g. 0/6/12/18
Example configuration:
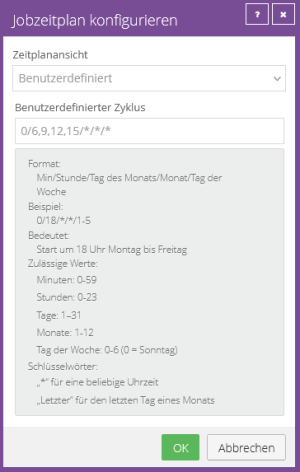
Run job manually
If you wish, you can also run jobs manually.
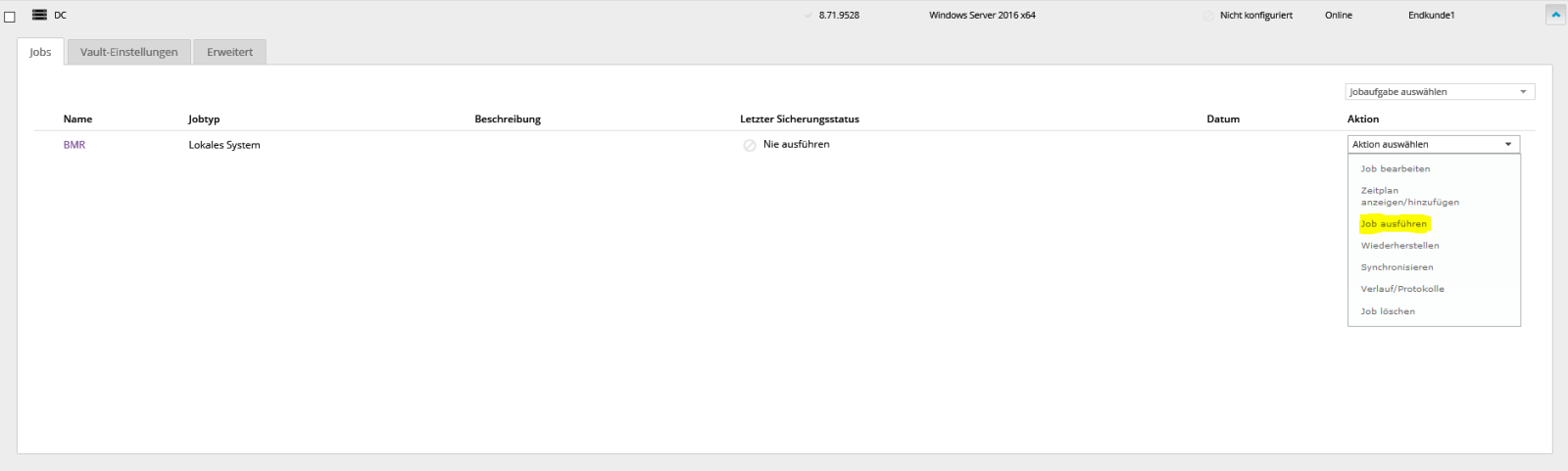
Click “Start Backup”.
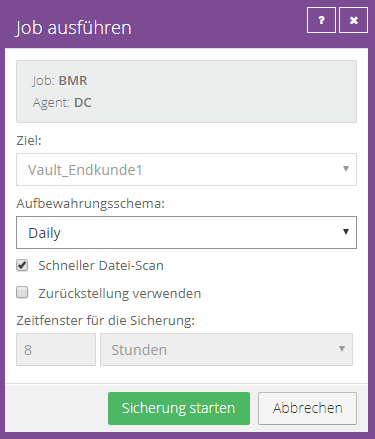
Completed backup process:
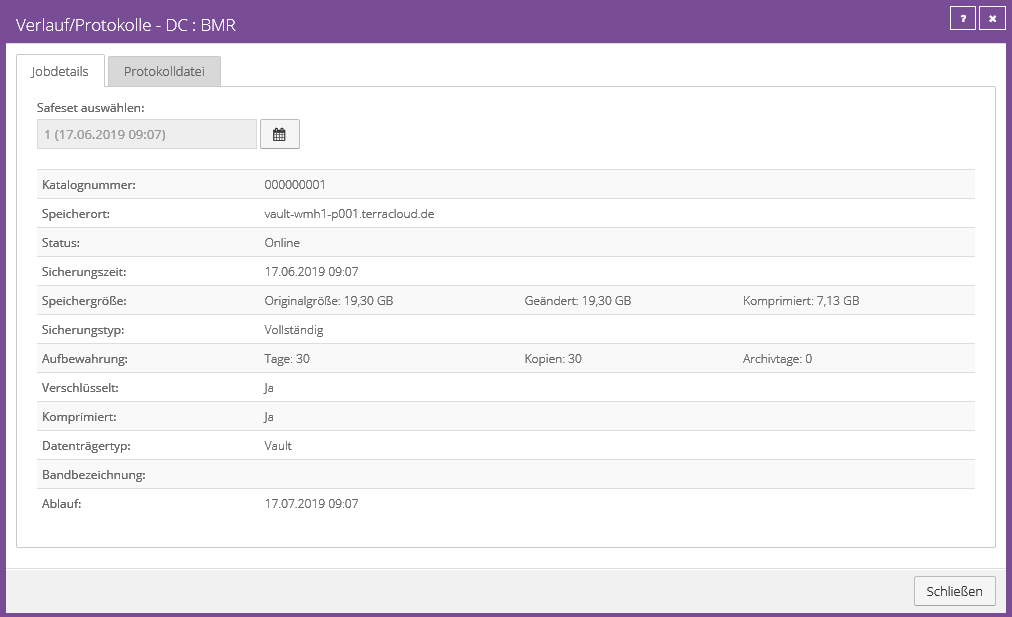
Since the agent is able to compress, in this case only 7.13 GB of data was transferred and stored in the vault for a complete Windows Server 2016 VM. The original size of the system is 19.30.
This is an initial backup, as 19.30 GB is also stored under Changed.
We can also see under the “Jobs” tab that the backup process was completed successfully:
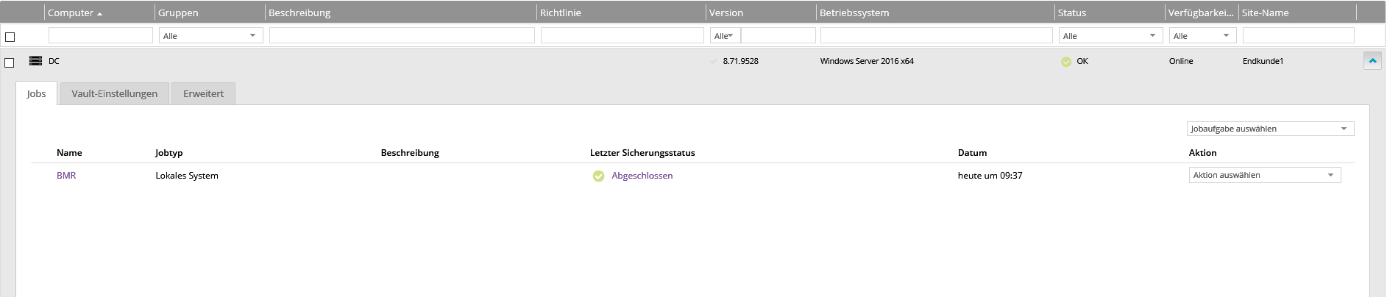 Further details can be viewed by clicking on “Completed” in the middle.
Further details can be viewed by clicking on “Completed” in the middle.
Reset function
The deferral option allows a backup to be completed after a defined period of time, regardless of how much data from the initial backup has already been transferred.
After the defined security window of, for example, eight hours, a safeset is created.
A deferral can be defined in the schedule and in manual execution:
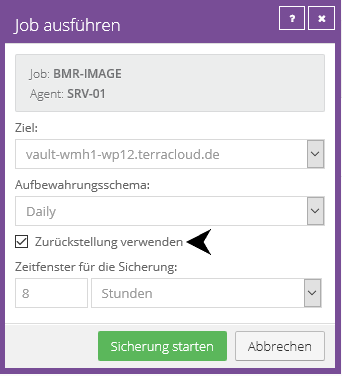
Important:
A backup with active deferral results in an incomplete backup.
Restoring from a backup with active holdback can only be done for a file-based job.
Recommendation:
The defer feature can be used exclusively for initial backup. You can select the deferral during manual execution or store it in the schedule.
We recommend placing a reminder in the agent description that the defer feature is active in the schedule. After the first successful completion of the backup without deferral, you can remove the feature from the schedule and the reminder from the agent description.
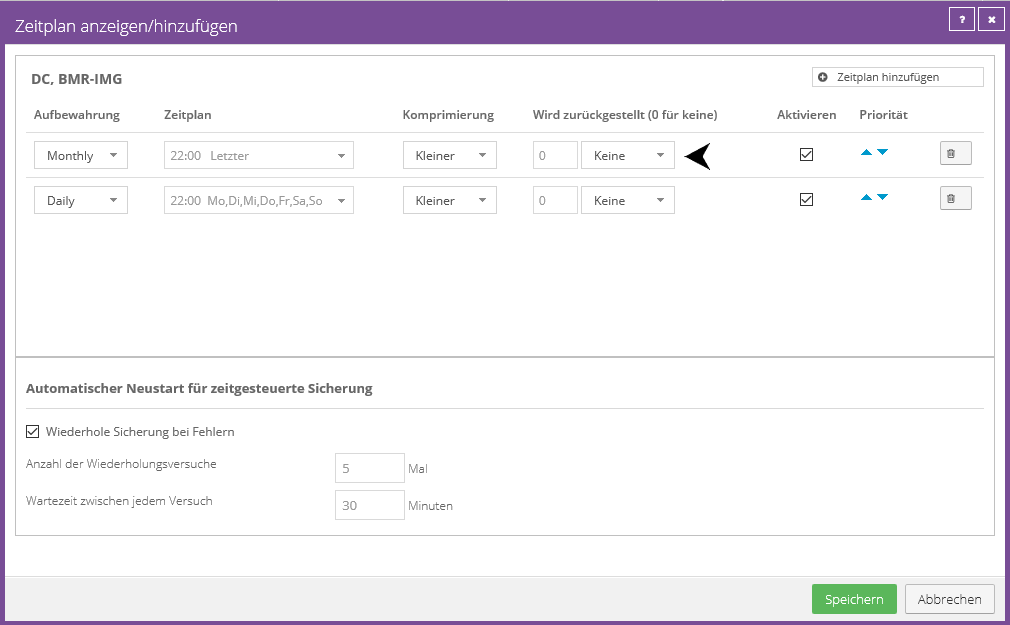
Deferral can be used to split the initial backup or seed backup into multiple backup operations. You will receive a warning in the log file until the backup job has been completely completed. With a BMR job, BMR protection is only available after the first successful completion without deferral.
Example:
Day 1:
The backup job is started for the first time with a deferral and ends the backup after a defined period of 8 hours and Safeset 1 has been created.
Day 2:
The backup will start again and create Safeset 2 after 8 hours.
Day 3:
On the third run, the backup job completes before the 8 hour period, Safeset 3 is created and the seed backup is completed successfully.
The status of the backup job changes from "Postponed with Warnings" to "OK".
Restore a backup job
After backing up data from a system, you can select “Restore” under “Actions” in the backup jobs.
Windows
Restore from a file-based backup
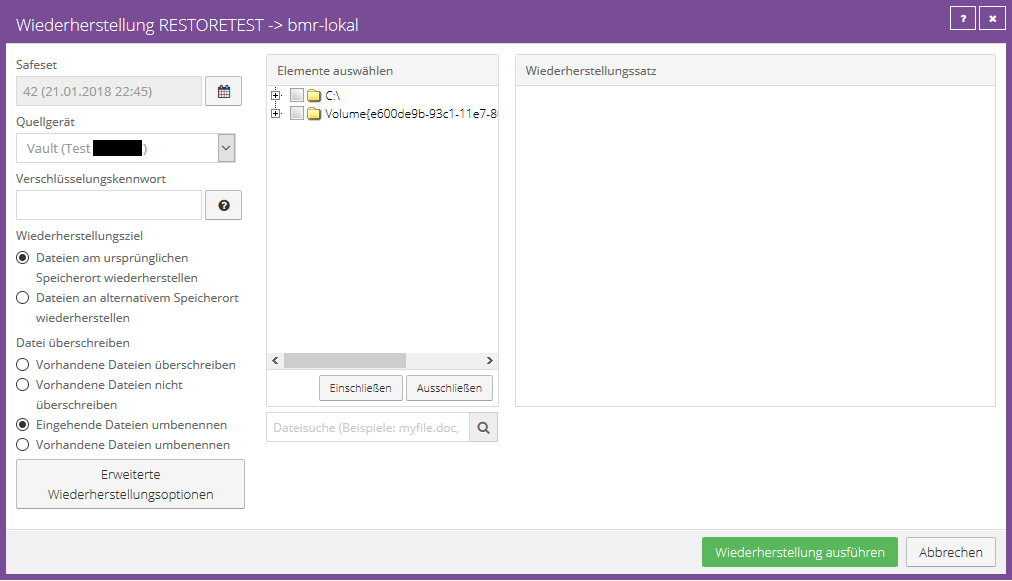
You can use the calendar button to select the safeset from which you want to restore the data.
Enter the job's encryption password. The Hint button displays your password hint once clicked.
The folders and files to be restored can be set using check boxes for complete folders or files and then included in the recovery using “Include”.
With the search function it is possible to search for specific files without looking for the file path.
The wildcard characters * (for any number of characters) and ? (for a single character).
However, the question mark cannot be used for an umlaut (ö,ä,ü). Select the appropriate files and add them to the recovery by clicking “Include Selected”.
To search for files in a specific backup folder, enter the desired path in the Search Path field.
When you include a folder in a restore, the subdirectories and files in that folder are also included by default.
If you only want to restore a portion of the subdirectories or files in a folder, you can add filters to the include record.
It is also possible, for example, to add a filter to restore only files with .doc or .docx extensions in a folder.
If you exclude a folder from a restore, the subdirectories and files in that folder are also excluded by default.
If you only want to exclude a portion of the subdirectories or files in a folder, you can add filters to the exclude record.
For example, you can add a filter to exclude only files with .exe extensions in a folder from recovery.
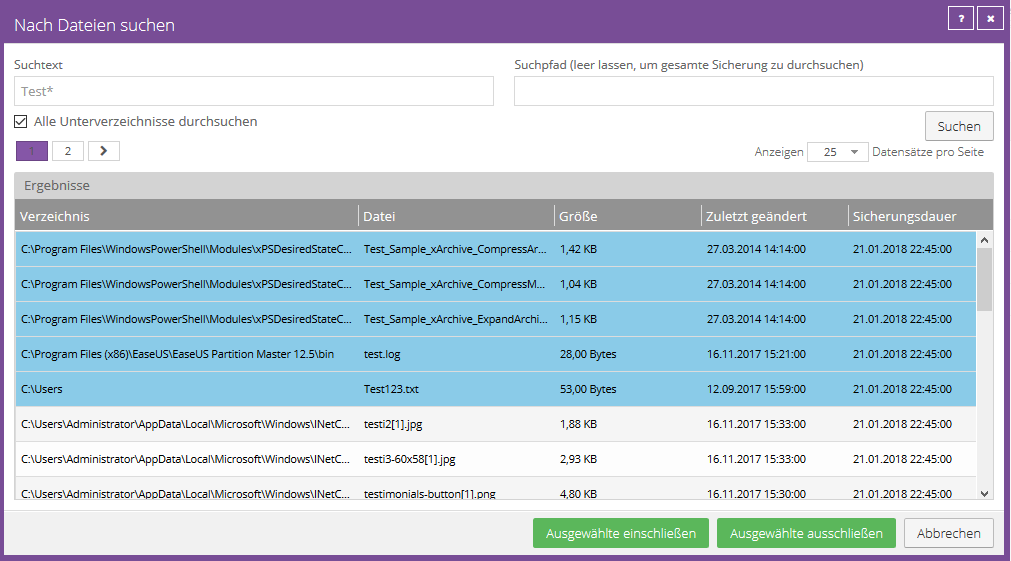
You have the options to restore the files to the original location or to an alternative location.
If you decide to use an alternative storage location, you can use the folder button to select the desired storage location.
You also have the options to overwrite existing files, not overwrite (this adds a numeric extension, e.g. .0001), rename incoming files and rename existing files.
Overwrite existing data
If you try to restore multiple files with the same name to an alternate location and select Overwrite Existing Files, only the last file restored will be retained.
Other files with the same name will be overwritten. To add a numeric extension (e.g. .0001) to a recovered filename, select Do not overwrite existing files.
For example, if you restore a file named "filename.txt" to a location where there is a file with the same name, an extension is added to the restored file name (for example, "filename.txt.0001").
Under no circumstances should you select the entire C: volume and let it overwrite the existing volume. This will result in serious damage to the system!
Rename existing files
To add a numeric extension (e.g. .0001) to an existing filename, select Rename Existing Files.
For example, if you restore a file named "filename.txt" to a location where there is a file with the same name, an extension is added to the existing file name (for example, "filename.txt.0001").
The name of the restored file is still “filename.txt”.
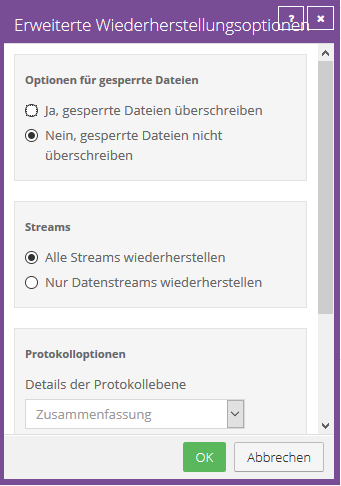
Advanced Recovery Options
Locked File Options
When restoring data from a local job, you can specify whether locked files should be overwritten by restored files with the same name.
To do this, select one of the following options:
- "Yes, overwrite locked files"
Files in the system that are locked during recovery will be overwritten with the recovered files upon reboot. This option must be enabled for system state or system volume restores.
- "No, do not overwrite locked files"
Files in the system that are locked during recovery will not be overwritten with the recovered files with the same name upon reboot.
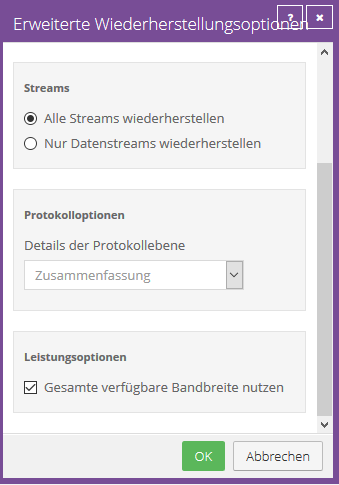
Streams
When you run backups, information from your files is captured in different streams.
The original data created by a user is called a data stream.
Other information such as security settings, data for other operating systems, file references and attributes are stored in separate streams.
When restoring data from a local job, you have the following options to choose from:
- "Restore all streams"
Restores all information streams. Use this option when restoring files to a system with an identical platform.
- "Restore data streams only"
Select this option for cross-platform restores. With this option, conflicts do not arise due to system-specific data streams.
Protocol options
From the list, select one of the following logging levels:
- Files: Provides more detailed information and is typically used for troubleshooting. Provides information about files that are being restored.
- Directory: Provides less detailed information than the Files logging level. Provides information about folders that will be restored.
- Summary: Provides top-level information including Vault/Agent version and backup size.
- Minimal: Provides top-level information including Vault/Agent version.
Changing the logging level only affects log files that are created afterwards. Log files that have already been created are not affected by this change.
Performance options
To use all available bandwidth for recovery, select "Use all available bandwidth."
Bandwidth throttling determines how much bandwidth an agent can consume for backups and restores.
For example, you can limit traffic so that online users are not impacted and allow unrestricted usage at night so that scheduled backups or restores can occur as quickly as possible.
Bandwidth throttling values are set at the machine (or agent) level and apply to backups and restores.
When three jobs are running simultaneously on a computer, each job receives 1/3 of the specified maximum bandwidth.
Possible bandwidth settings: Maximum bandwidth (upper limit) in MB per second that the agent is allowed to consume for all backups and restores.
Period of time during the day when throttling is activated. Only one time window can be specified.
There is no throttling outside the time window. The days of the week that throttling is enabled.
Once the bandwidth throttling window begins during an ongoing backup or restore, the maximum bandwidth is dynamically applied to the running process.
If the throttling window ends while a backup or restore is in progress, bandwidth throttling is removed.
If you change an agent's bandwidth settings while a backup or restore is in progress, the new settings do not affect the ongoing process.
The bandwidth settings are applied when the backup or restore starts and are not changed afterwards.
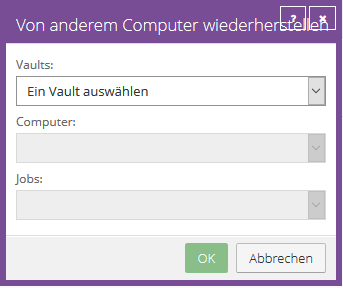
Restore from another computer (file based)
It is possible to restore some or all of the data backed up on one computer to another computer with the same characteristics.
To restore the data from another computer, you can redirect the data from a backup job in the Vault to another computer.
If the data was backed up with a plug-in, the same plug-in and the corresponding installation (e.g. Microsoft SQL) must also be present on the target computer.
The new computer then downloads information from the vault to restore the data to the new computer.
Example: Computer A backs up its data with Job A, Computer B restores Job A's data (Computer A's data) to Computer B.

Restore from an image-based backup
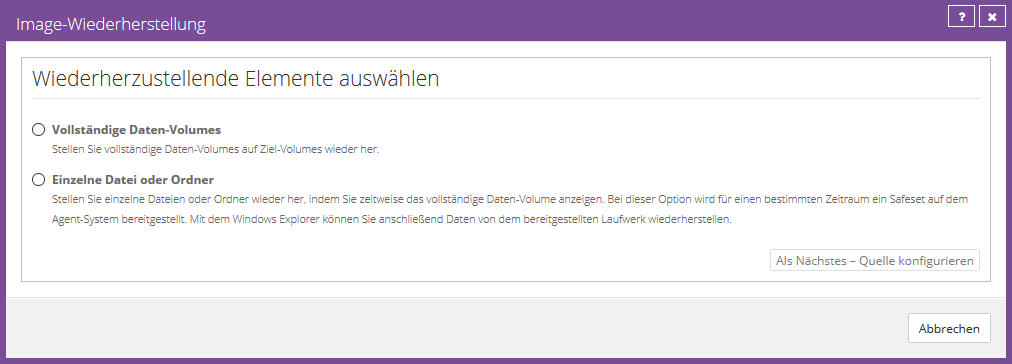
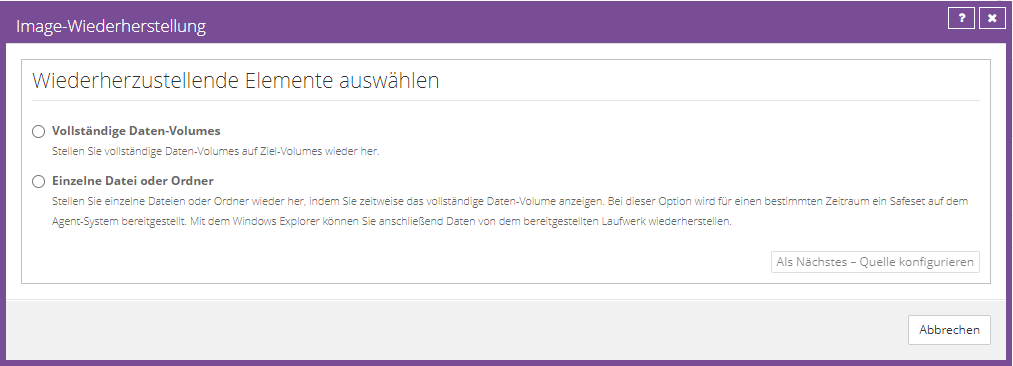
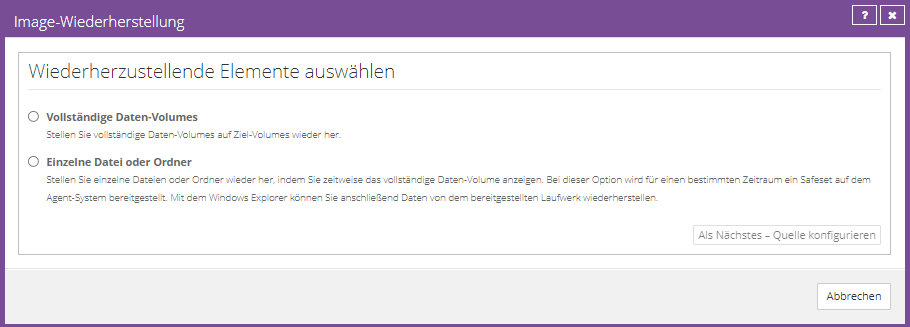
You can choose whether you want to restore a complete partition or individual files or folders.
Select the manufacturing you want and click “Configure Source Next”.
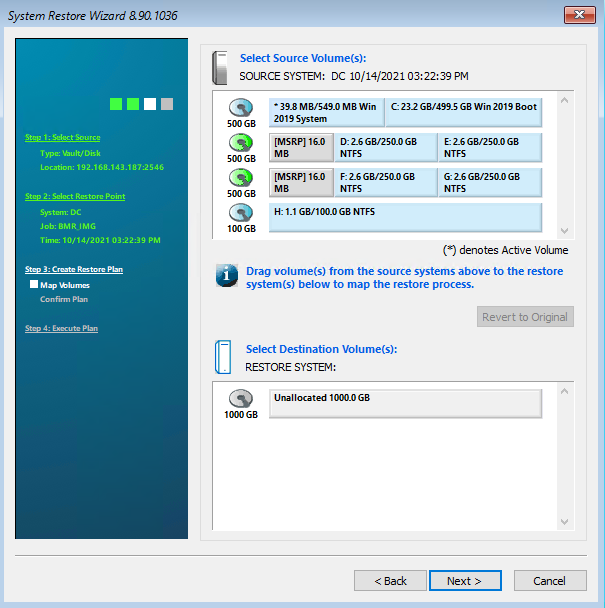
Volume Recovery
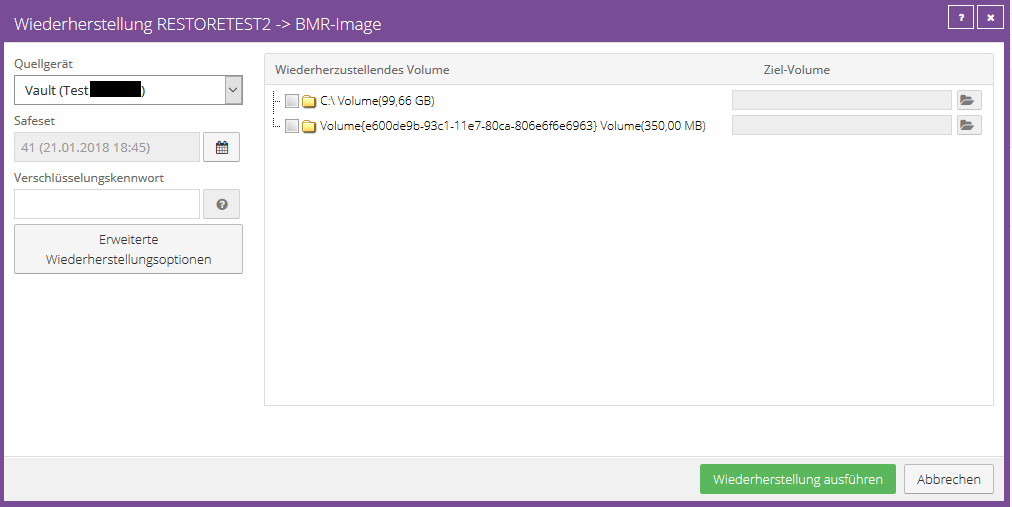
Select the desired volume to be restored.
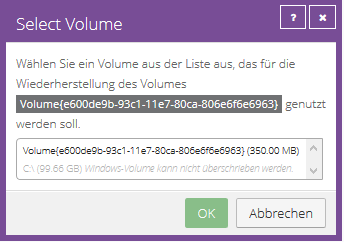
Next, select an existing volume to restore to.
Click “OK” and then click “Run Restore” to start the restore process.
File or folder recovery
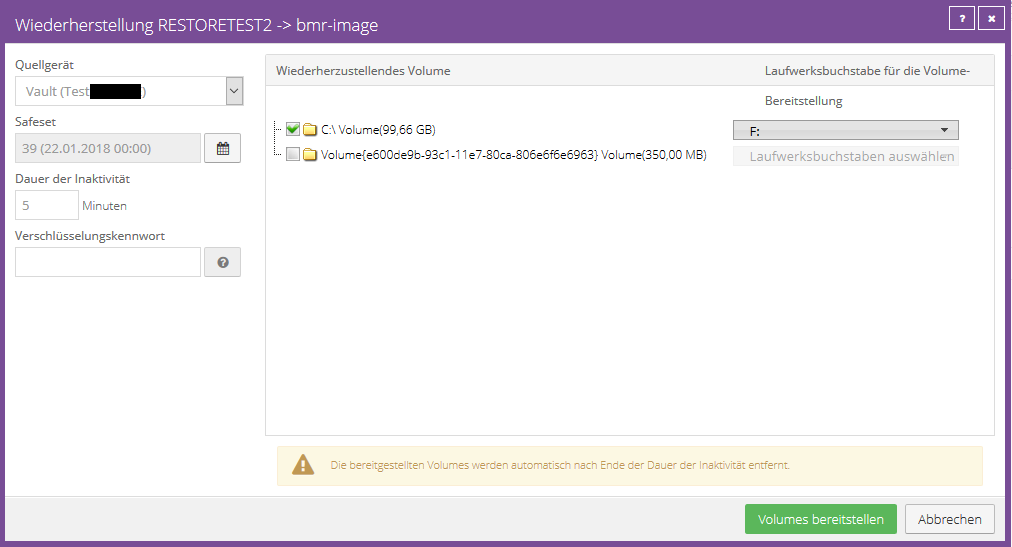
Select the volume from which individual files or folders should be restored and assign a valid drive letter. (Please do not use A & B)
Now click on “Mount Volumes”. The backed up volume is mounted on the affected agent and you can restore the required files or folders to a local volume by dragging and dropping them.
Under “Duration of inactivity”, set a generous time limit for how long the drive should be mounted. By default we recommend the value 60 minutes.
Restore from another computer (image based)
You can restore successfully backed up data to another computer with the same agent configuration.
To do this, you can transfer/copy existing backup jobs in the Vault to another computer.
Since an image job is a plugin job, the image plugin must exist on the target agent.
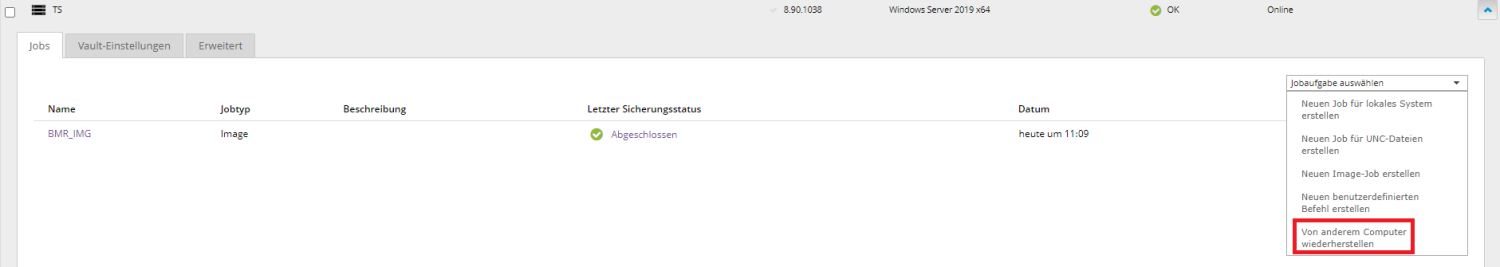
Example: Computer A is down/no longer in use, but now you need to restore data from Computer A. To do this, copy the job from computer A to computer B to perform a restore.
Select Computer B in the backup portal.
From the Select Job Task menu, click Restore from Another Computer.
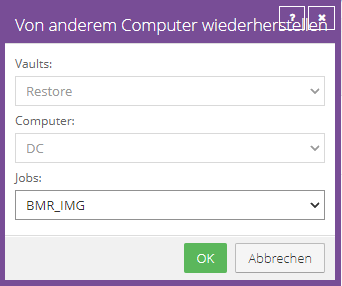
The Restore from Another Computer dialog box opens.

In the "Vaults" list, select the vault in which the backup of Computer A was stored. If the restore is to be carried out across vaults, the agent must first be registered with the source vault.
Once the correct vault is selected, you will find Computer A in the Computers tab.
After computer A is selected, you will find its job in the Jobs tab.
Confirm with OK once a selection has been made.
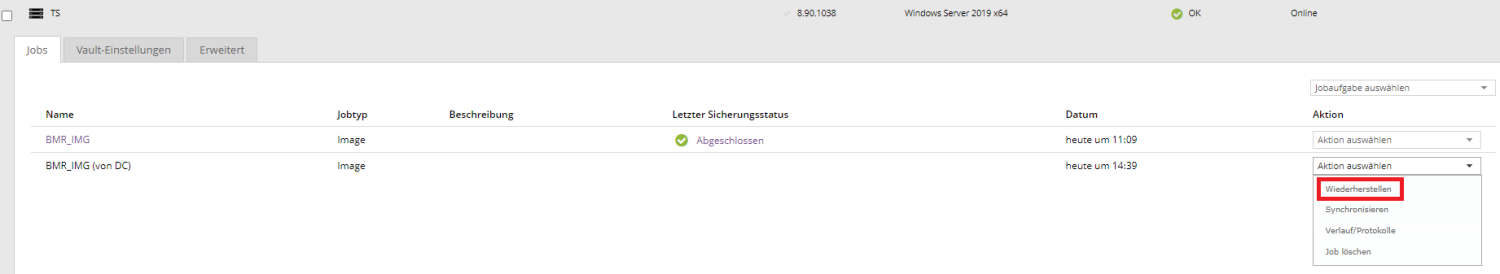
The portal attempts to download required job information to Computer B. Once these are downloaded, the job will appear in Computer B's Jobs tab.
A recovery process will start automatically. Once you have selected the desired restore here and entered the encryption password to decrypt required information, you can proceed with a normal image-based restore.
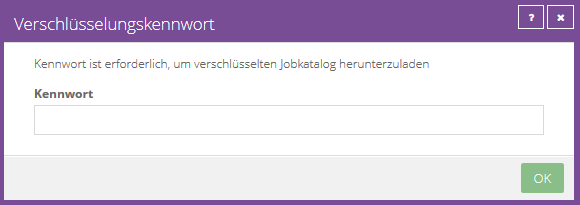
If an error occurs while downloading the job information, the restore cannot continue.
This can happen if the job information is not available or a required plugin is not installed on the target computer.
Make sure the required plugin is installed on the target computer before repeating the process. (Change installation via Agent Setup or via the "Select job task" action)
Restore from another computer
The Restore from another computer option allows users to transfer/copy a job to another agent for restore. For this purpose, the job information (job name, type, number of existing backups) is retrieved from the vault and then stored in the agent directory of the target agent. A temporary entry is then created in the Jobs tab.
This wizard contains the following steps:
- Select an existing Vault profile
- Select the computer that backed up the job to import
- Select the job to restore
- The wizard now copies the job into the agent directory of the affected agent
- Display of the job in the jobs tab of the affected agent
Linux
Restoring a backup is the most common usage, allowing you to restore anything from a single file to a directory structure to an entire system.
To start a restore, select a job (that is, highlight it) and do one of the following:
- Select Actions and Restore.
- Click the recovery icon (or use CTRL+R).
- Right-click a job in the left pane.
The recovery wizard will start. It offers the following options:
- Select a source device, vault, or directory type. Depending on which option you choose here, you can also select a vault and a backup. You can also choose to restore from a specific backup set or a series of backup sets.
- Enter the password if the backup is encrypted. If the backup is not encrypted, this window may not appear. If you forget the password, you will not have access to the backup data.
- Select the recovery objects (files or directories). You can expand the directories (if any) and select or deselect files to restore.
- Enter recovery destination options. You can choose to restore files to the original location or another location, create subdirectories, and overwrite existing files.
- Select the other recovery options. You can overwrite locked files and select all streams or only data streams. You can choose a log file with different levels of detail.
- Click the Finish button to start the restore process. The restore will be performed and the process information will be displayed.
You may want to view the log files after the process is complete. The recovery logs are identified by the prefix “RST” in the log list.
Assign alternative static IP for a BMR restore
By default, a BMR restore restores the original network configuration.
If you would like to assign an alternative configuration, for example to carry out a test restore, we recommend starting the system without network access first.
With a Hyper-V, for example, you could initially boot into the recovery ISO without a connected external vSwitch. After adjusting the network configuration, you can connect the VM to the vSwitch. This ensures that the system never goes online with the old IP address.
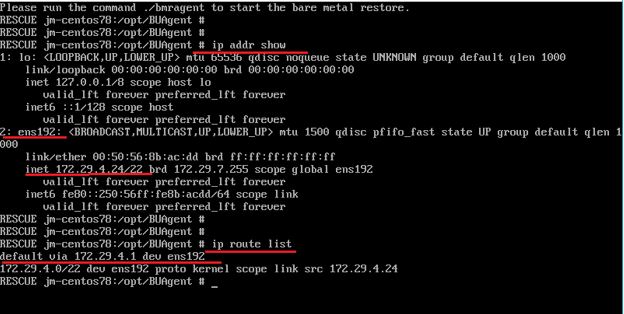
Please follow these steps to adjust the network configuration before restoring:
- Boot into the Restore ISO and initiate the restore until the step where you are asked to run ./bmragent.
- Find the name and configuration of the network interface using ip address show
- Take the interface offline by e.g. ip link set name of network interface down
- Delete the old IP address that you determined in the first step, e.g. ip address del 172.29.4.24/22 dev name of the network interface
- Configure a new IP address using, for example, the following command ip address add 172.29.4.29/22 dev name of the network interface
- Take the network interface back online after customization
- Finally, configure the default gateway using, for example, ip route del default and then ip route add default via 172.29.4.1 dev name of the network interface
In this screenshot you can see an example of step 1 from the instructions:
Bare Metal Restore
A bare metal restore is a complete restore of a secured system, including all components required for the boot process (e.g. the bootloader).
Disaster recovery options
The following flow chart shows you possible workflows and recommendations for action for various Disaster Recovery scenarios.
Export drivers of a secured system
You can export all drivers of a system using the following instructions:
- Create a directory in which the drivers should be stored, e.g. (C:\Drivers)
- Run this command with administrative permission in CMD:
dism /online /export-driver /destination:"C:\Driver"
You can add the exported drivers when creating a new restore iso. If complications arise during a BMR test restore, we recommend exporting the drivers of the protected system as described above and adding them to the restore ISO. Please keep this ISO or drivers separately.
Create Restore ISO
To perform a bare metal restore, you need a restore iso (.iso file).
The Restore ISO is based on Windows PE and also contains the recovery software of the TERRA CLOUD backup solution, which is started automatically as soon as the system boots into the ISO.
You can create this ISO yourself and use it for BMR restore of all your systems.
Download:
Please download the Bootable Media Creator from the Backup Portal.
Installation:
Now install the Bootable Media Creator, which also requires the Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit. By default you will be guided through the installation of the ADK components via the Bootable Media Creator Setup. Alternatively, you can use the following setups for the installation:
https://backup.terracloud.de/Download/adksetup.exe
https://backup.terracloud.de/Download/adkwinpesetup.exe
Please note that both the ADK setup and the WINPE setup must be executed.
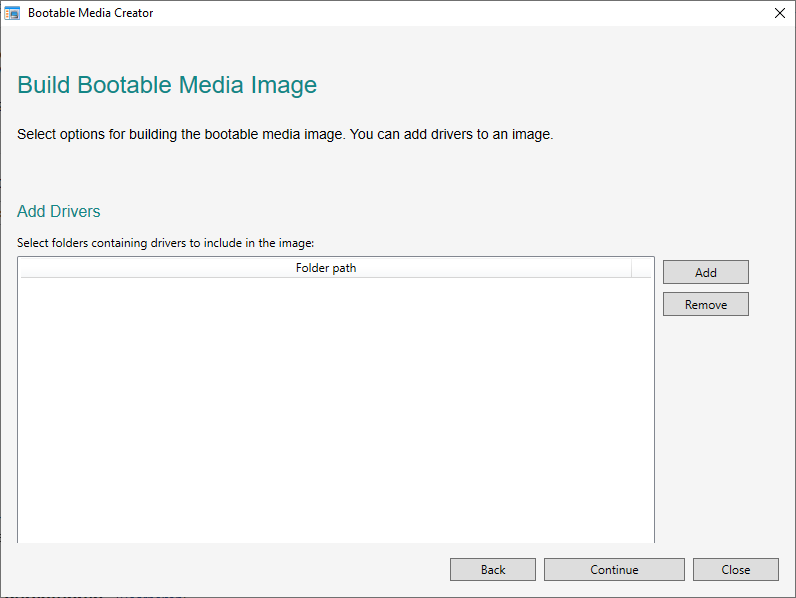
After installation, the image can be created very easily.
First start the Bootable Media Creator and simply select a target directory below.
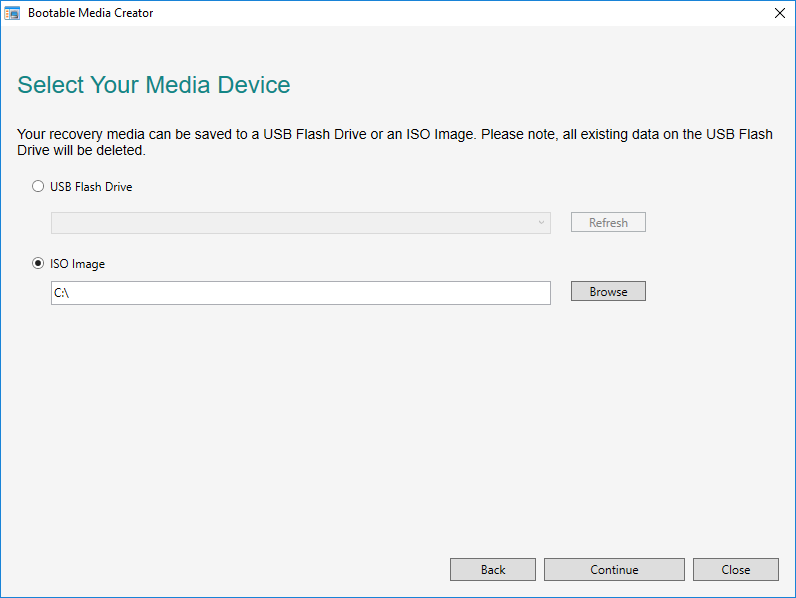
You can add exported drivers from Export Drivers in this step by selecting the driver directory using "add".
Now click on “Continue” to create the image.
The image can now be burned onto a CD or attached to a virtual machine, for example.
Perform restore
The following instructions show a typical restore operation in a virtual machine. The ISO file was attached to the virtual machine.
The legacy adapters must be used as network adapters under both VMware and Hyper-V.
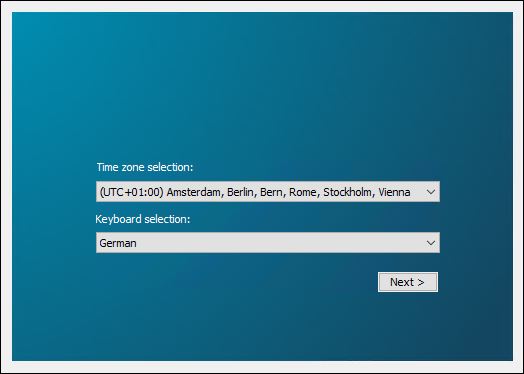
After restarting the machine, a connection to the machine must be established via the console. The following image then appears:
In the first step, configure the time zone and the desired language, then click Next.
In the following window, accept the license terms and then click on “Next”.
By default, the “System Restore” gets the IP address from a DHCP server. If there is no DHCP server or you want to assign the IP address manually, click on “Settings” in the main menu.
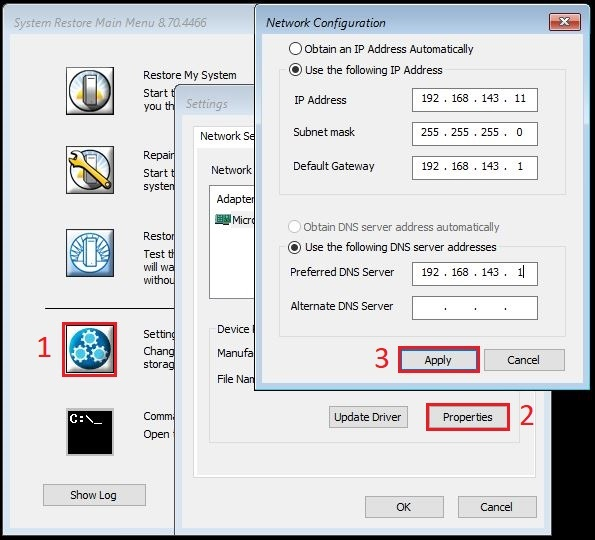
Select the network interface and then click “Properties”. Assign an IP address and confirm with “Apply”.
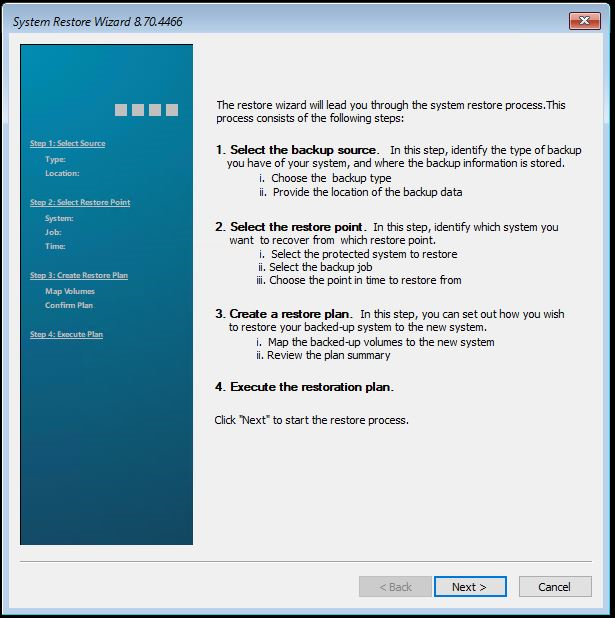
To perform a restore process, click on “Restore My System” in the main menu. Click "Next" in the wizard.
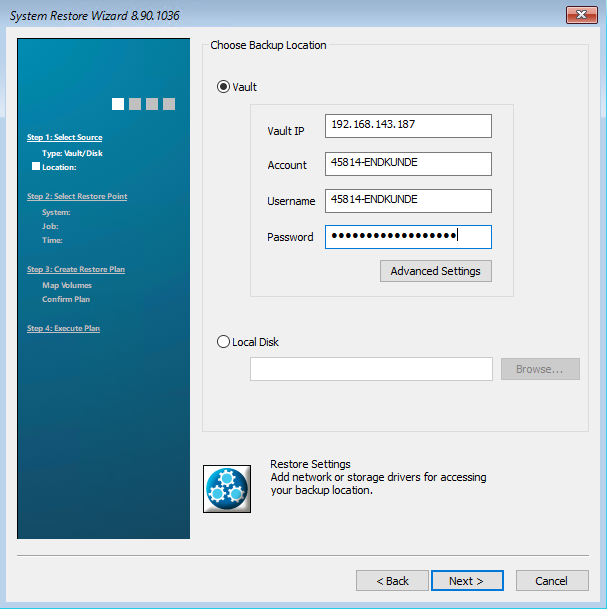
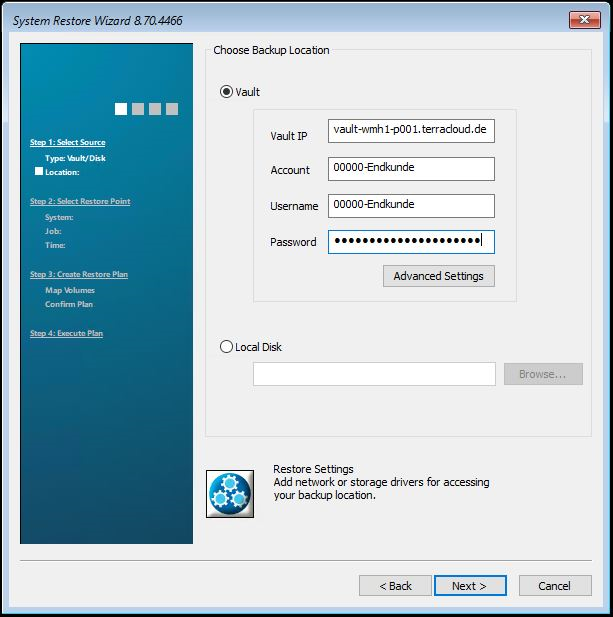
On the following page, enter your data for the vault (data storage) and confirm with Next. The system restore now tries to establish a connection to the vault.
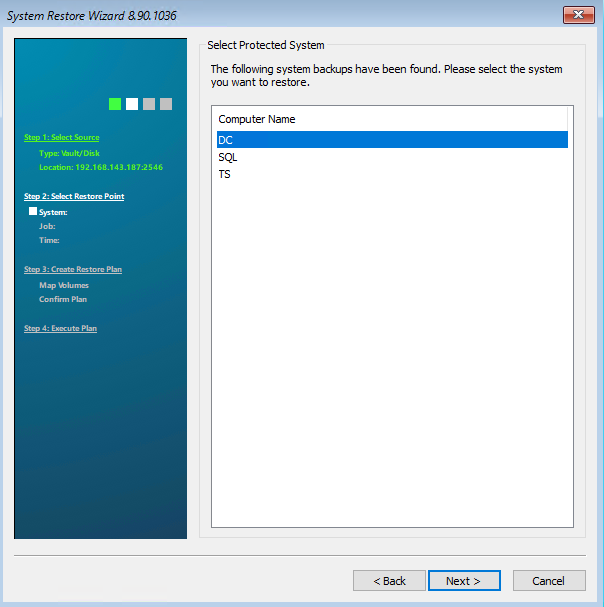
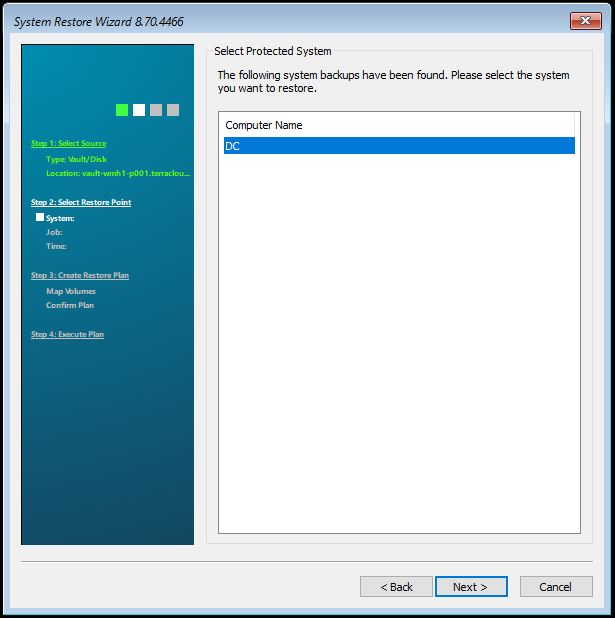
On the following page you will see all the computers that belong to your account. Select the computer you want to restore. Then click on “Next”.
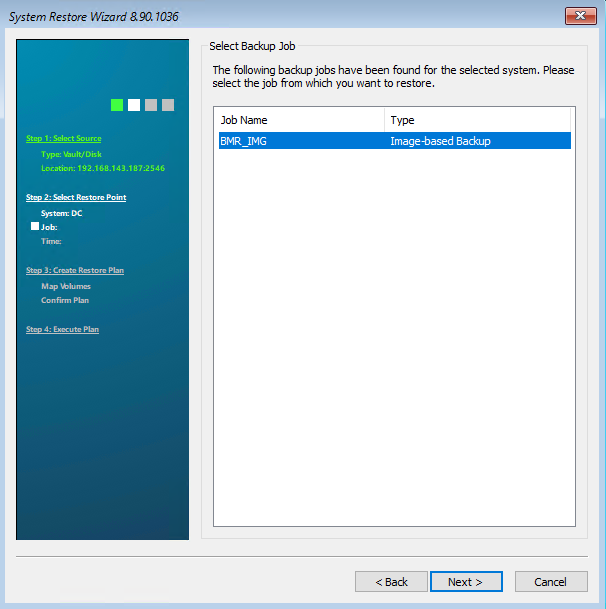
On the following page you will see all backup jobs that belong to this computer. Select the job you want to restore. Then click on “Next”.
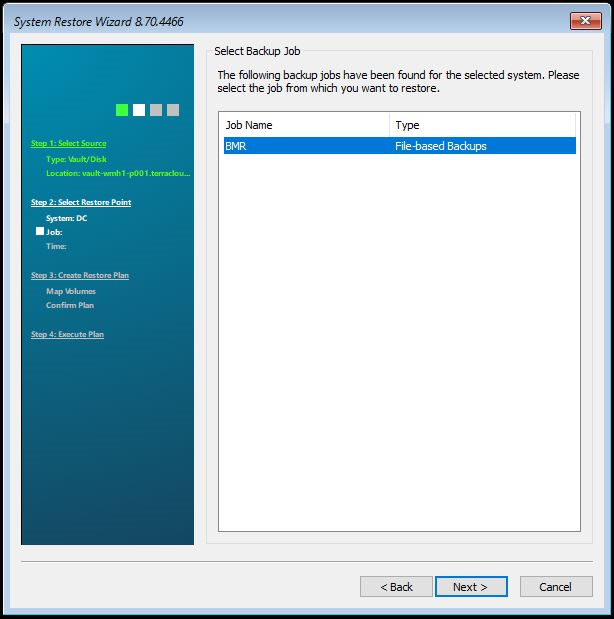
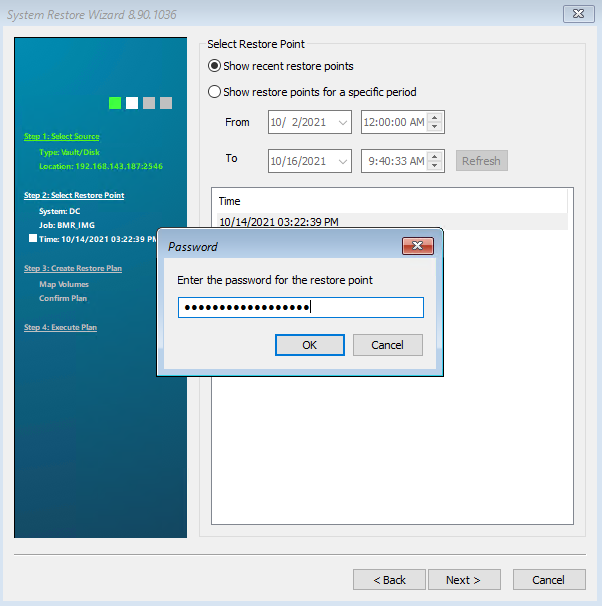
In the next step you can select which safeset should be backed up. Select the safeset you want and then click “Next”.
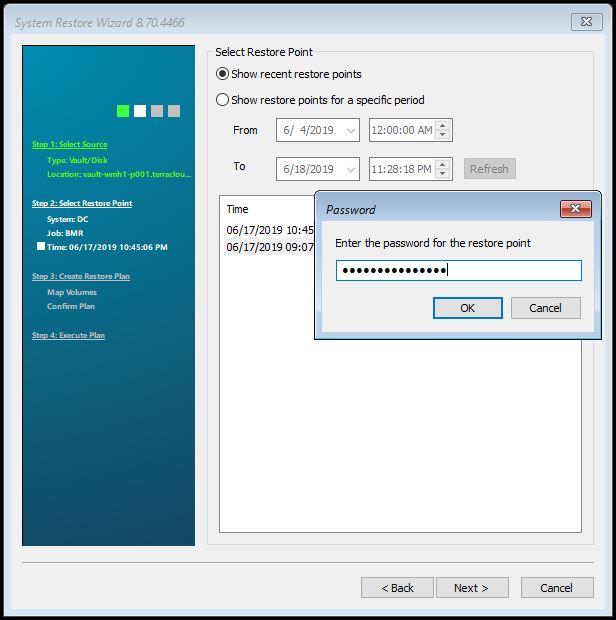
If you have set up a password for the backup job, a password query will appear. Enter the password and confirm with OK.
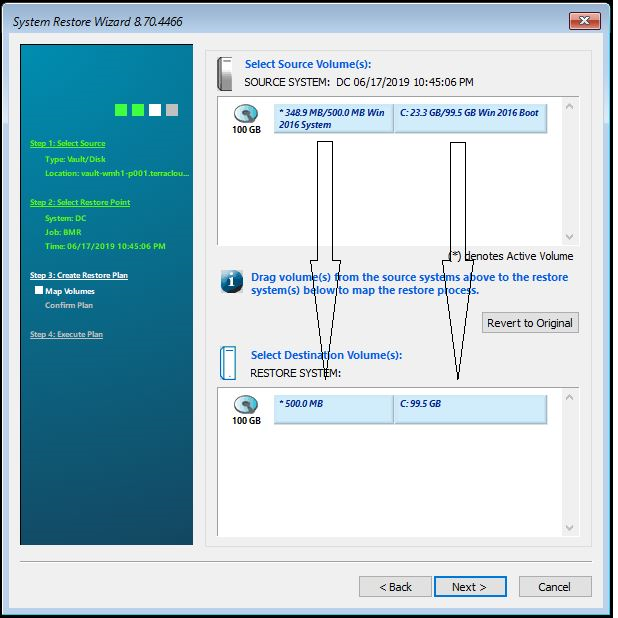
In the following step, the volumes that should be backed up can be selected. To do this, simply drag the partitions down into the “Destination” field.
Then click on “Next”.
In the last step, the settings can be checked again. Then check the box next to “Click here to confirm the restore plan”. Then click on “Next”.
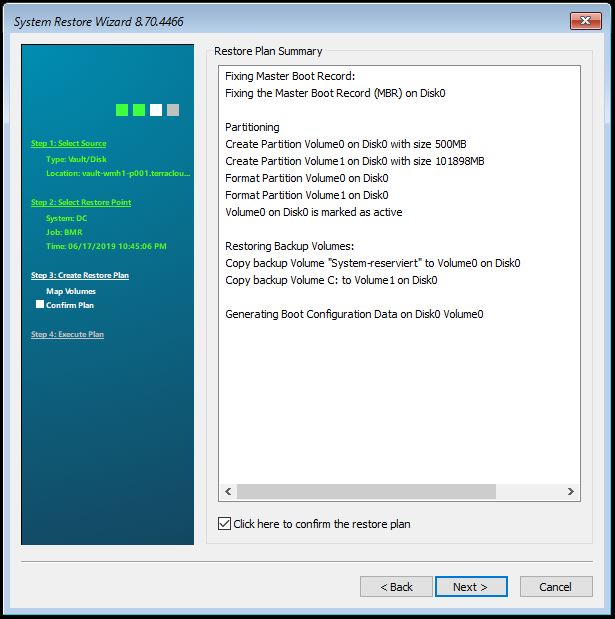
The restore process starts.
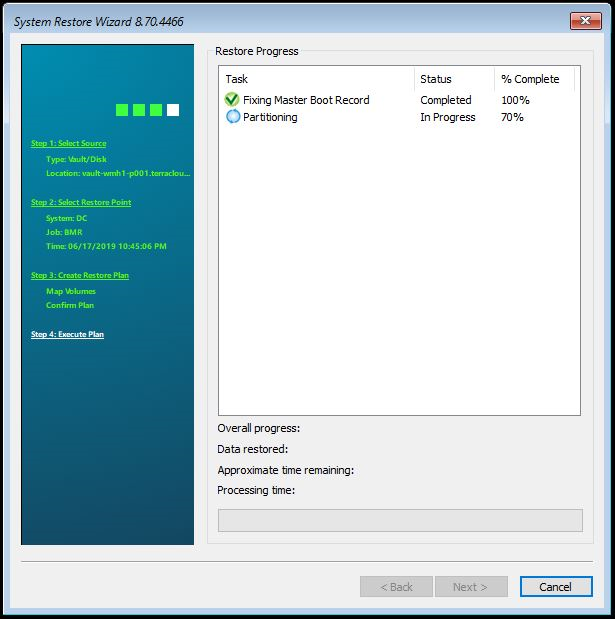
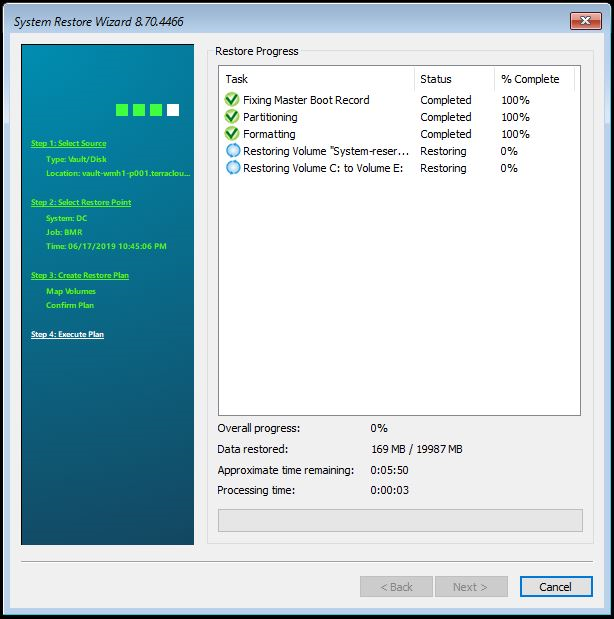
If the restore process has been completed successfully, please confirm by clicking OK to close the window. Exit the wizard and restart the server.
Backup satellites
Description and Benefits
The backup satellite is a hardware appliance or a virtual machine that is used in your end customer's network and can receive backups via the local network.
The satellite provides you with all vault functions, e.g. providing volumes from an image backup. The rental devices or virtual machines are made available to you by the TERRA Cloud and, depending on their size and performance, are billed monthly in addition to the required backup packages.
By using a satellite, you can implement a hybrid cloud backup solution, as backups are stored locally on a satellite and then replicated to a data center.
This backup concept enables the following advantages:
- Fast backup and restore, thanks to locally connected vault system (satellite)
- No acquisition costs as the hardware is provided to you
- Time decoupling between backup and replication possible
- Backup possible independently from the data center
- Initial backup can be performed directly against the satellite
- Your customer's bandwidth can be optimally utilized
Commissioning
After ordering your backup package including satellites, you will receive an email with the access data as soon as the vault account has been provided on the Basevault.
You will receive a separate notification after the satellite has been deployed and shipped to you.
After receiving the satellite, the following steps must be carried out (hardware satellites):
- Set up and launch satellite in your end customer's network
- You can reach the satellite interface via the local address of the satellite (either static IP or DHCP)
- Please note that the satellite interface can be accessed via HTTPS and may need to be enabled in the browser first
- You can use the interface to change the access data in the user administration and, if necessary, adjust the network configuration
- Please deactivate the bypass mode using the Deactivate bypass mode function 10.3.1.3
- The satellite is now prepared for productive use and must be saved as a backup target in the agents' vault settings (local IP of the satellite)
- Initial backups can optionally be carried out directly against the satellite
Commissioning a satellite VM:
- You will receive a Hyper-V VM container from TERRA Cloud Support, which you can import and virtualize under Hyper-V
- Please note that only Hyper Hosts are compatible with the Windows Server 2019 operating system or higher!
- Disk/network allocation must be done via Hyper-V Manager / VM Connect
- The remaining steps of commissioning a satellite VM are similar to commissioning a normal satellite
Satellite interface
System
Registration
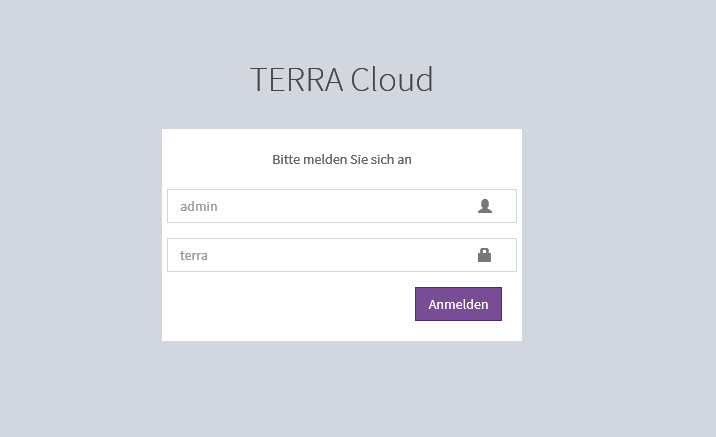
You can access the following interface in your browser using the satellite's IP address. There are two different users available, the image shows the administrative user who has
unrestricted access. In addition, there is a user who only has read rights; you can set the access data at a later date.
The default login details for the admin user are:
User = admin
Password = terra
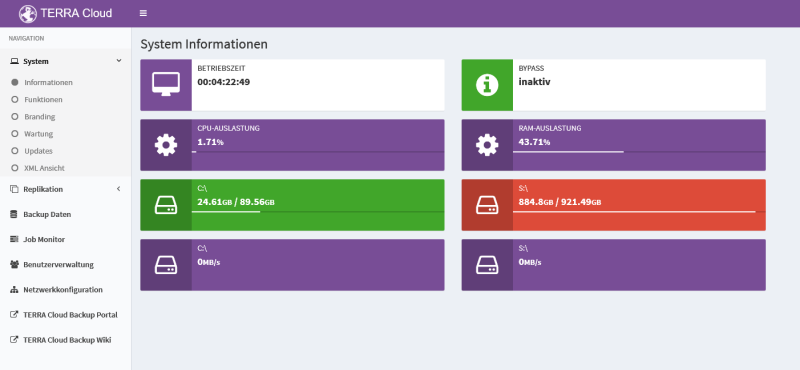
Informations
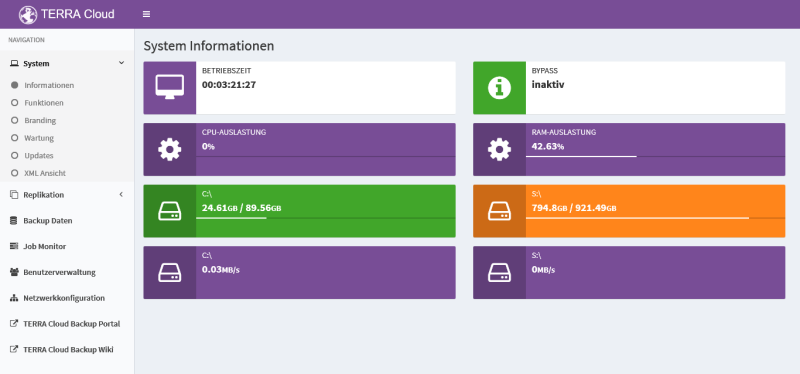
The Information item shows you the dashboard with all the important vital indicators of the hardware, e.g. CPU, RAM or hard drive utilization.
The satellite mode is also visible. A distinction is made between two modes, the active and inactive bypass mode.
With active bypass, the satellite rejects all agent requests, so communication for backups, restores, synchronizations or job creation takes place via the basevault. Accordingly, the Basevault address must be stored in the portal under the Vault Settings tab.
With the inactive bypass, the satellite is activated and accepts all agent requests, thereby enabling communication for backups, restores, synchronizations
or job creation takes place via the satellite. Accordingly, the IP address of the satellite must be stored in the portal under the Vault Settings tab.
Hard disk capacity:
Green = Between 0% and 85%
Orange = From 85% to 95%
Red = From 95% to 99.99%


Features
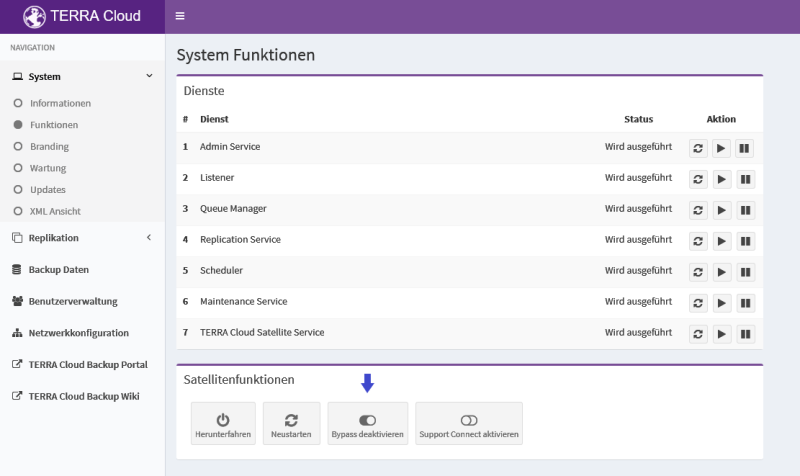
System functions:
Under Functions you will find a list of the relevant services stored on the satellite. Please check whether all services are running.
If a service is stopped, you can start it using the Play symbol. Please do not restart any services while the satellite is running.
Satellite functions:
You can use this interface to shut down the satellite, restart it, or manually start a replication process.
Disable bypass:
A satellite with bypass mode activated cannot accept backups and delegates them to the base vault. Please deactivate bypass mode so that the satellite can accept backups.
Activate Support Connect:
With this switch you allow TERRA CLOUD support to access the satellite via remote maintenance.
Branding
This function allows you to adapt the satellite interface to your company's CI. The configuration only needs to be carried out on one satellite, as you can export it and import it on other satellites.
There is also the option to add your own logo.
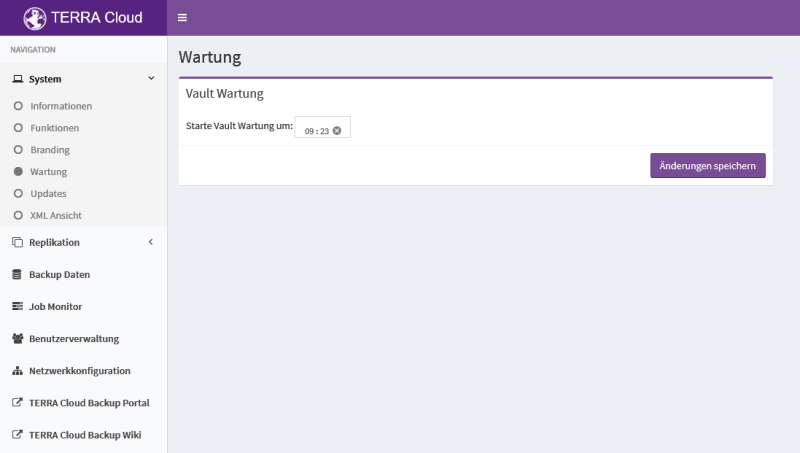
Maintenance
Vault maintenance checks the satellite's data stock every day at 9:23 a.m. for safesets that have exceeded their retention period; the number of retention days and copies must be exceeded. Expired safesets are deleted from the satellite.
You can adjust the start time of this maintenance if necessary.
Updates
You can search the satellite interface directly for current updates and import them.
XML View
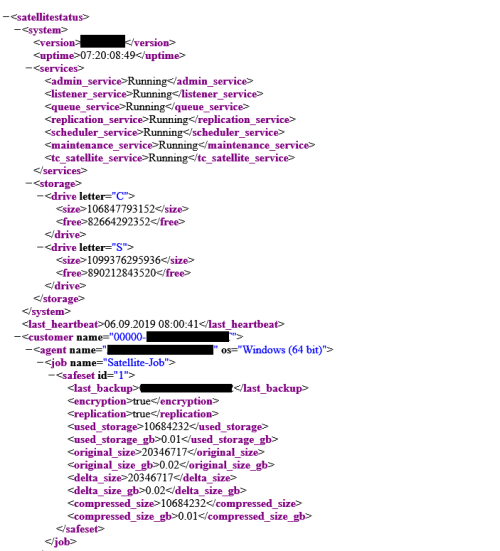
This menu item will take you to the XML output of the satellite in a new tab. This output lists all relevant information of the satellite and can be monitored.
You can incorporate this link into your own monitoring solution or use ready-made sensors. You can find ready-made sensors for Server-Eye and PRTG Network Monitor, the sensors can be found
under the search term “Terra Cloud Backup”.
Homepage Server-Eye
Replication
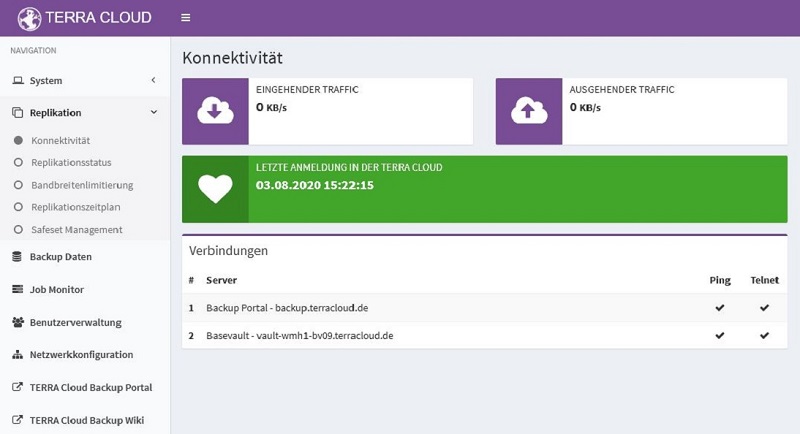
Connectivity
This overview shows you the status of the connection to the Basevault. The satellite transmits a "heartbeat" to the basevault at regular intervals.
In addition, the connection to the backup portal and the base vault is checked via ping and Telnet. This ensures that all necessary ports are activated for the satellite.< br>
During replication, for example, the outgoing network traffic rate can also be monitored.
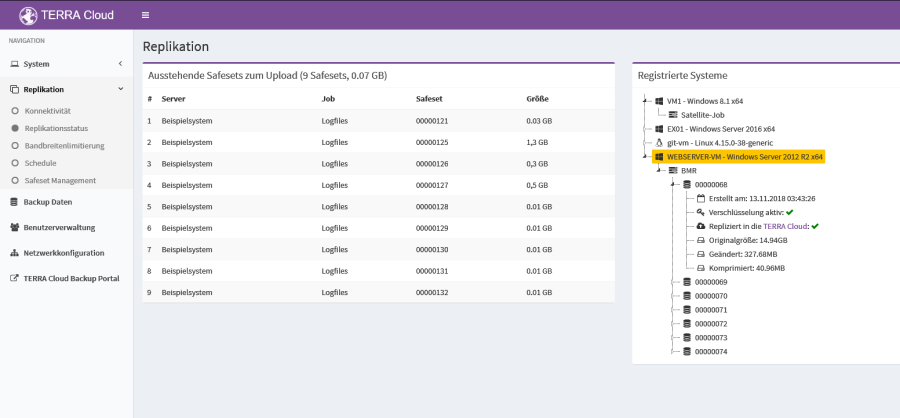
Replication Status
This overview shows you which safesets are still outstanding for replication to the data center; these are processed as if in a queue.
On the right side you can click through the satellite's current inventory and view more detailed information about individual safe sets, such as the compressed
Size or whether this safeset has already been replicated.
Bandwidth limitation
You can configure a bandwidth limit for satellite replication.
Please note that after an adjustment, the replication service restarts and ongoing replications are aborted.
If the connection is weaker, we recommend configuring the "Quality of Service" on the firewall for the satellite and assigning it a low priority.
This setting on the firewall ensures that, for example, on a holiday, the
. can be replicated with full bandwidth
Bandwidth allocation is therefore more flexible than a fixed bandwidth limit.
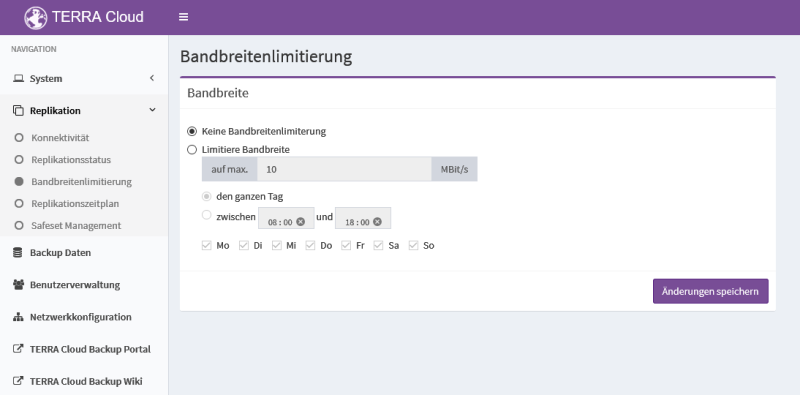
Replication Schedule
The replication schedule allows you to control whether to replicate immediately after a newly created backup and after
defined schedule or exclusively according to a configured replication schedule. This option is particularly recommended if
should be backed up during your customer's working hours, but replication should only start after working hours.
In this image you can see the configuration for a replication schedule that initiates a replication operation every day around 8 p.m.:
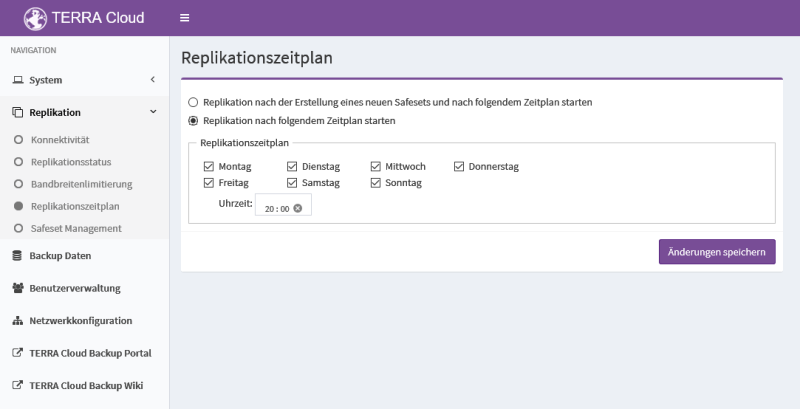
Safeset Management
Special configurations can be made on the satellite via Safeset Management; if configured incorrectly, these can affect the function of the satellite.
Changes can only be made after activation via the slider and may only be made after consultation with support.
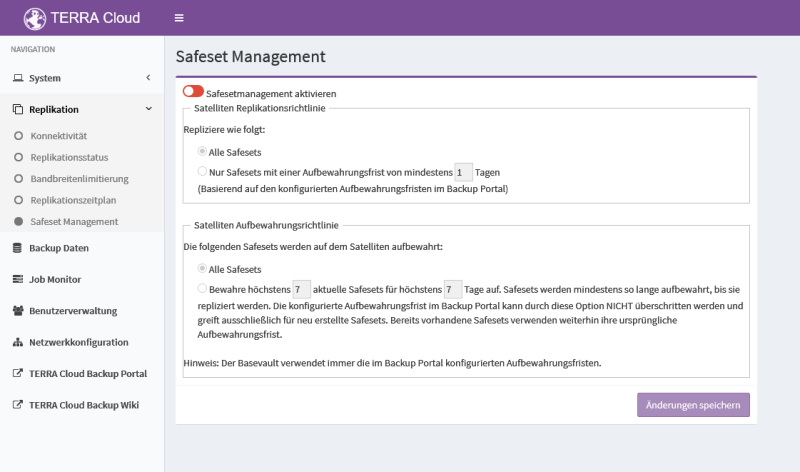
Backup data
You can use the satellite interface to delete entire systems, jobs or individual backup sets (safesets).
The deletion only applies to satellites; the data in the data center on the respective base vault remains unaffected.
Safe sets are displayed online; they are highlighted in black and can be selected by clicking in the checkbox.
Online safesets are characterized by the fact that they are stored locally on the satellite and are directly available there.
Safesets that are grayed out and cannot be selected are offline safesets.
An offline safeset represents a backup that does not exist on the Vault, but still exists on the Basevault.
Only meta information about these safesets is stored on the satellite.
Procedure for deletion:
System level deletion:
a) Check in the interface's job monitor that no process is running for the affected system. (If the Job Monitor tab is not available, update to the latest interface version)
b) Select the systems to be deleted and carry out the “Delete marked entries” action
c) Wait until the affected system is grayed out from the overview. (It may take some time)
d) Check the capacity of the satellite and start a quick storage optimization
Job level deletion:
a) Check in the interface's job monitor that no process is running for the affected job. (If the Job Monitor tab is not available, update to the latest interface version)
b) Mark the job to be deleted by selecting it and carry out the “Delete marked entries” action
c) Wait until the affected job has disappeared from the overview/grayed out. (It may take some time)
d) Check satellite capacity. If unchanged, start quick memory optimization
Safeset level deletion:
a) Check in the interface's job monitor that no process is running for the affected job. (If the Job Monitor tab is not available, update to the latest interface version)
b) Select the safe sets to be deleted and carry out the “Delete marked entries” action
c) Wait until all affected safe sets have disappeared from the overview/grayed out. (Depending on the size, the process can take a lot of time)
d) As soon as all safesets have disappeared/grayed out, start quick storage optimization
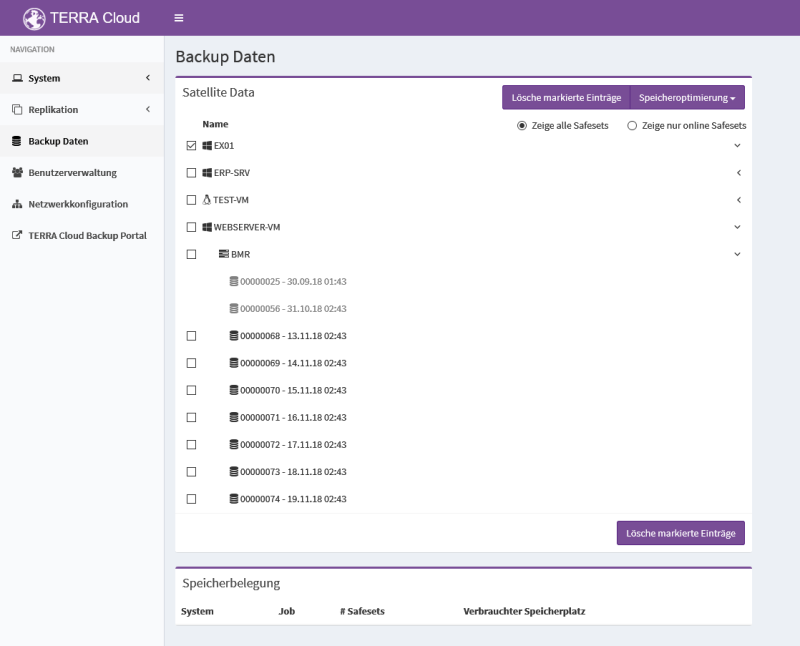
Job Monitor
You can view open or already completed processes in the Job Monitor.
Backups or restores can be monitored, as can replication processes.
The following screenshot shows a satellite that currently has no open jobs:
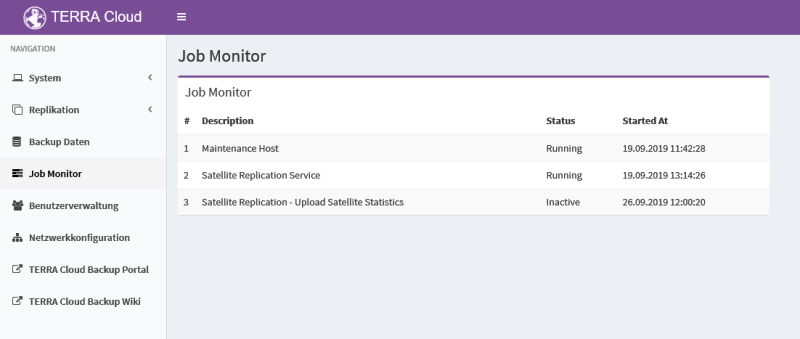
Jobs on the screenshot:
Maintenance Host = This process represents maintenance on the satellite, this process should always be displayed
Satellite Replication Service = Behind this process is the active replication service, this process should always be displayed
Satellite Replication - Upload Satellite Statistics = In the screenshot, this process is set to "Inactive" because it was completed successfully. In this job, the satellite passed information to the basevault.
User management
Within the user management you can define passwords for a total of two users. Which users are stored in total?
- Admin: This user has full access and is intended for administration of the satellite.
- User: This user only has read permission and can be issued to the end customer as required.
Network configuration
You can use the network configuration to pass on your desired settings directly to the satellite or use the “Activate DHCP” function.
As soon as DHCP has been activated, the network configuration assigned by the DHCP server will be displayed.
Initial backup FTP upload / send data carrier
Booking
The two processes can be added when initially booking a backup package or later in the order.
Recommended way
The Backup Assistant was equipped with the TERRA CLOUD initial backup tool. How the initial backup tool works is explained in the following short video: TERRA Cloud Initialbackup Tool
Please select a locally connected volume that was not included in the backup set as the destination for the initial backup. Also make sure that the affected volume does not end up in the backup set using the “Entire Server” option.
Network shares are not supported as a destination path.
After the initial backup has been created, it is recommended to check the backup log file. If no warnings/errors are visible here, this can be made available either via an external data carrier or by uploading it to our FTP server.
Manual way
As an alternative to the Backup Assistant, the initial backup can also be created manually. The following points should be taken care of in advance:
- Backup Agent installed on the desired system and registered on the portal.
- Backup job and schedule configured as desired.
- Schedule disabled so that the agent does not automatically attempt to backup to the vault.
Method
1.) Start backup for metadata transfer against the vault. This involves transmitting information required by the vault that is necessary for the import process. As soon as the status “Processing in progress” is visible, the process can be stopped.
2.) Create a folder structure in the target directory. To ensure smooth identification, we ask you to create the following folder structure:
\$ACCOUNT NAME$\$COMPUTER NAME$\$JOB NAME$
Example path:
D:\00000-EXAMPLE\srv-terracloud\bmrjob
Since this always involves encrypted data, an insufficient folder structure would result in a written query and thus a delay in the process.
3.) Start backup to the previously created path. The procedure in the portal looks like this:
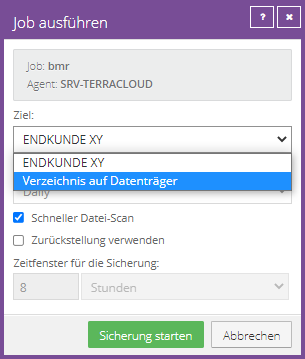
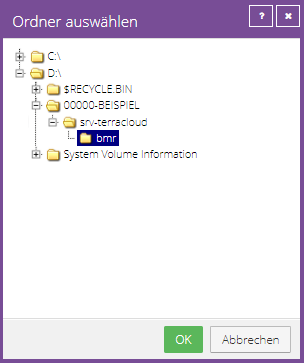
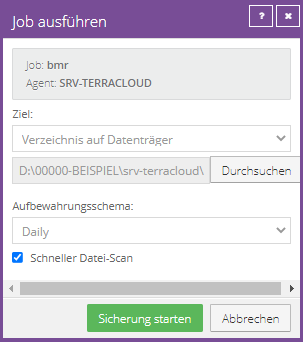
FTP Upload
Please make sure that the data is complete. Each job is divided into backup fragments, which are incremented numerically and are 1,048,576 KB in size except for the last fragment. Only the first fragment (Safesetnummer.SSI or 00000001.SSI) differs in name from the remaining files.
The initial backup created, whether manually or via the Assistant, can be uploaded to the TERRA Cloud FTP server.
For the upload you can e.g. B. the FileZilla Client can be used.
The necessary access data will be provided by us in the center after receipt of the booking.
Once the upload has been completed and checked, you can send us a short confirmation of the previously submitted information.
You will then receive a response from us as soon as there is news about the import.
Send in data carrier
Please make sure that the data is complete. Each job is divided into backup fragments, which are incremented numerically and are 1,048,576 KB in size except for the last fragment. Only the first fragment (Safesetnummer.SSI or 00000001.SSI) differs in name from the remaining files.
The data carrier can be sent together with the completed submission form to the following address:
TERRA CLOUD GmbH
Hankamp 2
32609 Hüllhorst
Notifications about the import status / shipping status of the data carrier are carried out via automated business processes.
Please do not send us unencrypted raw data from your end customer under any circumstances!
These will be sent back to the sender unprocessed.
Backup Export
To get data e.g. For example, if you want to store your data on a local medium for long-term backup, we can export your backups.
The export is encrypted and in the so-called vault format, so that the exported data must be read in with additional software before an agent can process and restore it.
Please note that this is a paid process. Further information about the process (offer, process, etc.) can be obtained from our cloud sales department: cloud@wortmann.de
As soon as you have received the desired data set, you can use the following steps. Continue steps.
You can find the required software at:
Secondary Restore Server
Secondary Restore Server
The Secondary Restore Server reads the exported data and presents it as a virtual vault in the existing network.
- Please navigate to the folder structure of the exported data in the Secondary Restore Server
- Store the data of the exported vault account, e.g. B. (45814-END CUSTOMER), as well as the vault account password
- Start sharing via the Secondary Restore Server (Start)
- Agents can then access the share as if it were a normal vault.
Restore individual files (Secondary Restore Server)
Once the data has been presented on the network, you can proceed as follows:
BMR Restore(Secondary Restore Server)
For instructions on how to initiate a BMR, see: Bare Metal Restore
Once the data has been presented on the network, you can proceed as follows:
Agent Skripting
Windows Agent
In addition to the portal, the Windows agent can also be started via command line or script.
Agent scripting is recommended, for example, to stop non-VSS-capable databases before backup (MySQL, MariaDB, etc.)
Address Windows Agent via command line
Please first change to the agent's installation directory in CMD or PowerShell, by default this is 'C:\Program Files\TERRA Cloud Backup\Agent\'
To start a backup, the following parameters must be passed to VV.exe:
- VV.exe backup JOBNAME /retention=RetentionName (CMD)
- .\VV.exe backup JOBNAME /retention=RetentionName (PowerShell)
You can use the /retention=RetentionName parameter to determine which retention type should be used.
Please replace "RetentionName" with the name of the retention period, which you can view in the Advanced Agent Settings.
Address Windows Agent via script
The desired commands can be stored in a script.
Recommended formats are .bat and .cmd
Scripts can be extended as desired, e.g. to store pre- and post-commands, i.e. commands before or after the backup.
Example script:
@echo off
cd "C:\Program Files\TERRA Cloud Backup\Agent"
echo "Start backup" >> backuplog.txt
VV.exe backup BMR /retention=Daily
echo "Backup performed" >> backuplog.txt
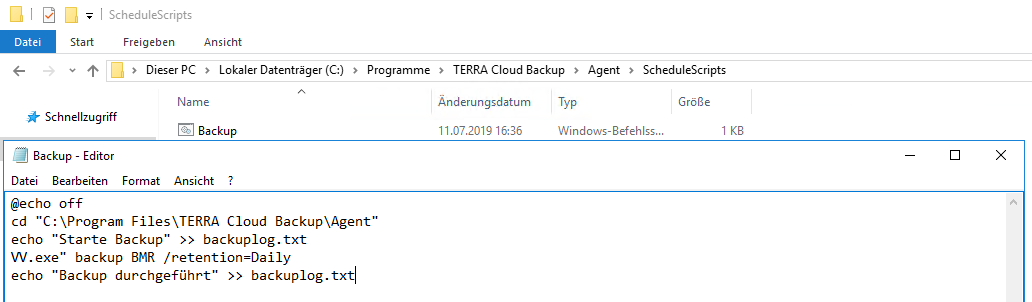
Run script before shutdown
You can integrate your created script into the system's pre-shutdown event with the following configuration. This is particularly recommended for client systems that are not consistently in use.
Please carry out the following steps to store a script:
- Open Local Group Policy Editor (WIN + R "gpedit.msc")
- Store your created script under "Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Scripts (Startup/Shutdown)
- Click "Shutdown" and add your script via "Add".
- Please adjust the following registry key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\gpsvc\PreshutdownTimeout
- This key defines the length of the pre-shutdown event, which is set to 15 minutes by default. Please increase this value so that a backup can be created during this time.
- In the Local Group Policy Editor, please navigate to "Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Scripts
- Adjust the "Specify maximum wait time for Group Policy scripts" setting. You can enter a value of up to 32,000 seconds or 0 for an infinite waiting time.
- Please note that you have adjusted the rights accordingly.
- We have described further information about this in the following Wiki article: PreshutdownTimeout Value Authorization
Create new custom command
This option gives you the opportunity to add a schedule to scripts that have already been created via the backup portal.
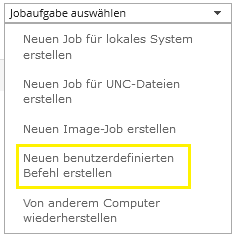
When you create a new custom command, the agent checks whether there are scripts stored in the agent directory in the "ScheduleScripts" batch files subfolder.
The standard path to this directory in which a script for this function can be stored:
C:\Program Files\TERRA Cloud Backup\Agent\ScheduleScripts
In the following screenshot you can see a selected script with a configured schedule:
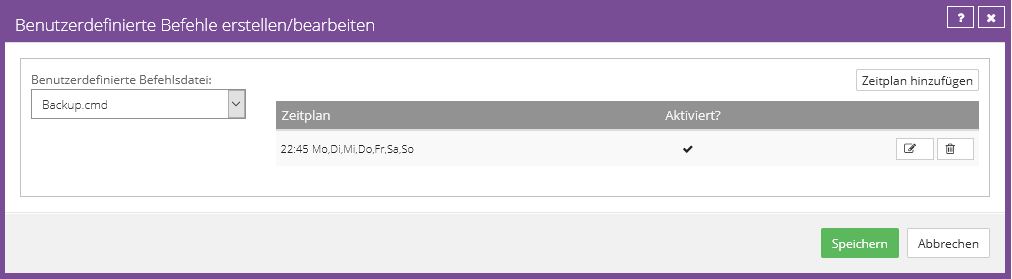
Recommendation:
A custom command's schedule can only be created as a single-line schedule.
Please check our Best Practice for agent scripting to avoid this disadvantage.
Agent Skripting Best Practice
The backup agent can be tailored to individual application scenarios through the use of scripts.
We recommend that you use the following instructions as a basis for your scenario.
Preparation:
What should be prepared before using the following scripts?
- Installing the agent on the system to be protected
- Link the system to the vault in the backup portal
- Create backup job(s), without a schedule
Step 1: Create batch file
Create a batch file (.bat) with the following structure
powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File "Path to PowerShell script\agentscripting_retention.ps1"
Please adapt this batch file later to the path and name of the PowerShell script you specified.
Copy the created batch script to the following folder in the agent installation directory:
C:\Program Files\TERRA Cloud Backup\Agent\ScheduleScripts (default)
In the Backup Portal for the system in question, under "Select job task" click "New_custom_command".
You can use this function to select a stored batch script and provide it with a schedule. Please configure the desired time. (e.g. 10 p.m.)
Function:
This batch file will later be started on a schedule by the backup agent itself. The batch file starts PowerShell and the second script.
Since PowerShell is much more extensive and flexible, the first script is only used to call PowerShell.
Step 2: Create PowerShell script
In this step you create the PowerShell script which is controlled by the batch script from Step 1.
This script is used to contact the backup agent to carry out a backup.
It is also possible to use different retention periods and to install pre- and postcommands.
Content:
Please create a PowerShell script (.ps1) with, for example, the following content:
Set Location "C:\Program Files\TERRA Cloud Backup\Agent"
$date = GetDate
$currentday = $date.Day
$lastday = [DateTime]::DaysInMonth($date.Year, $date.Month)
if ($lastday -eq $currentday){
Placeholder for pre-commands
.\VV.exe backup NamedesBackupJobs /quickscan=true /retention=Monthly
Placeholder for post commands
}
else{
Placeholder for pre-commands
.\VV.exe backup NamedesBackupJobs /quickscan=true /retention=Daily
Placeholder for post commands
}
Function:
This PowerShell script goes to the agent installation directory and checks the current date.
If the date equals the total number of days of the month (the dynamic last day of the month), a backup with the Monthly retention type is performed.
On all other days, the retention type "Daily" is used.
Advantages of this implementation:
- You can use the full functionality of PowerShell and customize this basic script as desired for your customers
- The schedule can be created via the Backup Portal and does not have to be implemented via the script
- You can use pre- and post-commands to stop databases before the backup that cannot be brought into a consistent state using VSS technology
Linux Agent
In addition to the portal, the Linux agent can also be accessed via created scripts.
You can contact the agents directly via a created script. As in the following example script (CustomScript.sh):
nano CustomScript.sh
cd /opt/BUagent
./VV backup RootDir
In the example, RootDir is the backup job name.
The script (e.g.: CustomScript.sh) must then be given the appropriate rights. To do this, please execute the following command:
chmod +x CustomScript.sh
Optionally, you can schedule scripts via the Backup Portal by completing the following steps:
- Under Linux, by default, no folder called "ScheduleScripts" is created in the installation directory. Please create this with e.g. mkdir ScheduleScripts
- Place the created script (.bat or .cmd) in the agent directory in the newly created ScheduledScripts folder
- In the Backup Portal, select "Create a new custom command" via "Select job task" and select your script
- Create a schedule for the script
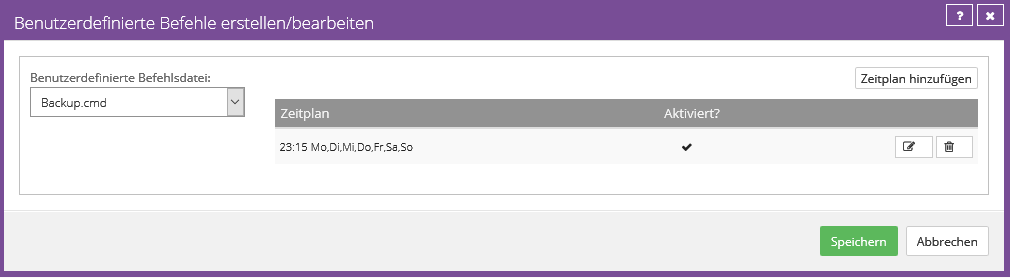
vSphere Recovery Agent
vSphere Recovery Agent Documentation
You can find extensive documentation and further information in vSphere Recovery Agent User Guide.
Installation
Bitte führen Sie das Setup des vSphere Recovery Agenten auf einem Windows Server System mit Zugriff zu der VMware Umgebung (vCenter oder standalone ESXi Host) aus. Beachten Sie dabei die Empfehlungen aus dem Abschnitt Best Practice. Bitte befolgen Sie die Anweisungen aus dem InstallShield des vSphere Recovery Agenten. Im letzten Schritt der Installation registrieren Sie das System über den eingegeben Benutzer und Kennwort in der erstellen Site Ihres Endkunden. Eine genaue Beschreibung des Installationsprozesses finden Sie im oben verlinkten User Guide.
Konfiguration des Agenten
Nach der erfolgreichen Installation und Registrierung am TERRA CLOUD Backup Portal können Sie nun das System am Vault hinzufügen, wie in System am Vault hinzufügen beschrieben.
Verbindung zu der vSphere-Umgebung
Bitte hinterlegen und speichern Sie die Zugangsdaten zur vSphere-Umgebung (vCenter oder standalone ESXi Host) in den Feldern der "Anmeldeinformationen". Sie erhalten unmittelbar eine Rückmeldung, ob die hinterlegten Zugangsdaten korrekt sind, bzw. die Umgebung erreicht werden kann.
Changed Block Tracking
Diese Funktion des Agenten ist nach der Installation bereits aktiviert und erlaubt eine schnelle und effiziente Deltasicherung der virtuellen Maschinen.
Weitere Informationen zu dieser Technologie finden Sie in der Wissensdatenbank von VMware.
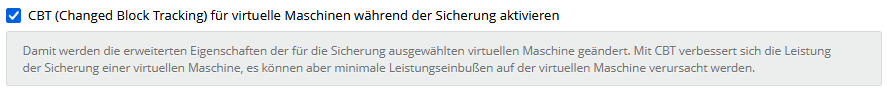
Automatisierte Wiederherstellungstests
Durch die Aktivierung der Option "Sicherung bei Fertigstellung überprüfen" wird nach dem Abschluss jeder Sicherung eine Wiederherstellungstests über eine schnelle VM-Wiederherstellung durchgeführt.
Nach dem Bootvorgang der virtuellen Maschine wird ein Screenshot des Anmeldemaske erstellt und im TERRA CLOUD Backup Portal gespeichert.
Um diese Funktion nutzen zu können, müssen die Voraussetzungen für die schnelle VM-Wiederherstellung erfüllt sein.
Bitte hinterlegen Sie den temporären Datenspeicher (Datastore) auf dem die VM für die Testwiederherstellung gestartet werden kann und den gewünschen ESXi Host.
Beispielkonfiguration:
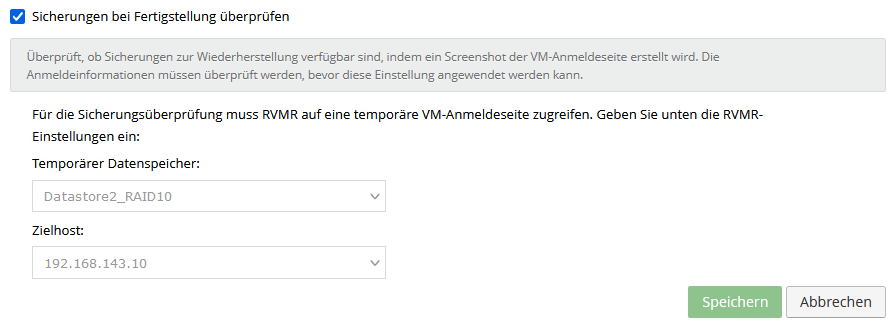
vSphere Backup Job erstellen
Sobald Sie die Installation und Konfiguration des Agenten abgeschlossen haben, können Sie einen neuen "Job für VMware vSphere" erstellen.
Auf dem folgenden Screenshot sehen Sie exemplarisch einen neuen Job für eine vSphere Umgebung. Bitte vergeben Sie einen Jobnamen und optional eine Beschreibung sowie das Verschlüsselungskennwort.
Sie können entweder alle virtuellen Maschinen in die Sicherung aufnehmen, indem Sie die Ebene "Virtuelle Maschinen" selektieren, alle virtuellen Maschinen sind damit rekursiv eingeschlossen. Diese Option bietet den Vorteil, dass neue virtuelle Maschinen automatisch in den Backup Job hinzugefügt werden.
Alternativ können Sie einzelne VMs auswählen und in den Sicherungssatz übernehmen.
Optional:Erweiterte Einstellungen:
Anwendungskonsistente Sicherung aktivieren
Sobald Sie die "anwendungskonsistente Sicherung aktivieren" kann ein anwendungskonsistenter Snapshot auf Basis eines Microsoft VSS Snapshots erstellt werden. Wir empfehlen diese Option zu aktivieren für alle virtuellen Maschinen mit Windows Gastbetriebssystem.
Protokolle der Datenbanktransaktionen kürzen
Zusätzlich zur anwendungskonsistenten Sicherung können Transaktionsprotokolle von Micorsoft Exchange oder SQL Server Instanzen gekürzt werden.
Bedrohungserkennung aktivieren
Bei der Sicherung aktiver virtueller Maschinen mit Windows Gastbetriebssystem kann der vSphere Recovery Agent das System auf aktive Ransomeware prüfen. Wir empfehlen diese Option zu aktivieren für alle virtuellen Maschinen mit Windows Gastbetriebssystem. Die Option "Bedrohungserkennung aktivieren" erfordert Zugangsdaten zum Gastbetriebssystem.
Diesen Sicherungsjob bei Fertigstellung überprüfen
Im Anschluss an die Sicherung wird ein Wiederherstellungstest der virtuellen Maschinen über eine schnelle VM-Wiederherstellung durchgeführt. Bitte beachten Sie, dass diese Funktion in der [Konfiguration] eingerichtet werden muss.
Globale VM-Anmeldeinformationen
Die eingetragen Zugangsdaten werden für alle virtuellen Maschinen im Sicherungssatz verwendet.
Gast-BS-Anmeldeinformationen
Sofern Sie Zugangsdaten individuell je virtueller Maschine vergeben möchten, können Sie diese unterhalb der virtuellen Maschine im Sicherungssatz eintragen, in dem Sie das Eingabefeld über den blauen Pfeil anzeigen lassen.
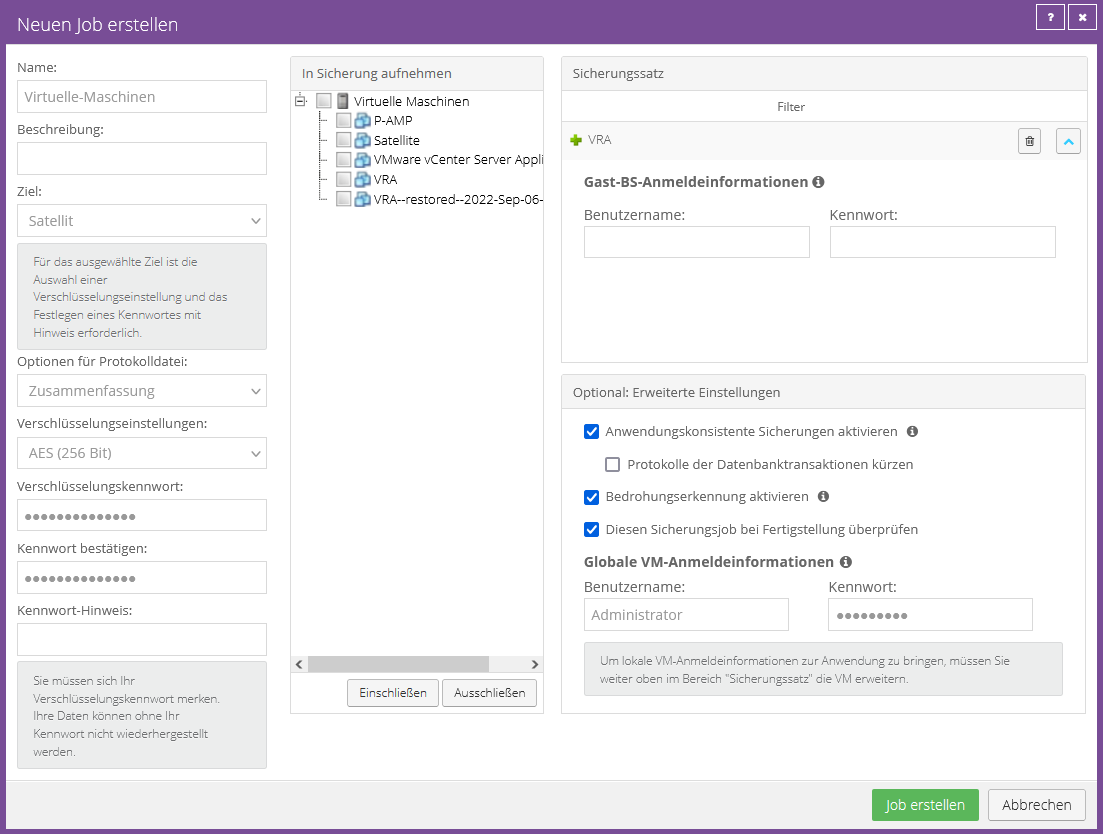
Rapid VM Recovery (schnelle VM-Wiederherstellung)
Die Wiederherstellungsoption schnelle VM-Wiederherstellung bietet Ihnen die Möglichkeit eine VM aus dem Backup zu starten.
Ausfallzeiten können durch den schnelle Zugriff drastisch reduziert werden, zusätzlich eignet sich die Funktion um in wenigen Minuten einen Wiederherstellungstest durchzuführen.
Vorraussetzung:
- Ausschließlich in Verbindung mit einem TERRA CLOUD Backup Satelliten oder TERRA CLOUD Backup Enterprise Vault verfügbar
- Jeder ESXi Host muss über einen Software ISCSI Adapter verfügen
- Der Datastore auf dem die VM gestartet wird kann entweder auf lokalem, ISCSI oder vSAN Storage liegen
- Ein Datastore auf den eine VM migriert werden soll kann zusätzlich zu den oben genannten Storagetypen auch auf einem NFS Share liegen
- Insgesamt müssen mindestens zwei Datastores vorhanden sein
- vSphere Recovery Agent 8.82 oder höher
- Der Windows Server, auf dem der VRA installiert ist, verfügt über das Windows Feature "iSCSI Target Server"
Exemplarische Konfigration eines ESXi Hosts für Rapid VM Recovery:
Auf folgendem Screenshot wurde über das vCenter ein iSCSI Software Adapter über "Add Software Adapter" hinzugefügt.
Zusätzlich wurde ein VMkernel-Adapter ohne aktivierte Service Rolle hinzugefügt, wie auf folgendem Screenshot zu sehen:
Vorgehensweise:
Sobald alle Vorraussetzungen erfüllt sind erhalten Sie unter "Wiederherstellen" eine zusätzliche "Option Virtuelle Maschine, die schnelle VM-Wiederherstellung nutzt":
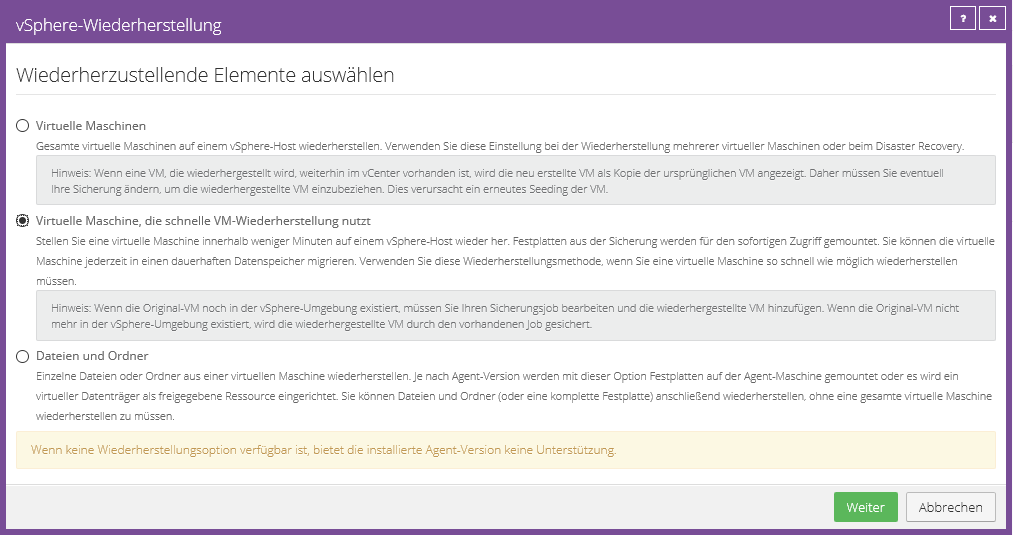
Im Anschluss kommen Sie in die Konfiguration der Wiederherstellung, in dieser können Sie neben Entscheidung welche VM wiederhergestellt werden soll auch definierten welcher Datastore verwendet werden soll.
Auf folgedem Screenshot sehen Sie den Datastore "Rapid VM Recovery Datastore", dieser wurde eigens für z.B. Wiederherstellungs und Funktionstest konfiguriert, während der Wiederherstellung können Sie die VM auf einen anderen Datastore migrieren, auf dem z.B. Ihre Produktivsysteme liegen.
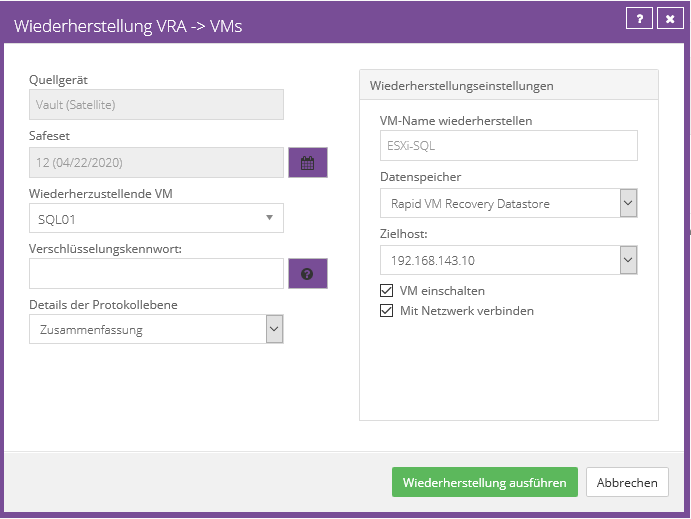
Best Practice
- Installieren Sie den vSphere Recovery Agent in eine eigene Windows Server VM, diese wird nach Möglichkeit nur für das Management bzw. Backup verwendet
- Halten Sie die vSphere Recovery Agent VM hochverfügbar über vSphere HA
- Nutzen Sie für das TERRA CLOUD Backup einen Satelliten um Rapid VM Recovery nutzen zu können
- Platzieren Sie die vSphere Recovery Agent VM im selben Subnetz wie die vCenter Server Appliance
- Aktivieren Sie die Option "Anwendungsbewusste Sicherung" im Backup Job
- Nutzen Sie Change Block Tracking für die Sicherung der virtuellen Maschinen, diese Einstellung finden Sie unter dem Reiter "vCenter-Einstellungen"
Hyper-V Agent
Dokumentation Hyper-V Agent
Die folgenden Abschnitte beinhalten unter anderem Informationen zur Einrichtung und Konfiguration des TERRA CLOUD Backup Hyper-V Agenten.
Eine umfangreiche Dokumentation und weitere Informationen finden Sie im Hyper-V Agent User Guide
Installation
Die folgende kompakte Anleitung beschreibt die wesentlichen Schritte der Einrichtung des TERRA CLOUD Backup Hyper-V Agenten.
Eine detailliertere Installationsanleitung entnehmen Sie bitte der Dokumentation Hyper-V Agent.
Reihenfolge der Einrichtung:
1. Installation TERRA CLOUD Backup Hyper-V Agent Management
2. Einrichtung des Management Agenten im Backup Portal (Verbindung zur Hyper-V Umgebung aufbauen, Computer am Vault hinzufügen)
3. Installation TERRA CLOUD Backup Hyper-V Agent Host
Single Host Hyper-V Systeme:
In diesem Szenario können Sie sowohl die den TERRA CLOUD Backup Hyper-V Management Agent als auch den Host Agent direkt auf dem Hyper-V Host ("Root"/"Parent" Partition) installieren.
Bitte beachten Sie trotzdem die oben aufgelistete Reihenfolge der Einrichtung.
Hyper-V Cluster:
Der TERRA CLOUD Backup Hyper-V Agent ist auf Grund seiner Aufspaltung in zwei Softwarekomponenten (Management und Host) optimal für einen Einsatz im Cluster geeigent.
Wir empfehlen den Management Agenten in eine administrative VM innerhalb des Hyper-V Clusters zu installieren, somit kann Sie auf verschiedenen Hosts betrieben werden und über den Failover Cluster hochverfügbar gehalten werden.
Nach der Durchführung von Einrichtungsschritt 1 und 2 können Sie im dritten Schritt den TERRA CLOUD Backup Hyper-V Agent Host auf allen Knoten des Hyper-V Clusters installieren.
TERRA CLOUD Backup Hyper-V Agent Management:
Schritt 1 der Einrichtung
Bitte installieren Sie das Setup auf dem gewünschten System und folgen Sie den Anweisungen innerhalb des Setups.
Im letzten Schritt wird analog zu allen anderen Agenten des TERRA CLOUD Backups die Registrierung am TERRA CLOUD Backup Portal konfiguriert. Sie können entweder direkt einen Benutzer innerhalb der Site mit ausreichender Berechtigung auswählen oder das System in Ihre Parent-Site registrieren und im Anschluss verschieben.
Schritt 2 der Einrichtung
Nach dem erfolgreichen Abschluss der Installation sollte das System in der gewählten Site im Portal erscheinen. Bitte folgen Sie den Anweisungen im Backup Portal, um eine Verbindung zu Hyper-V Umgebung aufzubauen und im Anschluss den Computer am Vault hinzuzufügen.
Installation TERRA CLOUD Backup Hyper-V Agent Host:
Schritt 3 der Einrichtung
Nach der erfolgreichen Konfiguration des Hyper-V Agenten in Schritt 2 können Sie den Host Agent auf allen Knoten des Hyper-V Clusters oder auf dem Single Host installieren.
Bei einer Cluster Installation sollte der FQDN des Systems angegeben werden, auf dem der Management Agent aktiv ist, um eine Verbindung zu dieser aufzubauen.
Nach der erfolgreichen Installation sollte der jeweilige Knoten unter dem Reiter "Hosts" im Backup Portal als online angezeigt werden.
Rapid VM Recovery (schnelle VM-Wiederherstellung)
Die Wiederherstellungsoption schnelle VM-Wiederherstellung bietet Ihnen die Möglichkeit eine VM aus dem Backup zu starten.
Ausfallzeiten können durch den schnellen Zugriff drastisch reduziert werden, zusätzlich eignet sich die Funktion um in wenigen Minuten einen Wiederherstellungstest durchzuführen.
Voraussetzungen
- Hybrides TERRA CLOUD Backup mit einem TERRA CLOUD Backup Satelliten oder TERRA CLOUD Backup Enterprise
- Hyper-V Checkpoints müssen für die gesicherten VMs aktiviert sein (weitere Informationen finden Sie unter: Hyper-V Checkpoints)
Automatic Bare Metal System Restore Test (ABSRT-Tool)
Allgemeines
Regelmäßige BMR-Testrücksicherungen sind eine Notwendigkeit für das Qualitätsmanagement eines Backup-Konzeptes.
Manuelle Tests sind jedoch zeit- und somit kostenintensiv, eine Automatisierung kann hier Abhilfe schaffen und den Zeitaufwand auf die Konfiguration und Kontrolle reduzieren.
Das ABSRT-Tool erstellt auf Basis von Microsoft Hyper-V virtuelle Maschinen, diese verfügen über ein präpariertes Restore ISO.
Alle Daten, die bei einer manuellen Rücksicherung eingegeben werden müssten wie z.B. der Systemname oder die Adresse des Vaultsystems werden aus einer CSV Datei ausgelesen und im Wiederherstellungsprozess eingetragen.
Für den Wiederherstellungstest wird dynamisch das aktuellste Safeset verwendet.
Nach dem Abschluss der automatisierten Konfiguration erfolgt eine vollständige Rücksicherung, inklusive dem Systemstart nach dem erfolgreichen Abschluss.
Um die Effizienz weiter zu steigern, können Sie die Wiederherstellung auch paralellisieren, indem Sie die Daten mehrerer BMR Backup Jobs in der CSV Datei hinterlegen.
Die aktuelle Version von ABSRT wird aufgrund von Kompatibilitätsproblemen lediglich auf Windows Server Betriebssystemen unterstützt.
Voraussetzungen
- Teilnahme an der TERRA CLOUD Backup Certified Specialist Schulung
- Mindestens einen Microsoft Hyper-V Host mit entsprechenden freien Kapazitäten für die Test-VMs
- Die Test-VMs benötigen Zugriff zu einem DHCP-Server
- Ein externe vSwitch muss zur Verfügung stehen
- Aktivierte Windows Server Lizenz
- Certified Specialist ABSRT Lizenz (per Anfrage im Supporterhältlich)
Einrichtung
Wenn Sie das ABSRT-Tool erstmalig starten, fragt Sie das Tool nach einer Certified Specialist ABSRT Lizenz:

Nachdem Sie eine gültige Lizenz eingegeben haben, erscheint die Auswahl des Installationspfades:
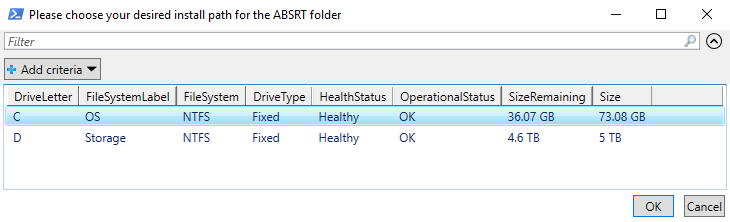
Anschließend werden folgende benötigte Komponenten überprüft/installiert:
- Hyper-V Installation
- Bootable Media Creator
- Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit
- Falls konfiguriert, VeraCrypt
Sollten Softwarekomponenten fehlen bzw. nicht auf dem aktuellen Stand sein, werden diese automatisch durch das Tool installiert.
Sofern die Hyper-V Komponente installiert wird, muss ein Neustart erfolgen.
Vorbereitung der CSV Datei
Bitte navigieren Sie in das Installationsverzeichnis des Tool und öffnen Sie den Ordner "CSV" (z.B. unter C:\ABSRT\CSV).
In diesem Order befindet sich die "Backups.csv" Datei, welche Sie als Basis Ihrer Konfiguration verwenden können.
Wichtig! Die erste Zeile dient als Legende und darf nicht angepasst werden!
Beispiel:
Vaultaddress,Vaultaccount,Vaultaccountpassword,Computername,Jobname,EncryptionPassword,VHDXCapacity,VMGeneration,VHDXStorage,VSwitchName,AmountOfPhysicalDisks,SendEmail
==> vault-wmh1-wp01.terracloud.de,00000-RESELLER,RtHKha451!HjioplÖ03,DC,BMR,hdakzeogsz1,300,2,D,extern,3,n
Hinweis:
Sofern ein Komma im Verschlüsselungskennwort vorhanden ist, muss das gesamte Verschlüsslungskennwort mit doppelte Anführungszeichen umschlossen werden.
Beispiel zum Verschlüsslungskennwort mit dem Sonderzeichen Komma:
"Ghgui385as,"
Sie können die CSV Datei unter einem beliebigen Namen abspeichern. Wir empfehlen für jeden Endkunden eine eigene CSV Datei anzulegen.
Erklärung der Parameter
Vaultaddress = FQDN des Vaultsystems
Vaultaccount = Vaultaccount, diesen können Sie z.B. aus Ihrem Vault-Profil entnehmen
Vaultaccountpassword = Dieses Kennwort haben Sie in der Bestätigung der Bereitstellung erhalten
Computername = Computername auf dem Vaultsystem, dieser muss nicht zwangsläufig dem im Backup Portal angezeigten Namen entsprechen, bitte prüfen Sie im Zweifel Ihren Reseller Report
Jobname = Name des Backup Jobs
EncryptionPassword = Das Verschlüsselungskennwort des ausgewählten Backup Jobs
VHDXCapacity = Bitte tragen Sie hier die Größe des wiederhergestellten Volumes an, sollte das System über mehrere Volumes verfügen tragen Sie bitten den Wert der größten in GB ein.
VMGeneration = Bitte beachten Sie, dass die Genaration der VM mit dem Quellsystem übereinstimmt. Die Angabe der Genaration in der CSV bestimmt den Algorithmus für die Zuweisung der Volumes im Wiederherstellungsvorgang.
VHDXStorage = Bitte geben Sie den Laufwerksbuchstaben für den Speicherort der VHDX an
VSwitchName = Name des externen vSwitch, dies können Sie aus dem Manager für virtuelle Switche entnehmen
AmountOfPhysicalDisks = Bitte geben Sie die Anzahl der Festplatten an über die das System verfügt
SendEmail = Ein optionaler Schalten, über den Sie eine E-Mail Benachrichtung konfigurieren können (n = nein, y = ja)
Wenn Sie mehrere Systeme gleichzeitig wiederherstellen wollen, fügen Sie einfach weiteren Zeilen ab Zeile 3 hinzu. Die Legendenzeile muss nicht kopiert werden.
Durchführung
Nachdem Sie eine oder mehrere CSV Dateien vorbereitet haben, können Sie das Tool erneut starten. Hier müssen Sie dann nur noch die CSV Datei auswählen, um eine Wiederherstellung anzustarten.
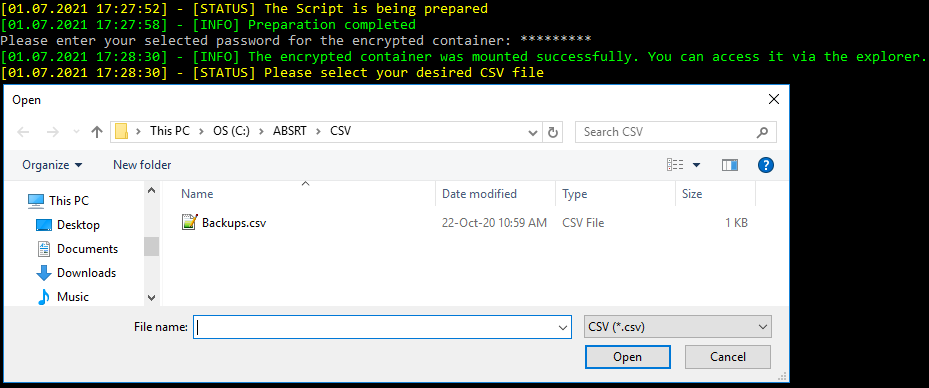
Eine kurze Demonstration finden Sie unter: Demovideo
Monitoring
Bei der Wiederherstellung wird ein weitere Prozess gestartet, welcher den Status der Wiederherstellung basierend auf dem Heartbeat der virtuellen Maschine überprüft.
Sobald ein Heartbeat vorhanden ist, wird ein Screenshot des Verbindungsfensters erstellt und im ABSRT Verzeichnis unter "Screenshots" abgelegt.
Sofern die SendEmail Option ausgewählt wurde, wird der Screenshot zusätzlich an die angegebene E-Mail Adresse versendet.
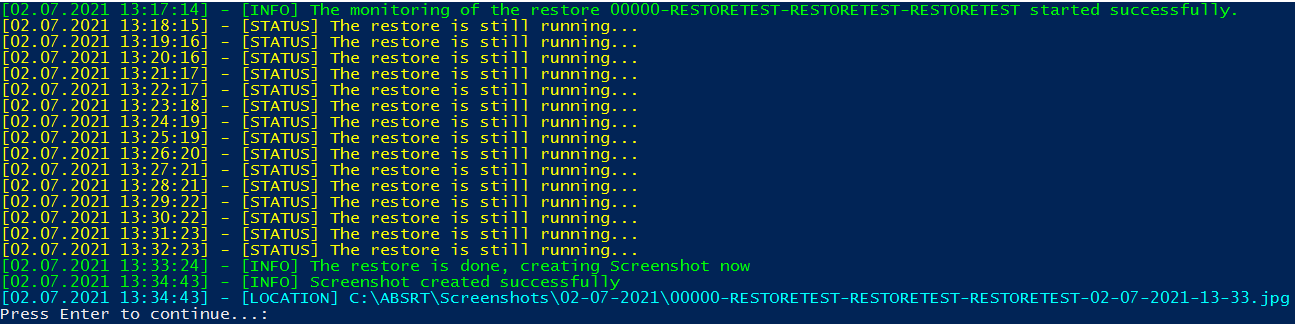
E-Mail Benachrichtigung ABSRT
Um die E-Mail Benachrichtigung verwenden zu können, müssen Sie die Datei C:\ABSRT\smtp.xml bearbeiten und ausfüllen:
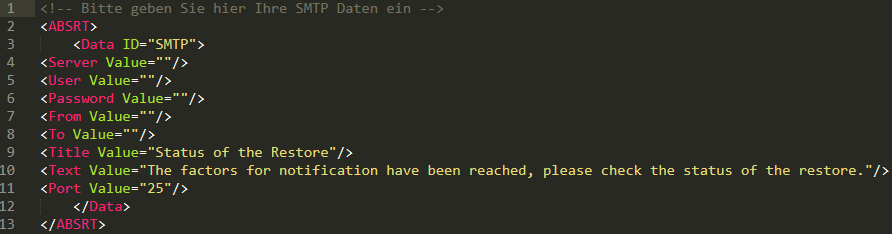
Das Skript überprüft vorab, ob die benötigten Felder ausgefüllt worden. Sofern ein Eintrag nicht ausgefüllt wurde, wird die Benachrichtigung übersprungen.
VeraCrypt
Funktion nachträglich aktivieren:
VeraCrypt REG-Key unter HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ABSRT\ entfernen
ABSRT.exe erneut starten und VeraCrypt aktivieren
Funktion nachträglich deaktivieren:
Container bei Bedarf unter C:\ABSRT\VeraCrypt entfernen
VeraCrypt REG-Key unter HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ABSRT\ entfernen
ABSRT.exe erneut starten und VeraCrypt verneinen
CSV Container neu erstellen:
Container unter C:\ABSRT\VeraCrypt entfernen
ABSRT.exe erneut starten und Passwort für neuen Container eingeben
Skriptbasierter Umgang ABSRT
Folgende Parameter können ausschließlich per PowerShell verwendet werden:
-Install [Switch] - "C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\ABSRT.exe -Install -DebitorNumber 12345 -License D133763385BAEFBFF9673C63Ab [-Vera Terra001!]"
-> Führt eine automatisierte Installation des ABSRT Tools durch. Der -Vera Parameter ist optional.
WICHTIG: Sofern die Hyper-V Rolle noch nicht installiert wurde, erfolgt ein automatischer Neustart nach Vollendung der Installation!
-Password [String] - "C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\ABSRT.exe -Password Terra001!"
-> Sorgt dafür, dass der VeraCrypt Container automatisch gemounted wird. Sofern das Passwort falsch ist, erfolgt eine manuelle Abfrage.
-CSV [String] - "C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\ABSRT.exe -Password Terra001! -CSV V:\CSV\TestCSV.csv [-NoPause]"
-> Sorgt dafür, dass die CSV Datei automatisch ausgewählt wird. Bitte immer den kompletten Pfad der CSV + Dateiendung angeben. (Shift + Rechtsklick -> "Als Pfad kopieren" kann hierfür verwendet werden)
-Uninstall [Switch] - "C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\ABSRT.exe -Uninstall"
-> Führt eine vollständige Deinstallation des ABSRT Tools durch. Die Hyper-V Rolle wird hierbei allerdings nicht deinstalliert. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie die Deinstallation erst durchführen, sobald keine von ABSRT erstellte VM im Hyper-V Manager existiert.
-Manual [Switch] - "C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\ABSRT.exe -Manual -Vaultaddress vault-wmh1-0002.terracloud.de -Vaultaccount 00000-RESTORE -Vaultaccountpassword wD5c9mP7-3bL1337l1th8W7xaB0T0m -Computername RESTORE -Jobname RESTORE -EncryptionPassword Terra001! -VHDXCapacity 1000 -VMGeneration 2 -VHDXStorage D -VSwitchName vSwitch -AmountOfPhysicalDisks 4 -SendEmail n"
-> Kann alternativ zur CSV Auswahl genutzt werden. Alle Parameter werden benötigt.
ABSRT Upgrade auf Version 9.30
1. Sicherstellen, dass keine VM mehr auf folgende ISOs zugreift:
2. ISOs aus den betroffenen Ordnern entfernen.
3. Das vorliegende Bootable Media Creator Setup aus dem Install-Verzeichnis entfernen und die neue Version hinterlegen.
Vorher:
Nachher:
Wichtig: Es darf nur ein Setup im Install-Verzeichnis vorhanden sein.
4. Anschließend können Sie die ABSRT Anwendung starten. Hier müsste zunächst die Neuerstellung
des Restore ISOs und die anschließende Bearbeitung des Restore ISOs ersichtlich sein.
Backup Assistant
Der TERRA CLOUD Backup Assistant ist eine Eigenentwicklung der TERRA CLOUD. Dieses Tool soll Sie im Umgang der TERRA CLOUD Backup Lösung unterstützen.
Status
Auf der rechten Seite des Tools finden Sie Informationen der "Verbindungen" und "Software"-Versionen.
Sollte eine Verbindung zu den Portalservern nicht möglich sein, prüfen Sie bitte die entsprechenden Ports.
Des Weiteren können Sie über den Backup Assistant den TERRA CLOUD Backup Windows Agenten installieren bzw. aktualisieren.
Agenten Installation
Sollte der Backup Agent noch nicht auf dem betroffenen System installiert sein, kann dieser mithilfe des Tools herunterladen und installieren.
Bitte hinterlegen Sie zunächst die Zugangsdaten eines Backup Portal Benutzers, der sich in der entsprechenden Kunden-Site befindet.
Sofern Sie eine automatische Jobeinrichtung wünschen, können Sie dies direkt dort anhaken. Dafür wird lediglich ein Verschlüsselungskennwort von Ihnen benötigt, welches vergeben werden soll.
Weitere Informationen zur automatischen Agentenkonfiguration finden Sie hier.
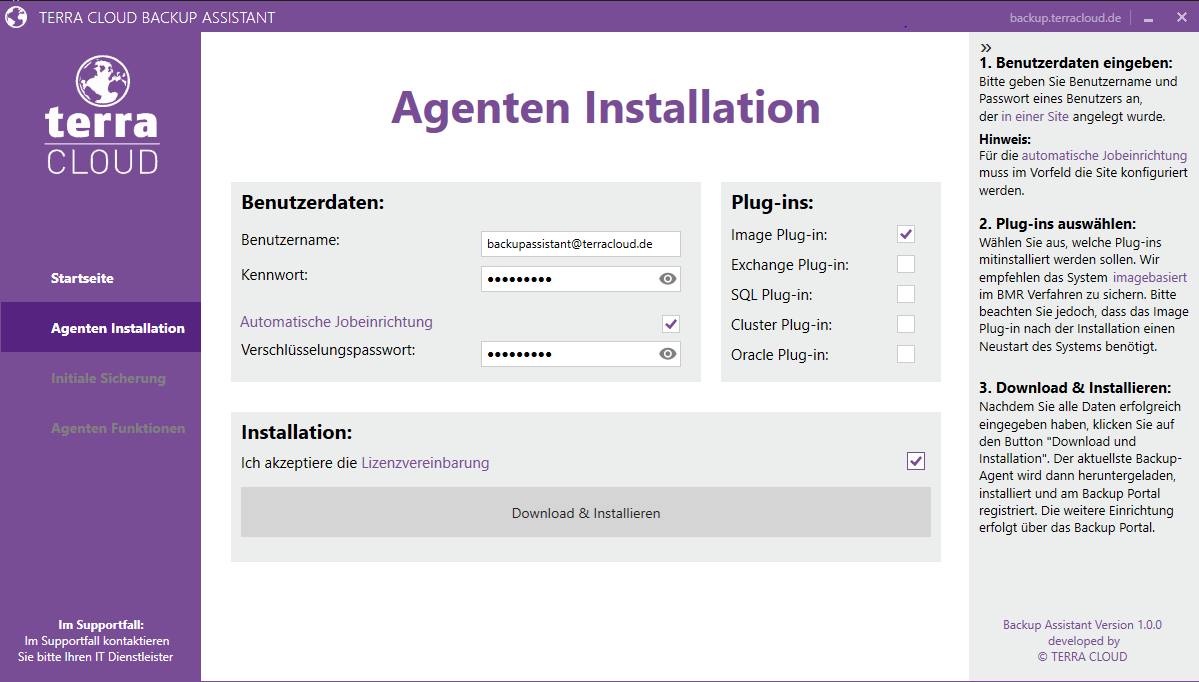
Nach dem Sie die benötigten Plugins ausgewählt haben und die Lizenzvereinbarung aktzeptiert haben wird der aktuellste Backup Agent im Hintergrund heruntergeladen und installiert.
Initiale Sicherung
Dieses Feature stellt die gleichen Optionen dar, welches auch für das Initialbackup Tool zur Verfügung stehen. Vorgestellt wird dieses Tool im folgendem Video
Agenten Funktionen
Die Funktion "Agent Funktionen" bietet Ihnen die Möglichkeit bereits erstelle Backup Jobs des installierten Windows Agenten auszuführen und Informationen zu bereits erstellten Sicherungen wie die Größe oder dem Sicherungstatus einzusehen.
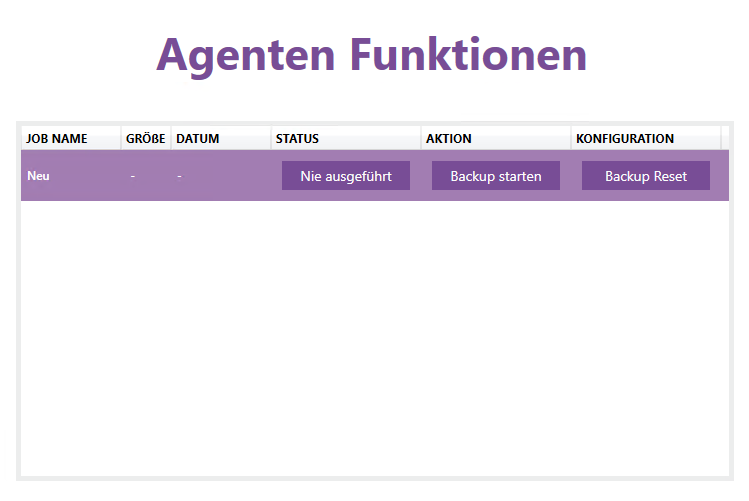
Backup Reset
Mithilfe dieser Funktion werden Metadaten (z.B. die Deltainformationen) aus dem Job-Verzeichnis des ausgewählten Backup Jobs entfernt.
Nach der Löschung führt das Tool eine Synchronisation durch, um die entfernten Metadaten neu erstellen zu lassen.
Dieser Vorgang kann einige Zeit in Anspruch nehmen.
Für die Entstörung von verschiedene Fehlerbilder kann dieser Vorgang notwendig sein.
Beispiel:
Deltazuordnungsdatei ist beschädigt
Support Bundle
Bei dem Support Bundle werden alle notwendigen Informationen und Logs wie zum Beispiel VSS-Logs, Event-Logs des Systems sowie Backup Job Logs zusammengeführt und in eine .zip Datei gepackt.
Diese kann uns bei diversen Supportfällen unterstützen die Ursache herauszufinden.
Überwachung
Reiter "Überwachung" im TERRA CLOUD Backup Portal
Diese Funktion des TERRA CLOUD Backup Portals bietet Ihnen eine umfangreiche Übersicht über den Status aller Backup Jobs.
Zusätzlich werden Ihnen offene Prozesse der Agenten angezeigt (laufende Sicherungen, Wiederherstellungen usw.).
Diese Übersicht kann kundenübergreifend über die Parentsite abgerufen werden oder innerhalb einer erstellten Site und damit für einen spezifischen Endkunden abgerufen werden.
Neben dem Sicherungsstatus ist der Wert der letzten abgeschlossenen Sicherung besonders wichtig, da sie dieses Datum mit dem Datum der letzten Sicherung abgleichen können.
Aus der Kombination dieser Informationen können Sie abschätzen, ob eine fehlgeschlagene Sicherung kritisch ist, da das Datum der letzten abgeschlossenen Sicherung z.B. zu weit in der Vergangenheit liegt.
Offene Prozesse:
Offene Prozesse erkennen Sie an dem Kreis, bestehend aus zwei Pfeilen und der Zahl daneben, wenn Sie auf das Symbol klicken werden Sie direkt zu der Übersicht über den Prozess weitergeleitet.
Export der Überwachungsübersicht per Mail
Sie können für die Überwachungsansicht über das Dropdown Menü 'E-Mail/Zeitplan' einen regelmäßigen Export in verschiedenen Dateiformaten einplanen.
Für eine automatische Auswertung eines Monitoring oder Ticketsystems können Sie z. B. das Dateiformat 'CSV' wählen.
Wenn Sie einen Export für einen einzelnen Endkunden wünschen, können Sie diesen über einen Site Benutzer mit der Rolle "Administrator" konfigurieren.
Bitte melden Sie sich dazu mit dem Site Benutzer im Backup Portal an und konfigurieren Sie den Export innerhalb dieses Endkunden.
Der Export aus dem folgenden Beispiel beinhaltet die Backup Jobs aller Sites/Endkunden.
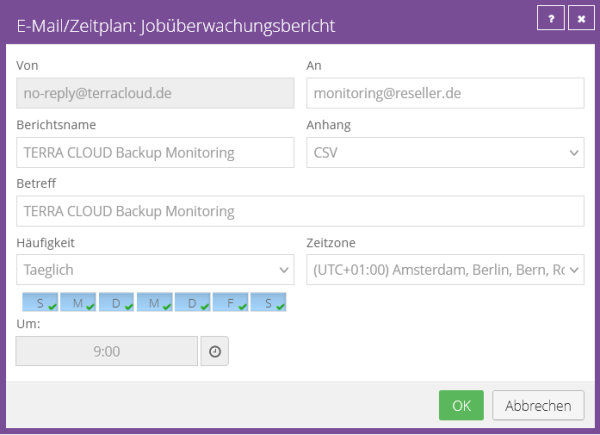
Jobstatus in XML-Datei auswerten
Der Windows, Linux und vSphere Recovery Agent speichern Informationen zum letzten Sicherungsstatus und z. B. der Sicherungsgröße in einer XML-Datei.
Die folgenden Pfade beziehen sich auf das Standard-Installationsverzeichnis.
Linux Agent:
/opt/BUAgent/<JOBNAME>/BackupStatus.xml
Windows Agent:
C:\Program Files\TERRA Cloud Backup\Agent\<JOBNAME>\BackupStatus.xml
vSphere Recovery Agent:
C:\Program Files\vSphere Recovery Agent\<JOBNAME>\BackupStatus.xml
Mögliche Ergebnisse für "<agentdata:result></agentdata:result>":
- UNKNOWN: Der Jobstatus ist aktuell unbekannt.
- COMPLETED: Der Job ist abgeschlossen oder mit Fehlern/Warnungen abgeschlossen.
- CANCELLED: Der Job wurde manuell abgebrochen.
- FAILED: Der Job ist fehlgeschlagen, bitte überprüfen Sie die Logfiles.
- NO_FILES: Es konnte keine Sicherung durchgeführt werden, da keinen Dateien durch diesen Job geschützt werden.
Verbrauchsberichte
Die TERRA CLOUD stellt Ihnen zur Überwachung der für das Lizenzmodell relevanten Verbrauchswerte unterschiedliche Berichte zur Verfügung.
TERRA CLOUD Backup Reseller Report
Dieser Bericht zeigt Ihnen die Verbrauchswerte aller Backup-Accounts Ihrer Endkunden.
Der Datenbestand bezieht sich auf den 15. Kalendertag eines Monats und bildet die Abrechnungsgrundlage für den jeweiligen Monat.
Versendet wird der Bericht ab dem 16. Kalendertag eines Monats an den Backup Master Account / Cloud Master Account (TERRA CLOUD Center).
Beispielausschnitt aus dem Reseller Report

TERRA CLOUD Backup Billing Report
Zusätzlich zum TERRA CLOUD Backup Reseller Report erhalten Sie den TERRA CLOUD Backup Billing Report im CSV-Dateiformat.
Die Verbrauchswerte für die Abrechnung des TERRA CLOUD Backups sind in diesem Bericht für Sie je Endkunde zusammengefasst.
Wir empfehlen diesen Bericht als Grundlage für eine automatisierte Abrechnung z. B. auch für das TERRA CLOUD Backup Enterprise Lizenzmodell.
Inhalt des Berichtes:
Active vault Vault: Der Name des aktiven Vaults
account Native protected data in GB: Die Summe der nativ geschützten Datenmenge des Endkunden
Computer amount: Die Summe der Gerätelizenzen
Additional safesets: Die Summe des zusätzlichen kostenpflichtigen Safeses
TERRA CLOUD Backup Customer Report
Optional können Sie im TERRA CLOUD Center einen Endkunden Bericht zu Ihrer TERRA CLOUD Backup Bestellung hinzufügen.
In diesem Bericht erhalten Sie bzw. Ihr Endkunde wöchentlich die Verbrauchsübersicht und den Status der Backups.
Die Darstellung entspricht dem Reseller Report, beinhaltet jedoch nur die Datensätze für den jeweiligen Endkunden.
FAQ
VSS
Anbei eine kleine Erklärung zum Thema VSS:
Was ist eigentlich VSS?
- VSS ist die Abkürzung ist eine Herleitung von "Volume Snapshot Service"
- Übersetzt: Volumen Schattenkopie Dienst
- Seit Windows XP / Windows Server 2003 implemtiert, dient zur Erstellung von Versionsständen (Snapshots)
- Ein Snapshot ist eine Momentaufnahme eines Volumens (read-only)
- VSS arbeitet auf Blockebene
- VSS-Technik wird bei den meisten Backuplösungen eingesetzt die Windows Systeme sichern
- VSS Fehler sind bei diesen Backuplösungen die Hauptstörungsquelle
Bestandteile der VSS-Technik
VSS-Writer:
- jede VSS-fähige Anwendung installiert ihren eigenen VSS-Writer auf dem System, dieser wird benötigt um seine Applikation in einen konsistenten Zustand zu bringen
VSS-Requestor:
- jedes Programm welches konsistente Daten benötigt kann zu einen Requestor werden, in unserem Fall der Backup Agent
VSS-Provider:
- Der Provider erstellt und verwaltet die Schattenkopien von Daten im System
Verschlüsselungskennwort eines Backup Jobs vergessen
Sollten Sie das Verschlüsselungskennwort eines Backup Jobs vergessen haben gibt es keine Möglichkeit Dateien aus dem Backup Job wiederherzustellen.
Eine Änderung des Kennworts ist durch uns nicht möglich.
Verschlüsselungskennwort eines Backup Jobs ändern
Sie haben die Möglichkeit das Verschlüsselungskennwort neu zu setzen. Dazu gehen Sie im Backup-Portal zu dem entsprechenden Backup Job und anschließend auf "Job bearbeiten".
Links können Sie nun ein neues Kennwort setzen. Dabei zu beachten ist, dass Sicherungen, die mit dem alten Verschlüsselungskennwort erstellt wurden auch nur mit diesem wiederhergestellt werden können.
Hier wäre unsere Empfehlung den Backup Job zu löschen und einen neuen Backup Job mit dem neuen Verschlüsselungskennwort zu erstellen.
Granular Restore Tool - Lizenz
Während der Installation des Granular Restore Tools werden Sie nach einer Lizenz gefragt.
Bitte senden Sie uns eine E-Mail inklusive Ihrer Kundennummer mit dem Betreff "Granular Restore Lizenz" an support@terracloud.de
Wir werden Ihnen dann eine entsprechende Lizenz zur Verfügung stellen.
Löschung von Daten auf einem Vault
Falls Sie einen Job oder Server aus dem Backupportal löschen, verbleiben die Daten aus Sicherheitsgründen weiterhin auf dem Vault.
Um die Daten endgültig zu entfernen, benötigen wir einen expliziten Löschauftrag. Dieser muss die folgenden Informationen enthalten:
- Accountname
- Servername
- Ggf. Jobname
- Ggf. Safesets
Erneut registrieren
Die Funktion "Erneut registrieren" ermöglicht es die lokal gespeicherte Konfiguration des Agenten gegen eine auf dem Vault abgespeicherte Konfiguration eines Computers zu ersetzen bzw. die bestehende zu ergänzen. Dies ist zum Beispiel notwendig nach einer Neuinstallation des Agenten, da der Agent nach einer Neuinstallation nicht konfiguriert wird.
Die aktuelle Konfiguration kann z. B. durch die Funktion ergänzt werden, sofern Sie einen Backup Job im Portal und somit vom Agenten entfernt haben, der Datenbestand und die Konfigration jedoch noch auf dem Vault vorhanden ist. Nach der erneuten Registrierung wird der fehlende Backup Job wieder im Portal angezeigt.
Vorgehensweise:
1. Bitte wählen Sie im Backupportal den betroffenen Agenten aus. Unter dem Reiter "Vault-Einstellungen" finden Sie die Aktion "Erneut registrieren".
2. Laden Sie hier nun das für die Kundensite erstellte Vault-Profil, anschließend kann die Aktion "Computer laden" ausgeführt werden.
3. Auf der rechten Seite werden nun alle Systeme angezeigt, welche sich auf dem betroffenen Vault befinden.
4. Nachdem Sie das betroffene System ausgewählt haben und die Aktion "Speichern" ausgeführt haben, wird die Konfiguration zurückgespielt.
5. Bearbeiten Sie nun die vorhandenen Jobs und tragen Sie jeweils das Verschlüsslungskennwort ein. Anschließend muss jeder betroffene Job synchronisiert werden.
6. Sobald die Synchronisation erfolgreich abgeschlossen wurde, können Sie die betroffenen Jobs ausführen.
Sicherung einer DATEV SQL Datenbank
Bei der Sicherung einer DATEV SQL Datenbank gibt es im Vergleich zu einer "gewöhnlichen" SQL Datenbank Sicherung einige Besonderheiten. In der Regel hat der Administrator/in keinen Vollzugriff auf die Datenbank und somit kann das SQL Plug-in nicht eingesetzt werden. Zusätzlich kann es zu Problemen bei einer filebasierten Sicherung kommen, da der Zeitstempel der Datenbankdatei (MDF Datei) zum Teil zurückgesetzt wird.
Transaktionsprotokolle müssen nicht abgeschnitten werden, da für die DATEV SQL Datenbank die Umlaufprotokollierung konfiguriert ist.
Empfohlenes Sicherungskonzept:
Das System sollte über eine imagebasierte BMR Sicherung geschützt werden, da bei dieser partitionsbasierten Sicherungsmethode der Zeitstempel der Datenbankdatei irrelevant ist.
Wie läuft die Migration der Backups von Bestandskunden auf ein TCBE-Vaultsystem ab?
Ausgangssituation:
Sie haben aktuell für Ihre Kunden Backup Standard bzw. Backup Basic Pakete gebucht und möchten die Sicherungen Ihrer Kunden auf ein neues TCBE-Vaultsystem umziehen lassen.
Satelliten:
Bitte beachten Sie, dass Backup Pakete in Verbindung mit einem Satelliten nicht auf ein TCBE-Vaultsystem umgezogen werden können.
Satelliten können nur in Verbindung mit einem dedizierten Basevault verwendet werden. Basevaults sind speziell für die Kommunikation mit Satelliten optimiert, daher ist ein Mischbetrieb auf einem Vaultsystem nicht möglich. Wir empfehlen, falls Sie Satelliten im Einsatz haben, nur Ihre Kunden ohne Satellit umzuziehen.
Vorbereitung:
Bitte bereiten Sie für den Migrationsprozess die folgenden Schritte vor:
- Bestellen Sie das TCBE-Vaultsystem in der gewünschten Location auf Ihr Unternehmen (Bitte beachten Sie die Bereitstellungszeit von bis zu 10 Werktagen)
- Lösen Sie nach der Bereitstellung Ihres neuen Vaultsystems eine Bestellung für einen Vault-Account für jeden Ihrer Kunden aus (Die Vault-Accounts können Sie auf die jeweiligen Kunden schlüsseln)
- Erstellen Sie eine Gegenüberstellung in z.B. Microsoft Excel mit dem alten Vault-Account (z.B. 12345-DRMEY) und dem neu bestellten Vault-Account, auf Ihrem TCBE-Vault z.B. (12345-DRMEYER)
- Bei der Bereitstellung Ihres Vaultsystems wird automatisch ein Support Ticket für den Migrationsprozess erzeugt, bitte sprechen Sie in diesem die Zeitspanne für die Migration ab
Ablauf während der Migration:
Am Morgen des Migrationstages wird der Prozess durch das Team der TERRA CLOUD gestartet. Sie erhalten eine Benachrichtigung per E-Mail welche Accounts zur Migration gestartet wurden.
Sie können direkt nach dem Start der Migration die neuen Sicherungsziele für die Agenten hinterlegen, wie in Anleitung für die Anpassungen im Backup Portal beschrieben.
Bitte beachten Sie, dass während der Migration keine Sicherungen durchgeführt werden können, da beide Accounts durch die Migration gesperrt sind.
In der Regel schließen die Migrationen am selben Werktag ab, sodass die Sicherungen der Backup Agenten, die per Zeitplan gestartet werden, gegen den migrierten Datenbestand auf dem dedizierten Vault erfolgen können.
Wie läuft die Migration technisch ab?
Der Migrationsprozess startet einen Kopiervorgang der die hinterlegten Computer / Backup Jobs / Safesets aus dem alten Account von dem Shared Vault in den Account auf dem TCBE-Vaultsystem überträgt.
Wie viele Endkunden können pro Migrationstag umgezogen werden?
In der Regel können ca. 5 Endkunden pro Tag umgezogen werden, dies hängt von der Größe der jeweiligen Accounts ab ca. 1,5 TB (nativ geschützte Datenmenge)
Was passiert mit den alten Accounts nach der Migration?
Nach dem Abschluss des gesamten Migrationsprozesses müssen die alten Accounts noch von Ihnen gekündigt werden, da es sonst zu Doppelberechnung kommen kann.
Selbstverständlich steht Ihnen während des Migrationsprozesses ein Teammitglied des Supports als Ansprechpartner für mögliche Rückfragen zur Verfügung.
Gibt es Kennworteinschränkungen für den Backup Agent?
Es gibt eine Längenbeschränkung von 31 Zeichen für alle Kennwörter mit dem TERRA Cloud Backup Agent. Dies schließt ein:
- Verschlüsselungskennwörter
- Kennwort-Hinweise
- SQL-Anmeldeinformationen
- VRA-Anmeldeinformationen
- Oracle-Anmeldeinformationen
- SMTP-Anmeldeinformationen
- Kennwort für Vault-Anmeldeinformationen
- etc...
Nur diese Zeichen sind für die Verwendung in den Feldern für Verschlüsselungskennwort und Hinweis zulässig: a-z, A-Z, Á-ÿ, 0-9, Leerzeichen, !@#$%^&*()_-+=[]{}|'":;,<.>?~`´